
Chiasmata is formed during
A. Zygotene
B. Pachytene
C. Diplotene
D. Leptotene
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Chiasmata is the point of contact of non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. It is seen in the meiotic cell division. Meiosis involves division of sex chromosomes.
Complete step by step answer:
To solve the question we must know about the stages of meiotic division.
Meiotic division is a special type of division in sex cells to produce male and female gametes. In this process two phases of division take place which produce four haploid cells. Prior to division, genetic material of both the parents are crossed over to form new combinations in each chromosome. There are two meiotic divisions, I and II. Before meiosis S phase begins in which the DNA replicates so that two sister chromatids are formed. The cell enters meiotic prophase whose stages are as follows-
Leptotene is the first stage of meiosis where the chromosomes appear as threads.
Zygotene is the second stage of meiosis where the pairing of homologous chromosomes takes place.
Pachytene stage, the crossing over takes place.
Diplotene – In this stage the crossing over (intermixing of the parental genes) is completed. Chiasmata is formed at the location where crossing over has taken place.
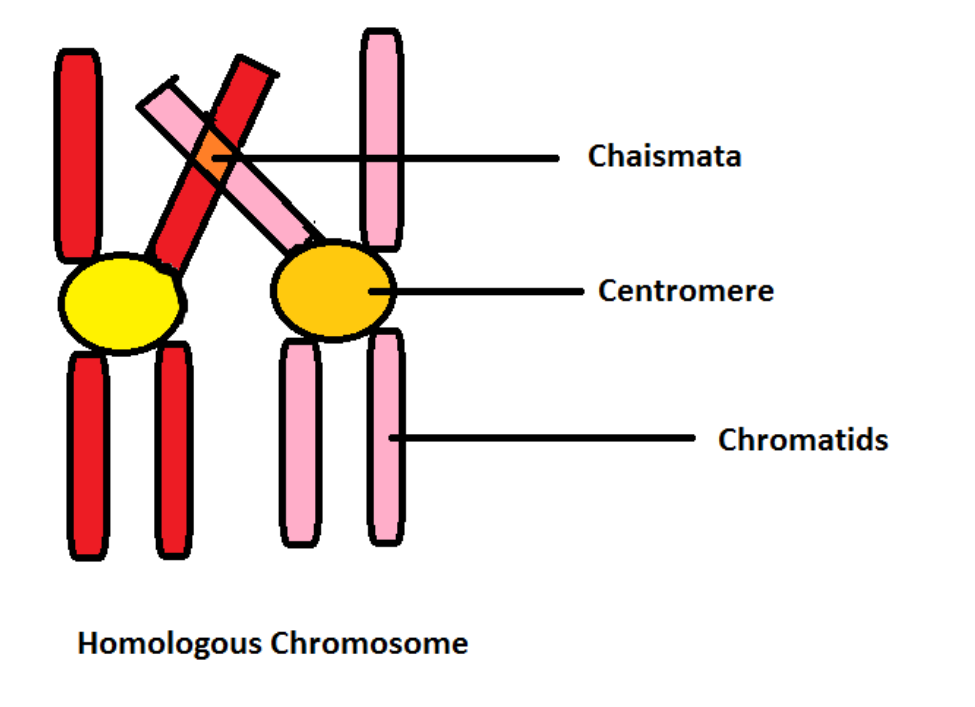
Diakinesis is the condensation of chromosomes.
Thus the correct answer is C. Chiasmata is formed in the Diplotene phase of prophase 1.
Note:
In the prophase I of meiosis crossing over take place. The point at which the crossing over takes place is called the chiasmata. Diplotene phase is the last stage of prophase 1 after which chromosomes condense.
Complete step by step answer:
To solve the question we must know about the stages of meiotic division.
Meiotic division is a special type of division in sex cells to produce male and female gametes. In this process two phases of division take place which produce four haploid cells. Prior to division, genetic material of both the parents are crossed over to form new combinations in each chromosome. There are two meiotic divisions, I and II. Before meiosis S phase begins in which the DNA replicates so that two sister chromatids are formed. The cell enters meiotic prophase whose stages are as follows-
Leptotene is the first stage of meiosis where the chromosomes appear as threads.
Zygotene is the second stage of meiosis where the pairing of homologous chromosomes takes place.
Pachytene stage, the crossing over takes place.
Diplotene – In this stage the crossing over (intermixing of the parental genes) is completed. Chiasmata is formed at the location where crossing over has taken place.

Diakinesis is the condensation of chromosomes.
Thus the correct answer is C. Chiasmata is formed in the Diplotene phase of prophase 1.
Note:
In the prophase I of meiosis crossing over take place. The point at which the crossing over takes place is called the chiasmata. Diplotene phase is the last stage of prophase 1 after which chromosomes condense.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




