
Cauda equina is the part of
(a) Horse
(b) Tail of horse
(c) Spinal cord
(d) None of the above
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Cauda equina is part of an area of nervous tissue that, along with the brain, forms the central nervous system. This provides the route for messages to be transmitted and received by the brain. The name Cauda equina comes from the Latin word that defines much of the hind part of an animal.
Complete step by step answer:
A pack of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets, consists of the second through fifth pairs of lumbar nerves, the first through fifth pairs of sacral nerves, and the coccygeal nerve, both of which originate from the spinal cords’ lumbar enlargement and conus medullaris, is the cauda equina (Latin meaning the tail of the horse). A horse tail-like structure is formed. The lumbar cistern, a subarachnoid space inferior to the conus medullaris, occupies the cauda equina.
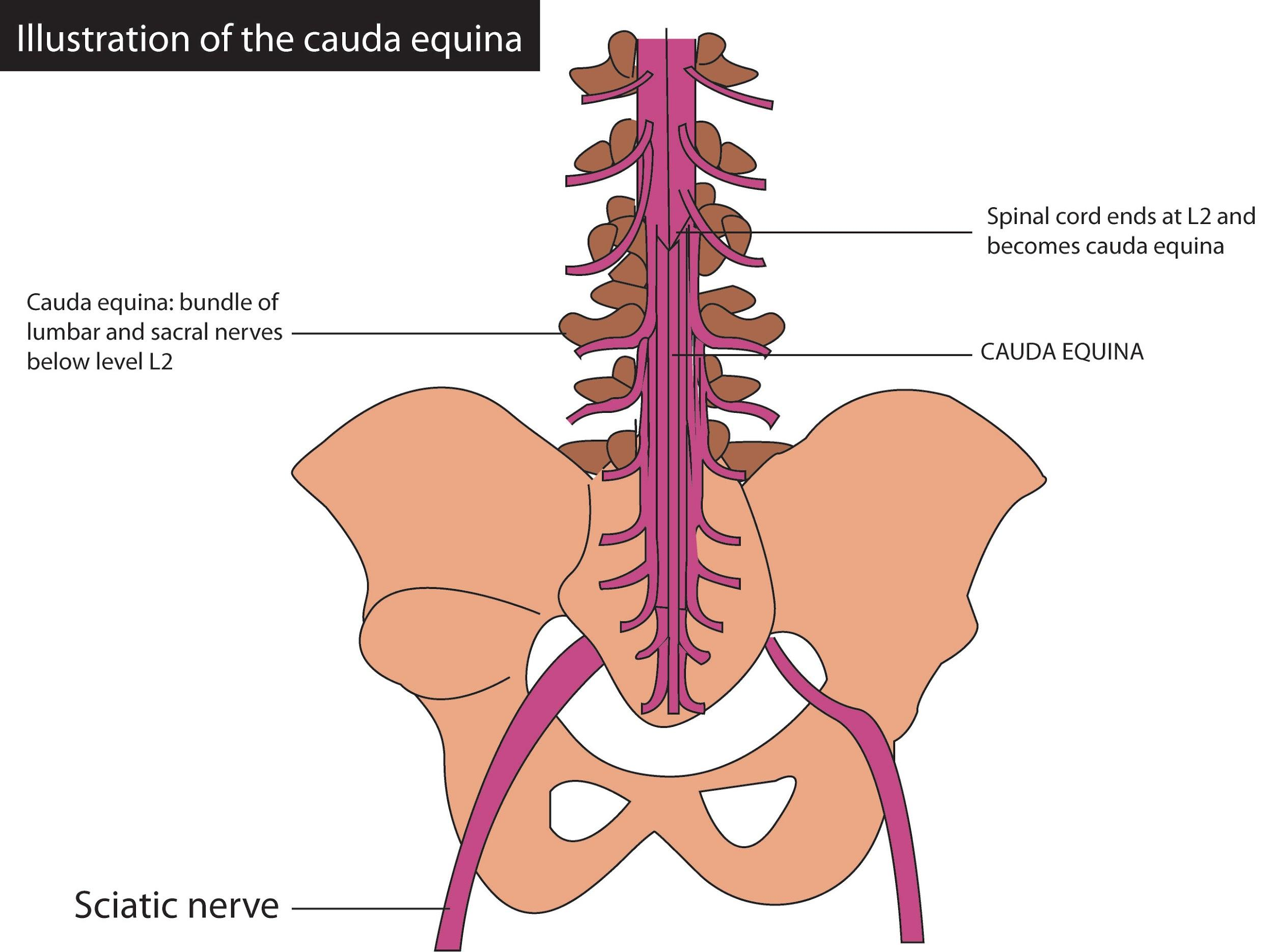
In order to include motor innervation of the hips, knees, ankles, feet, internal anal sphincter, and external anal sphincter, the nerves comprising the cauda equina innervate the pelvic organs and lower limbs. In addition, the cauda equina refers to the perineum sensory innervation and, in part, the bladder parasympathetic innervation.
So, the correct answer is, 'Spinal Cord'.
Additional information:
Cauda equina syndrome can be diagnosed when the nerve roots of the cauda equina become extremely compressed. This condition is considered extreme, as the patient will permanently lose bowel and bladder function and may result in permanent leg paralysis. Surgery would usually be performed to alleviate the compression of the nerves when cauda equina syndrome is diagnosed.
Note: At its root, the cauda equina has approximately 10 fiber pairs. They are made up of three to five pairs of lumbar fibers, five pairs of sacral fibers, and one coccygeal nerve. Sending and receiving messages between the lower limbs and the pelvic organs, consisting of the bladder, rectum, and internal genital organs, is the primary feature of the cauda equina.
Complete step by step answer:
A pack of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets, consists of the second through fifth pairs of lumbar nerves, the first through fifth pairs of sacral nerves, and the coccygeal nerve, both of which originate from the spinal cords’ lumbar enlargement and conus medullaris, is the cauda equina (Latin meaning the tail of the horse). A horse tail-like structure is formed. The lumbar cistern, a subarachnoid space inferior to the conus medullaris, occupies the cauda equina.

In order to include motor innervation of the hips, knees, ankles, feet, internal anal sphincter, and external anal sphincter, the nerves comprising the cauda equina innervate the pelvic organs and lower limbs. In addition, the cauda equina refers to the perineum sensory innervation and, in part, the bladder parasympathetic innervation.
So, the correct answer is, 'Spinal Cord'.
Additional information:
Cauda equina syndrome can be diagnosed when the nerve roots of the cauda equina become extremely compressed. This condition is considered extreme, as the patient will permanently lose bowel and bladder function and may result in permanent leg paralysis. Surgery would usually be performed to alleviate the compression of the nerves when cauda equina syndrome is diagnosed.
Note: At its root, the cauda equina has approximately 10 fiber pairs. They are made up of three to five pairs of lumbar fibers, five pairs of sacral fibers, and one coccygeal nerve. Sending and receiving messages between the lower limbs and the pelvic organs, consisting of the bladder, rectum, and internal genital organs, is the primary feature of the cauda equina.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




