
What is the chemical formula of Aluminium sulphate?
Answer
503.7k+ views
Hint: Ionic compounds consist of ions but the overall compound has to be neutral, therefore the crisscross charge balancing method should be used to ensure the overall neutrality and determine the formula of aluminium sulphate.
Complete answer:
Aluminium sulphate is an ionic compound consisting of Aluminium cations and sulphate anions. Its molecular formula can be determined by the crisscross method of balancing charge.
The crisscross method is a method used for balancing the charge of an ionic compound by interchanging the charge numbers of reacting ions with the number of ions needed to form a neutral compound.
Aluminium belongs to the thirteenth group of the modern periodic table and has a total of three valence electrons. Due to its electropositive nature it is capable of giving away all the three valence electrons and acquiring a positive charge of magnitude\[3\].
Sulphate is a divalent anion that accepts two electrons from the metal it is attached to.
In order to balance the charges, we need to make sure that the product of the number of cations in a molecule and its charge is equal to the product of the number of anions in the molecule and its charge.
\[{\text{number of cations}} \times {\text{charge on cation}} = {\text{number of anions}} \times {\text{charge on anion}}\]
Therefore in the crisscross method, the charge on anion determines the number of cations in the molecule and the charge on cation decides the number of anions in the molecule and then the numbers are reduced to the simplest ratio possible.
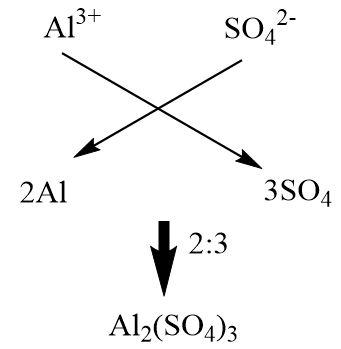
Hence, the formula of Aluminium sulphate is \[A{l_2}{(S{O_4})_3}\]
Note:
The six water molecules written separately after a dot in the chemical formula of Carnallite represent the water of hydration or crystallization. This indicates that each crystal contains a total of six water molecules trapped inside the crystal along with the salts present in it.
Complete answer:
Aluminium sulphate is an ionic compound consisting of Aluminium cations and sulphate anions. Its molecular formula can be determined by the crisscross method of balancing charge.
The crisscross method is a method used for balancing the charge of an ionic compound by interchanging the charge numbers of reacting ions with the number of ions needed to form a neutral compound.
Aluminium belongs to the thirteenth group of the modern periodic table and has a total of three valence electrons. Due to its electropositive nature it is capable of giving away all the three valence electrons and acquiring a positive charge of magnitude\[3\].
Sulphate is a divalent anion that accepts two electrons from the metal it is attached to.
In order to balance the charges, we need to make sure that the product of the number of cations in a molecule and its charge is equal to the product of the number of anions in the molecule and its charge.
\[{\text{number of cations}} \times {\text{charge on cation}} = {\text{number of anions}} \times {\text{charge on anion}}\]
Therefore in the crisscross method, the charge on anion determines the number of cations in the molecule and the charge on cation decides the number of anions in the molecule and then the numbers are reduced to the simplest ratio possible.

Hence, the formula of Aluminium sulphate is \[A{l_2}{(S{O_4})_3}\]
Note:
The six water molecules written separately after a dot in the chemical formula of Carnallite represent the water of hydration or crystallization. This indicates that each crystal contains a total of six water molecules trapped inside the crystal along with the salts present in it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




