
What is the chemical name of the Niacin? Why is it required for the body?
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: Niacin is also known as Nicotinic acid. Niacin is a type of Vitamin B, that performs various processes that are related to the DNA.
Step by step answer:
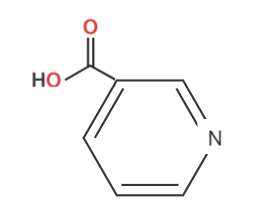
Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid, is popularly known by its common name, Vitamin \({B_3}\).
Its chemical name or IUPAC name is Pyridine-3-carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is \({C_6}{H_5}N{O_2}\).
As niacin is a type of Vitamin B, thus, it is soluble in water, as Vitamin B is a water-soluble Vitamin.
The food items that are usually obtained from animals like meat, beef, pork, seafood, etc. have a high quality of Niacin in it. However, it is found less in eggs and dairy items, as compared to the other animal products. Spices are also considered an active source of Niacin.
Niacin is required by our bodies because it is the precursor of several coenzymes in our bodies. These co-enzymes include NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) and NADP (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate). These co-enzymes help in the process of DNA repair. They are also used in many hydrogen-transfer processes in our body. NAD is actively commonly in catabolic processes, whereas, the NADP is active commonly in the anabolic processes.
Note: The deficiency of niacin causes pellagra in the body. This disease is characterized by lesions of skin and mouth. Other symptoms and signs include anemia, tiredness, and headaches.
Other conditions like diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia, and hyperpigmentation of the skin are also observed due to the severe deficiency of the Niacin. If the deficiency is left untreated, it could also lead to death.
Step by step answer:
Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid, is popularly known by its common name, Vitamin \({B_3}\).
Its chemical name or IUPAC name is Pyridine-3-carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is \({C_6}{H_5}N{O_2}\).

As niacin is a type of Vitamin B, thus, it is soluble in water, as Vitamin B is a water-soluble Vitamin.
The food items that are usually obtained from animals like meat, beef, pork, seafood, etc. have a high quality of Niacin in it. However, it is found less in eggs and dairy items, as compared to the other animal products. Spices are also considered an active source of Niacin.
Niacin is required by our bodies because it is the precursor of several coenzymes in our bodies. These co-enzymes include NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) and NADP (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate). These co-enzymes help in the process of DNA repair. They are also used in many hydrogen-transfer processes in our body. NAD is actively commonly in catabolic processes, whereas, the NADP is active commonly in the anabolic processes.
Note: The deficiency of niacin causes pellagra in the body. This disease is characterized by lesions of skin and mouth. Other symptoms and signs include anemia, tiredness, and headaches.
Other conditions like diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia, and hyperpigmentation of the skin are also observed due to the severe deficiency of the Niacin. If the deficiency is left untreated, it could also lead to death.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




