
Characteristics of cardiac muscles are that they
(a) Contract quickly and get fatigued
(b) Contract quickly and do not get fatigued
(c) Contract slowly and get fatigued
(d) Contract slowly and do not get fatigued
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: For both skeletal and smooth muscle, the cardiac muscle shares essential characteristics. Functionally, like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle produces heavy contractions. However, it has intrinsic mechanisms, such as smooth muscle, to cause continuous contraction.
Complete step by step answer:
The cardiac muscle is characterized by striped muscle fibers, linked by intercalated discs, where the membranes are specialized to allow easy passage of electrical signals. Cardiac muscles can stay in contraction for a prolonged time, like smooth muscles. Cardiac muscles can contract easily, much like skeletal muscles. In cardiac muscle cells, the formation of contractile proteins often allows stronger contractions when the fibers are stretched, which makes the heart pump more efficiently.
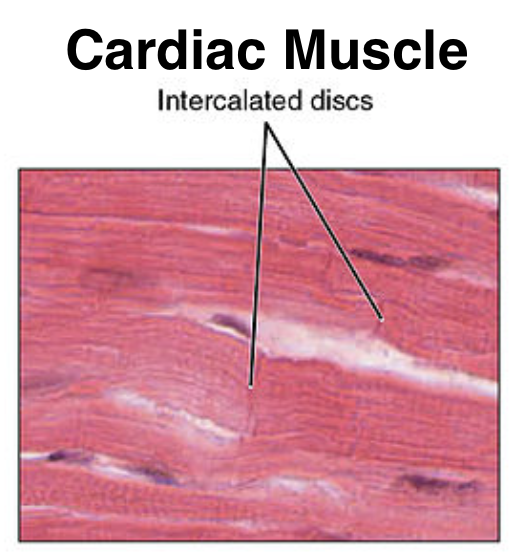
Additional information:
- The muscles in the heart contract rapidly and do not get tired.
- The muscle of the heart is often referred to as the myocardium or heart muscle.
- A striated, involuntary muscle is a cardiac muscle.
- The dominant tissue of the heart's wall is cardiac muscle.
- The cardiac muscle consists of cardiac muscle cells known as cardiomyocytes.
- In a similar way, the cardiac muscle contracts as the skeletal muscle contracts.
- The disorder caused by cardiac muscle is cardiomyopathy.
So, the correct answer is ‘contract quickly and do not get fatigued’.
Note: Cardiac muscle cells are only located in the heart and are specialized in powerfully and efficiently pumping blood during our lifespan. Cardiac muscle tissue cells are characterized by four features: they are involuntary and intrinsically regulated, striated, branched, and single nucleated.
Complete step by step answer:
The cardiac muscle is characterized by striped muscle fibers, linked by intercalated discs, where the membranes are specialized to allow easy passage of electrical signals. Cardiac muscles can stay in contraction for a prolonged time, like smooth muscles. Cardiac muscles can contract easily, much like skeletal muscles. In cardiac muscle cells, the formation of contractile proteins often allows stronger contractions when the fibers are stretched, which makes the heart pump more efficiently.

Additional information:
- The muscles in the heart contract rapidly and do not get tired.
- The muscle of the heart is often referred to as the myocardium or heart muscle.
- A striated, involuntary muscle is a cardiac muscle.
- The dominant tissue of the heart's wall is cardiac muscle.
- The cardiac muscle consists of cardiac muscle cells known as cardiomyocytes.
- In a similar way, the cardiac muscle contracts as the skeletal muscle contracts.
- The disorder caused by cardiac muscle is cardiomyopathy.
So, the correct answer is ‘contract quickly and do not get fatigued’.
Note: Cardiac muscle cells are only located in the heart and are specialized in powerfully and efficiently pumping blood during our lifespan. Cardiac muscle tissue cells are characterized by four features: they are involuntary and intrinsically regulated, striated, branched, and single nucleated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




