
What changes can be observed in the length of the I band during muscle contraction?
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: The I band contains the actin filaments which are twice in number compared to myosin filaments in a single sarcomere. Each I band is subdivided into two halves by a Z disc. During muscular contraction the region of overlap between actin and myosin filaments increases.
Complete answer:
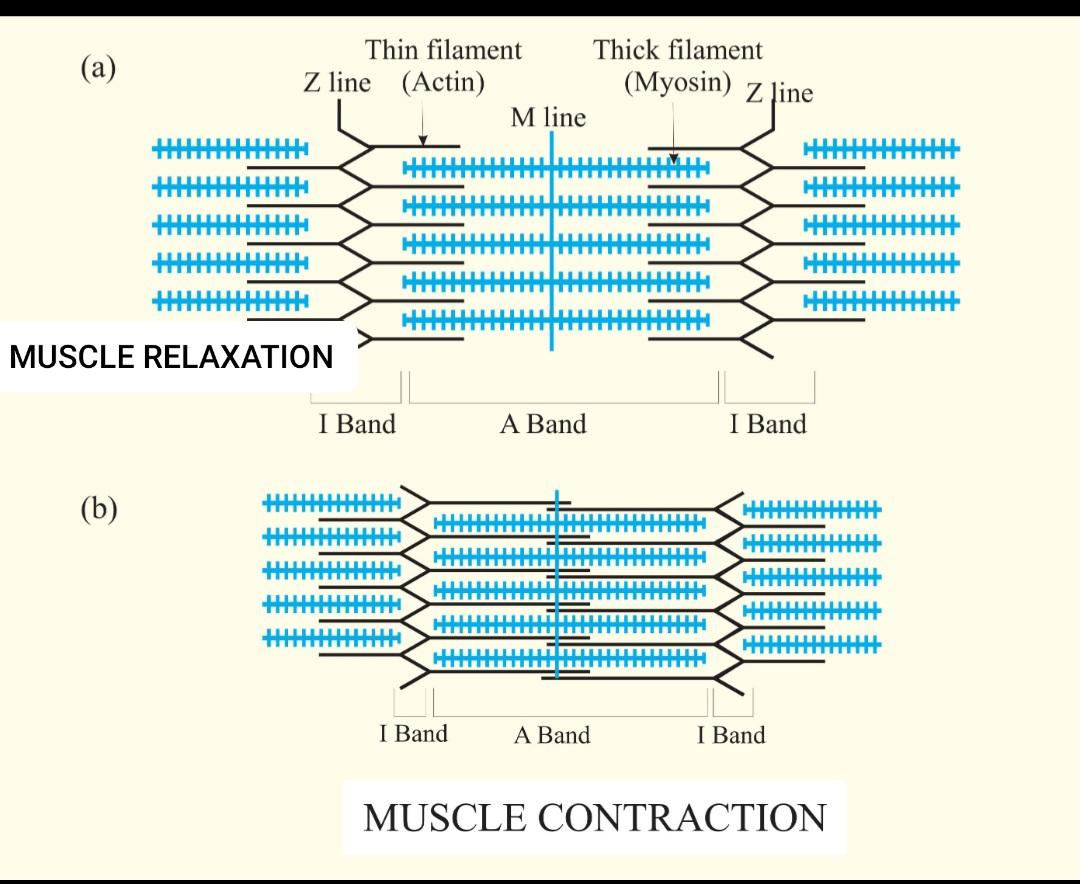
The following changes are observed in the I band during muscle contraction:
-Progressive shortening of the I band occurs.
-Gradually the I band disappears, at this time the fibril has shortened to almost 65% of its initial resting length.
Additional Information: The Muscle contraction is usually related to the activation of the sites which generate tension within the muscle fibers. The contraction doesn't always mean muscle shortening because muscle tension is often produced without changes in muscle length, like when holding an important book or a dumbbell at an equivalent position. When the contraction will be terminating, it will be followed by muscle relaxation, which may be a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. Muscle contractions will be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes but the muscle length remains equivalent. In contrast, a muscle contraction is isotonic if muscle tension remains equivalent throughout the contraction.
Note: If the muscle length gets shorter, the contraction is concentric; if the muscle length lengthens, the contraction is eccentric. In natural movements which include locomotor activity, muscle contractions are multifaceted as they're ready to produce changes in length and tension during a time-varying manner. Therefore, neither length nor tension is probably going to stay equivalent in muscles that contract during locomotor activity.
Complete answer:
The following changes are observed in the I band during muscle contraction:
-Progressive shortening of the I band occurs.
-Gradually the I band disappears, at this time the fibril has shortened to almost 65% of its initial resting length.
Additional Information: The Muscle contraction is usually related to the activation of the sites which generate tension within the muscle fibers. The contraction doesn't always mean muscle shortening because muscle tension is often produced without changes in muscle length, like when holding an important book or a dumbbell at an equivalent position. When the contraction will be terminating, it will be followed by muscle relaxation, which may be a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. Muscle contractions will be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes but the muscle length remains equivalent. In contrast, a muscle contraction is isotonic if muscle tension remains equivalent throughout the contraction.
Note: If the muscle length gets shorter, the contraction is concentric; if the muscle length lengthens, the contraction is eccentric. In natural movements which include locomotor activity, muscle contractions are multifaceted as they're ready to produce changes in length and tension during a time-varying manner. Therefore, neither length nor tension is probably going to stay equivalent in muscles that contract during locomotor activity.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




