
Ce (Atomic number=58) is a member of:
A) s-block elements
B) p-block elements
C) d-block elements
D) f-block elements
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: We must know the electronic configuration of elements in order to categorize as s, p, d and f block elements. Electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons into orbitals. The atoms are inert if the atom has filled electron configuration. If the outermost shell isn't filled then to fill the outermost shell, it accepts or donates electrons between other atoms. The valency of an atom is the number of electrons present within the outermost shell. If the electrons are shared between covalent compounds then it's termed as co-valency.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that the valency of an atom is the number of electrons present within the outermost shell. If the electrons are shared between covalent compounds then it's termed as co-valency.
The following must be kept in mind before writing any electronic configuration.
Electrons in an atom are characterized by a set of four quantum numbers and the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a shell (energy level) is based on principal quantum number (n).
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a shell is calculated by the formula \[2{n^2}\] where the shell number. When n=1, maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated are \[\;2 \times {\left( 1 \right)^2} = 2\]
The subshells into which electrons are distributed are based on the azimuthal quantum number, denoted by ‘l’. When n=4 the subshells correspond to $l = 0$, $l = 1$, $l = 2$and $l = 3$ which are named the s, p, d and f subshells respectively.
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated by a subshell is given by the formula \[2 \times \left( {2l + 1} \right)\] So s, p, d and f subshells can accommodate $2$, $6$, $10$ and \[14\]electrons respectively
If two electrons are filled in the ‘s’ subshell of the first shell, the electronic configuration is noted as \[1{s^2}\].
The Afbau (build-up) principle and the electronic configuration of atoms provide a theoretical foundation for the periodic classification into s-block, p-block, d-block and f-block elements.
The Afbau principle states that in the ground state of an atom or ion, electrons fill atomic orbitals of the lowest available energy levels before occupying higher levels. For example, the 1s subshell is filled before the 2s subshell is occupied.
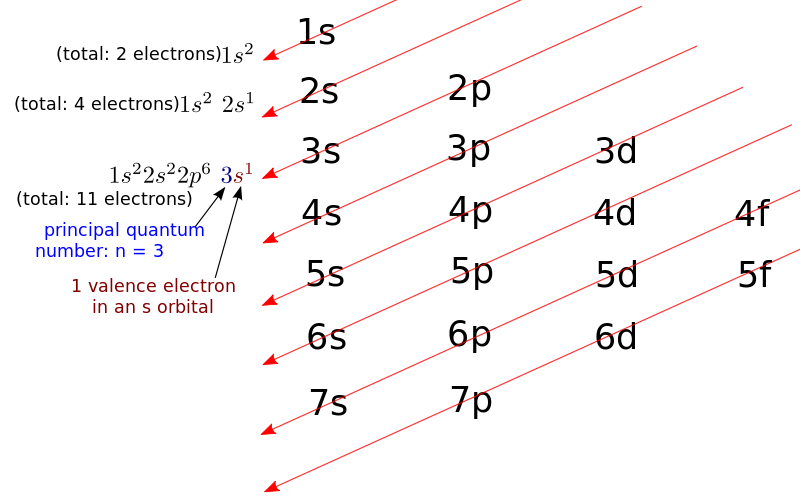
Image: The order in which electrons are filled in atomic orbitals as per the Aufbau principle.
Pauli’s exclusion principle: This principle states “no two electrons in the same atom have the same values for all four quantum numbers”.
Hund’s Rule of maximum multiplicity: The rule states that for a given electron configuration, the lowest energy term is the one with the greatest value of spin multiplicity. This implies that if two or more orbitals of equal energy are available, electrons will occupy them singly before filling them in pairs.
As given in the question, the atomic number of $Ce$ is $58$.Therefore there are 58 electrons which are distributed in the manner: \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2}3{d^{10}}4{s^2}4{p^6}4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^6}6{s^2}4{f^1}5{d^1}\].
Since $Ce$ has entered into the f-orbital, it can be concluded that Ce is an f-block element.
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: It must be noted while writing the electronic configurations that there are exceptions such as in case of Cu, Cr, etc. This is because Fully-filled orbitals and half-filled orbitals have extra stability. Also, while obeying the Afbau’s principle, the highest orbital to which the electron enters gives the categorization of to which block the element belongs. However, the electronic configuration of an element can also be written in a short form using the nearest noble gas configuration. For example, Ce (58) can be written as \[\left[ {Xe} \right]{\text{ }}6{s^2}4{f^1}5{d^1}\].
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that the valency of an atom is the number of electrons present within the outermost shell. If the electrons are shared between covalent compounds then it's termed as co-valency.
The following must be kept in mind before writing any electronic configuration.
Electrons in an atom are characterized by a set of four quantum numbers and the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a shell (energy level) is based on principal quantum number (n).
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a shell is calculated by the formula \[2{n^2}\] where the shell number. When n=1, maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated are \[\;2 \times {\left( 1 \right)^2} = 2\]
The subshells into which electrons are distributed are based on the azimuthal quantum number, denoted by ‘l’. When n=4 the subshells correspond to $l = 0$, $l = 1$, $l = 2$and $l = 3$ which are named the s, p, d and f subshells respectively.
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated by a subshell is given by the formula \[2 \times \left( {2l + 1} \right)\] So s, p, d and f subshells can accommodate $2$, $6$, $10$ and \[14\]electrons respectively
If two electrons are filled in the ‘s’ subshell of the first shell, the electronic configuration is noted as \[1{s^2}\].
The Afbau (build-up) principle and the electronic configuration of atoms provide a theoretical foundation for the periodic classification into s-block, p-block, d-block and f-block elements.
The Afbau principle states that in the ground state of an atom or ion, electrons fill atomic orbitals of the lowest available energy levels before occupying higher levels. For example, the 1s subshell is filled before the 2s subshell is occupied.

Image: The order in which electrons are filled in atomic orbitals as per the Aufbau principle.
Pauli’s exclusion principle: This principle states “no two electrons in the same atom have the same values for all four quantum numbers”.
Hund’s Rule of maximum multiplicity: The rule states that for a given electron configuration, the lowest energy term is the one with the greatest value of spin multiplicity. This implies that if two or more orbitals of equal energy are available, electrons will occupy them singly before filling them in pairs.
As given in the question, the atomic number of $Ce$ is $58$.Therefore there are 58 electrons which are distributed in the manner: \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2}3{d^{10}}4{s^2}4{p^6}4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^6}6{s^2}4{f^1}5{d^1}\].
Since $Ce$ has entered into the f-orbital, it can be concluded that Ce is an f-block element.
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: It must be noted while writing the electronic configurations that there are exceptions such as in case of Cu, Cr, etc. This is because Fully-filled orbitals and half-filled orbitals have extra stability. Also, while obeying the Afbau’s principle, the highest orbital to which the electron enters gives the categorization of to which block the element belongs. However, the electronic configuration of an element can also be written in a short form using the nearest noble gas configuration. For example, Ce (58) can be written as \[\left[ {Xe} \right]{\text{ }}6{s^2}4{f^1}5{d^1}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




