
Carnivores which eat other carnivores are called
A. Primary consumers
B. Secondary consumers
C. Tertiary consumers
D. None of the above
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: An organism that only eats the flesh or meat of other animals is known as a carnivore. Such animals that are hunted by carnivores are called prey that are directly or indirectly dependent on plants for their nutrition.
Complete answer:
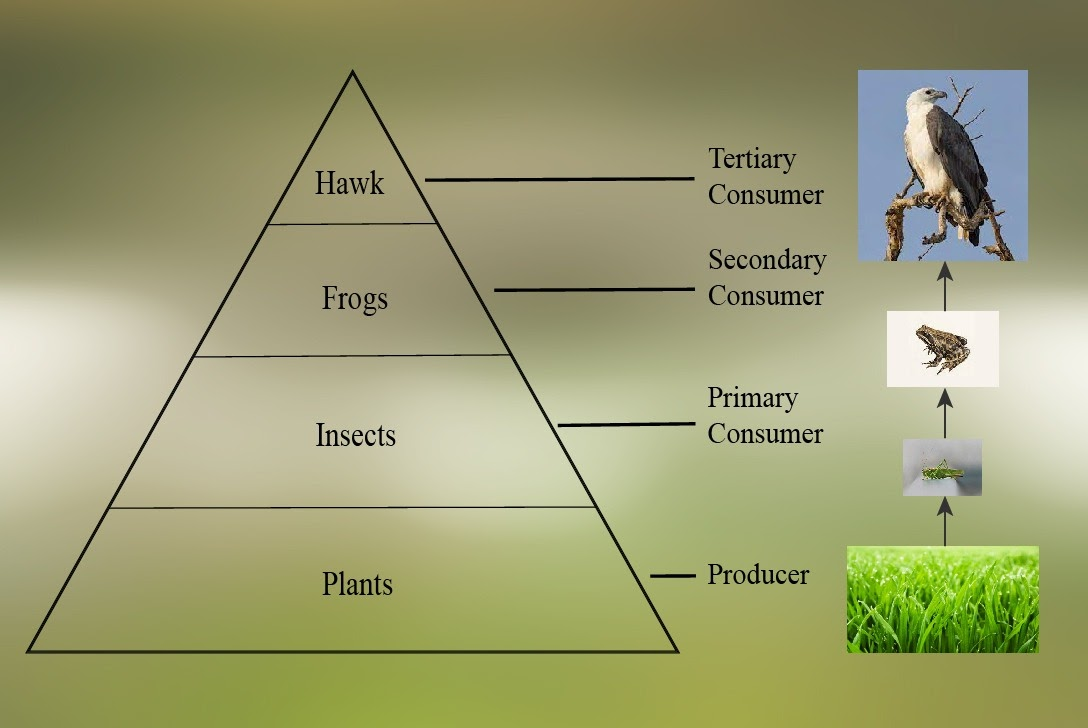
Carnivores that eat other carnivores are called tertiary consumers or consumers of the third order. Tertiary consumers or consumers of third-order include the secondary carnivores. Wolf can be taken as an example of an organism designating such a location in a food web as it dwells upon the secondary consumers (primary carnivores) like foxes (that eat rats and rabbits). Another classic example of tertiary consumers are killer whales or orcas that depend upon sea lions and seals (that depend upon fishes, squids and octopuses for nutritional needs).
Therefore, option C, Tertiary consumers is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
Primary consumers or consumers of the first order: This group of organisms include herbivores that directly depend upon the producers (plants). Herbivores of the terrestrial ecosystem include rabbits, the rats, mice, deer, goat, grasshoppers, grazing cattle etc. Similarly, herbivores of the aquatic ecosystem include crustaceans, molluscs etc.
Secondary consumers or consumers of the second order: This group of organisms include the primary carnivores, e.g., centipedes, fishes, frogs, snakes, predatory birds, wild cats, foxes etc. which feed upon the herbivores.
Tertiary consumers: These are present at the top levels of food chains. As the amount of energy is reduced at every trophic level of the food chain, these tertiary consumers need to intake a larger quantity of the food as compared to other lower trophic levels.
Note:
The carnivores are not only animals but they also include some plants and fungi. A few examples are venus flytrap, sundew, some moulds and mildew. These are important to keep a check on the population of herbivores and other animals.
Complete answer:
Carnivores that eat other carnivores are called tertiary consumers or consumers of the third order. Tertiary consumers or consumers of third-order include the secondary carnivores. Wolf can be taken as an example of an organism designating such a location in a food web as it dwells upon the secondary consumers (primary carnivores) like foxes (that eat rats and rabbits). Another classic example of tertiary consumers are killer whales or orcas that depend upon sea lions and seals (that depend upon fishes, squids and octopuses for nutritional needs).
Therefore, option C, Tertiary consumers is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
Primary consumers or consumers of the first order: This group of organisms include herbivores that directly depend upon the producers (plants). Herbivores of the terrestrial ecosystem include rabbits, the rats, mice, deer, goat, grasshoppers, grazing cattle etc. Similarly, herbivores of the aquatic ecosystem include crustaceans, molluscs etc.
Secondary consumers or consumers of the second order: This group of organisms include the primary carnivores, e.g., centipedes, fishes, frogs, snakes, predatory birds, wild cats, foxes etc. which feed upon the herbivores.
Tertiary consumers: These are present at the top levels of food chains. As the amount of energy is reduced at every trophic level of the food chain, these tertiary consumers need to intake a larger quantity of the food as compared to other lower trophic levels.

Note:
The carnivores are not only animals but they also include some plants and fungi. A few examples are venus flytrap, sundew, some moulds and mildew. These are important to keep a check on the population of herbivores and other animals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




