
Chromosome duplication without nuclear division refers to
(a) Meiosis
(b) Mitosis
(c) Androgenesis
(d) Endomitosis
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: This is often found in insects and tissues of some vertebrates, which form cells with a polyploid nucleus. Polytene chromosomes (huge chromosomes) are also formed as a result of this process.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Endomitosis is the process of chromosome divides or doubles without nuclear division which leads to the formation of a polyploidy nucleus where one nucleus will have multiple sets of chromosomes.
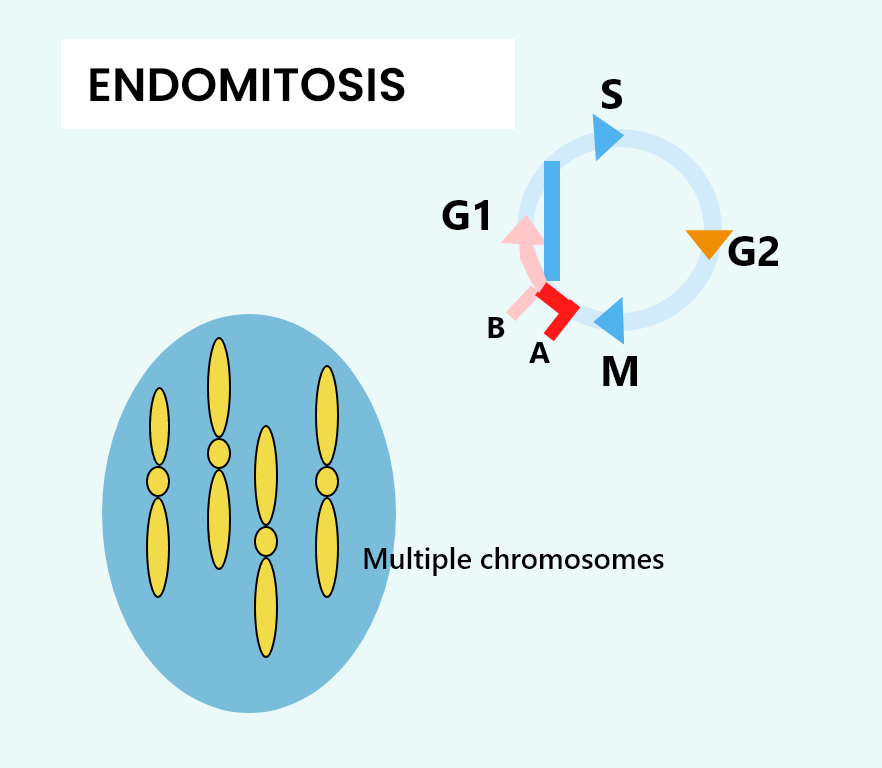
So, the correct answer is ‘Endomitosis’.
Additional Information:
- In- plant cells endomitosis is commonly found in tapetum where the nuclear membrane does not disappear, but the chromosomes are condensed more than that of normal mitosis during the metaphase.
Meiosis: A process where a single cell produces four daughter cells by replicating twice, where each cell contains half of the original amount of genetic material from the parent cell.
- Gametes (sex cells – egg in females and sperm in males) are produced by meiosis. The process of meiosis is divided into two major stages known as meiosis I and meiosis II.
Mitosis: A process where a single parent cell divides or replicates into two identical daughter cells, which is commonly known as cell replication or binary division.
- Mitosis occurs in our normal cells by which the cells increase their number and also replaces dead cells.
- Mitosis is divided into 5 stages, which are Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Androgenesis: The process of formation of embryos without the genetic material from oocytes.
- In androgenesis, there is no participation by the female reproductive cell in the process of reproduction.
Note:
- In mitosis, the daughter cells are genetically identical, wherein meiosis the daughter cells are not genetically identical and result in the formation of haploid daughter cells.
- Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes in which one set is obtained from each parent, where haploid cells have just a single copy of each chromosome.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Endomitosis is the process of chromosome divides or doubles without nuclear division which leads to the formation of a polyploidy nucleus where one nucleus will have multiple sets of chromosomes.

So, the correct answer is ‘Endomitosis’.
Additional Information:
- In- plant cells endomitosis is commonly found in tapetum where the nuclear membrane does not disappear, but the chromosomes are condensed more than that of normal mitosis during the metaphase.
Meiosis: A process where a single cell produces four daughter cells by replicating twice, where each cell contains half of the original amount of genetic material from the parent cell.
- Gametes (sex cells – egg in females and sperm in males) are produced by meiosis. The process of meiosis is divided into two major stages known as meiosis I and meiosis II.
Mitosis: A process where a single parent cell divides or replicates into two identical daughter cells, which is commonly known as cell replication or binary division.
- Mitosis occurs in our normal cells by which the cells increase their number and also replaces dead cells.
- Mitosis is divided into 5 stages, which are Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Androgenesis: The process of formation of embryos without the genetic material from oocytes.
- In androgenesis, there is no participation by the female reproductive cell in the process of reproduction.
Note:
- In mitosis, the daughter cells are genetically identical, wherein meiosis the daughter cells are not genetically identical and result in the formation of haploid daughter cells.
- Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes in which one set is obtained from each parent, where haploid cells have just a single copy of each chromosome.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




