
Chordates are distinguished from the non-chordates by the presence of
(a)A solid ventral nerve cord
(b)The dorsal tubular nerve cord
(c)Paired nerve chord
(d)Ganglionated nerve node
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: This structure is hollow, single, and tube-like. It is present above the notochord and alimentary canal. The development of this structure occurs from embryonic ectoderm. They are different on the basis of their structure.
Complete answer:
Chordates are distinguished from non-chordates based on three main characteristics:
-Notochord
-Dorsal tubular central nervous system or dorsal tubular nerve cord
-Pharyngeal gill clefts
Therefore the most appropriate answer for this question would be the dorsal tubular nerve cord. The anterior part of this structure forms the brain while the remaining part forms the spinal cord.
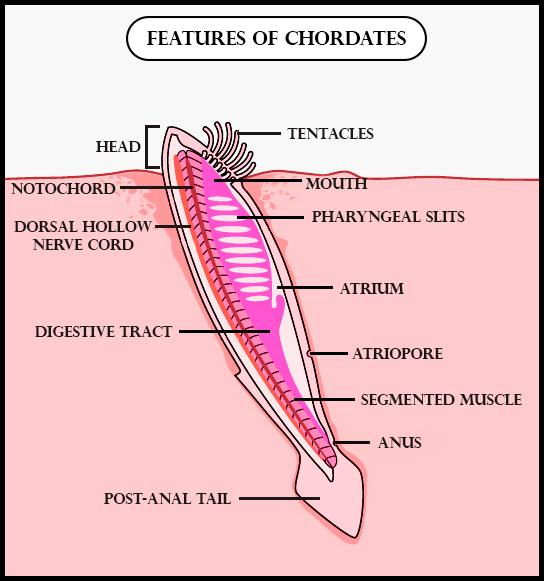
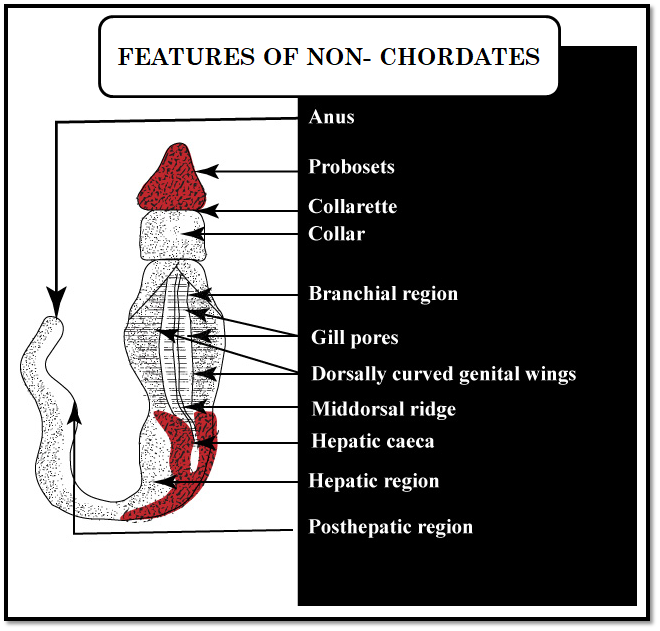
Additional Information: -The chordates have a notochord and pharyngeal gill slits at some stage of development.
-The bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and coelomate gives an organ level of organization that makes the chordates unique features.
So, the correct answer is, ‘dorsal tubular nerve cord.’
Note: -Chordate basic traits are first evolved in the invertebrates having bilateral symmetry, cephalization, segmentation, coelom marked by physical and behavioral specialization.
-The smallest animal in chordates is the Philippine gody, about mm long.
-The largest animal in chordates is the Blue Whale, about 35 m long.
Complete answer:
Chordates are distinguished from non-chordates based on three main characteristics:
-Notochord
-Dorsal tubular central nervous system or dorsal tubular nerve cord
-Pharyngeal gill clefts
Therefore the most appropriate answer for this question would be the dorsal tubular nerve cord. The anterior part of this structure forms the brain while the remaining part forms the spinal cord.
| -Phylum Chordates | -Phylum Non-Chordates |
| -A strong but flexible rod present beneath the nerve cord called the notochord. | -The absence of a notochord or backbone is an important feature. |
| -A tail that extends past the anus. | -The absence of a post-anal tail in this phylum. |
| -Embryos have gill slits on the walls of pharynx functions in both feeding and respiration. | -In this group, the animals respire through the body surface, gill, or tracheae. |
| -A nerve cord parallels the notochord and gut which anterior ends develop into the brain. | -The non- chordates show the absence of notochord and the pharynx is not perforated by gill slits. |
| -The presence of the block of muscle surrounding the notochord and nerve cord- Myotomes. | -Absence of myotomes. |
| -Chordates are further divided into- Vertebrate, Urochordata, and Cephalochordata. | -Non- chordates are further divided into- Protozoa, Porifera, Coelenterata, Platyhelminthes, Nemathelminthes, Echinodermata, Hemichordata |


Additional Information: -The chordates have a notochord and pharyngeal gill slits at some stage of development.
-The bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and coelomate gives an organ level of organization that makes the chordates unique features.
So, the correct answer is, ‘dorsal tubular nerve cord.’
Note: -Chordate basic traits are first evolved in the invertebrates having bilateral symmetry, cephalization, segmentation, coelom marked by physical and behavioral specialization.
-The smallest animal in chordates is the Philippine gody, about mm long.
-The largest animal in chordates is the Blue Whale, about 35 m long.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




