
$CD$-$4$ receptor is associated with
(a) AIDS
(b) Cancer
(c) Malaria
(d) Pneumonia
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The $CD$-$4$ receptor is a glycoprotein present on the surface of immune cells. It is depleted in certain diseases and conditions. A disease uses this receptor to enter immune cells and spread infection.
Complete step by step answer:
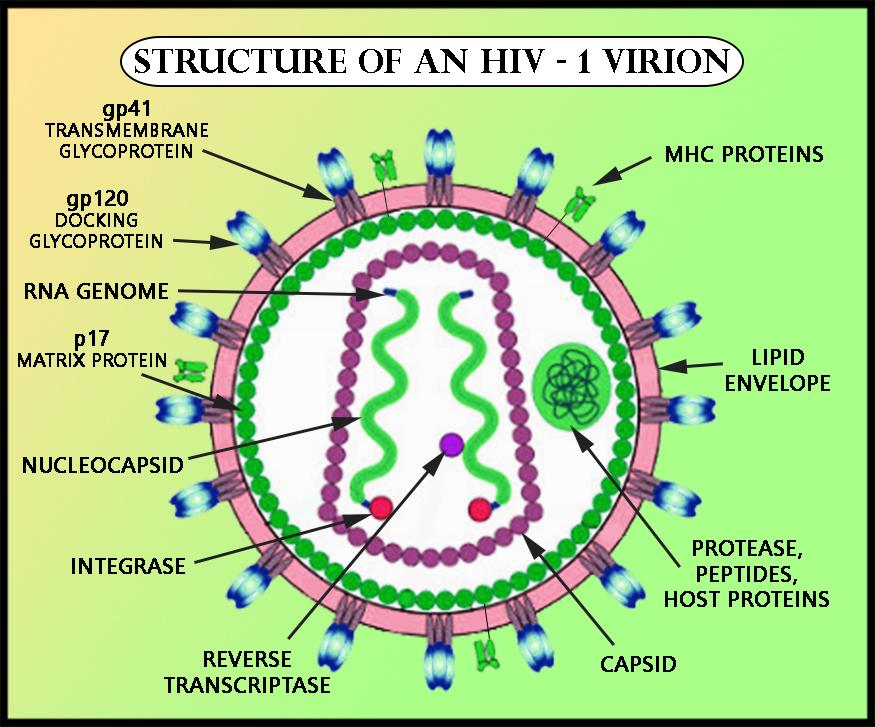
- $CD$-$4$ (cluster of differentiation-4) receptor is a glycoprotein present on the surface of immune cells, such as T-lymphocytes.
- AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) is caused due to retrovirus HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and is mainly characterized by a damaged immune system.
- HIV enters into the helper T-lymphocytes through $CD$-$4$. It uses the $CD$-$4$ receptor and uses its viral envelope protein $gp120$ to do so. The binding of $gp120$ to $CD$-$4$ allows the virus entry inside the helper T-cell, thus infecting and destroying it. After the formation and release of more viral particles, more helper T-cells are infected, thus leading to the destruction of the immune system.
So, the correct answer is ‘AIDS’.
Additional Information: AIDS is not a congenital disease. It is transmitted from one person to another through various ways, such as unprotected sex with an infected partner, sharing needles in case of intravenous drug abusers, by transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products, and from an infected mother to her unborn child. Apart from T-lymphocytes, HIV enters the human body through the macrophages. The RNA genome of the virus replicates to form viral DNA with the help of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. Thus, the host cell is infected with viral DNA and is programmed to produce more virus particles. These virus particles then proceed to infect other cells.
Note: A retrovirus is a virus that inserts its RNA into a host with a DNA genome. The virus employs its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to transcribe a copy of DNA from RNA which gets incorporated into the genome.
Complete step by step answer:
- $CD$-$4$ (cluster of differentiation-4) receptor is a glycoprotein present on the surface of immune cells, such as T-lymphocytes.
- AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) is caused due to retrovirus HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and is mainly characterized by a damaged immune system.
- HIV enters into the helper T-lymphocytes through $CD$-$4$. It uses the $CD$-$4$ receptor and uses its viral envelope protein $gp120$ to do so. The binding of $gp120$ to $CD$-$4$ allows the virus entry inside the helper T-cell, thus infecting and destroying it. After the formation and release of more viral particles, more helper T-cells are infected, thus leading to the destruction of the immune system.

So, the correct answer is ‘AIDS’.
Additional Information: AIDS is not a congenital disease. It is transmitted from one person to another through various ways, such as unprotected sex with an infected partner, sharing needles in case of intravenous drug abusers, by transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products, and from an infected mother to her unborn child. Apart from T-lymphocytes, HIV enters the human body through the macrophages. The RNA genome of the virus replicates to form viral DNA with the help of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. Thus, the host cell is infected with viral DNA and is programmed to produce more virus particles. These virus particles then proceed to infect other cells.
Note: A retrovirus is a virus that inserts its RNA into a host with a DNA genome. The virus employs its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to transcribe a copy of DNA from RNA which gets incorporated into the genome.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




