
Cell in \[G0\] phase of cell cycle
A. Exit cell cycle
B. Enter cell cycle
C. Suspend cell cycle
D. Terminate cell cycle
Answer
561k+ views
Hint:Cell cycles, or cell-division cycles, are events that occur within a cell in sequence and result in the division into two daughter cells. These sequences of events include the replication of DNA and its organelles in a process called cell division, as well as the partitioning of its cytoplasm and other components into two daughter cells. Approximately one billion cells die every hour, and one billion cells are produced in the body.
Complete answer:
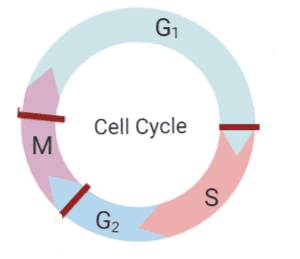
Four different stages of the cell cycle: The \[G1\] phase, the S phase (synthesis), the \[G2\] phase (collectively referred to as the interphase), and the M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). The M step is a mixture of two processes: -mitosis, in which the nucleus of the cell divides, and cytokinesis, in which the cytoplasm of the cell divides, into two daughter cells. Cells that have stopped dividing semi-permanently or reversibly are part of a cycle called the \[G0\] phase.
In an adult animal, certain cells do not differentiate, e.g., nerve cells, whereas several cells often divide only to replace cell loss due to damage or cell death.
This type of cell is still in the \[G0\] phase. The cell cycle's \[G0\] phase is also known as the quiescent period.
The cell remains metabolically active in this phase but does not proliferate until it is called upon to do so. Cells stop the cell cycle for some time in the \[G0\] phase of the cell cycle, but they do not terminate the cell cycle entirely. They leave the cell cycle when a cell reaches the \[G0\] process.
The correct answer, therefore, is the A-exit of the cell cycle.
Note: The cell cycle starts with the \[G0\] step. Non-dividing cells are added from \[G1\] to the \[G0\] state and may remain at \[G0\] for long periods of time. Some of the cells are semi-permanently part of the \[G0\] pathway and are understood as post-mitotic cells.
Complete answer:
Four different stages of the cell cycle: The \[G1\] phase, the S phase (synthesis), the \[G2\] phase (collectively referred to as the interphase), and the M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). The M step is a mixture of two processes: -mitosis, in which the nucleus of the cell divides, and cytokinesis, in which the cytoplasm of the cell divides, into two daughter cells. Cells that have stopped dividing semi-permanently or reversibly are part of a cycle called the \[G0\] phase.

In an adult animal, certain cells do not differentiate, e.g., nerve cells, whereas several cells often divide only to replace cell loss due to damage or cell death.
This type of cell is still in the \[G0\] phase. The cell cycle's \[G0\] phase is also known as the quiescent period.
The cell remains metabolically active in this phase but does not proliferate until it is called upon to do so. Cells stop the cell cycle for some time in the \[G0\] phase of the cell cycle, but they do not terminate the cell cycle entirely. They leave the cell cycle when a cell reaches the \[G0\] process.
The correct answer, therefore, is the A-exit of the cell cycle.
Note: The cell cycle starts with the \[G0\] step. Non-dividing cells are added from \[G1\] to the \[G0\] state and may remain at \[G0\] for long periods of time. Some of the cells are semi-permanently part of the \[G0\] pathway and are understood as post-mitotic cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




