
Cisternae is found in
(a) Only mitochondria
(b) Only endoplasmic reticulum
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi body
(d) Only Golgi body
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: In two organelles present in the eukaryotic cell, Cisternae is found. The folding of protein molecules and their transportation is the responsibility of one organelle. The other organelle is a collection of stacked membranes that assist with protein packaging.
Complete answer:
The flattened membrane-bound tube-like structure found in both the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus is a cisternae. In the Golgi apparatus, the cis-cisternae, followed by the medial cisternae, then the trans-cisternae as they pass away from the endoplasmic reticulum. It assists in the transport of proteins and other enzymes from Golgi. Cisternae transport proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum to the vesicles of the Golgi apparatus.
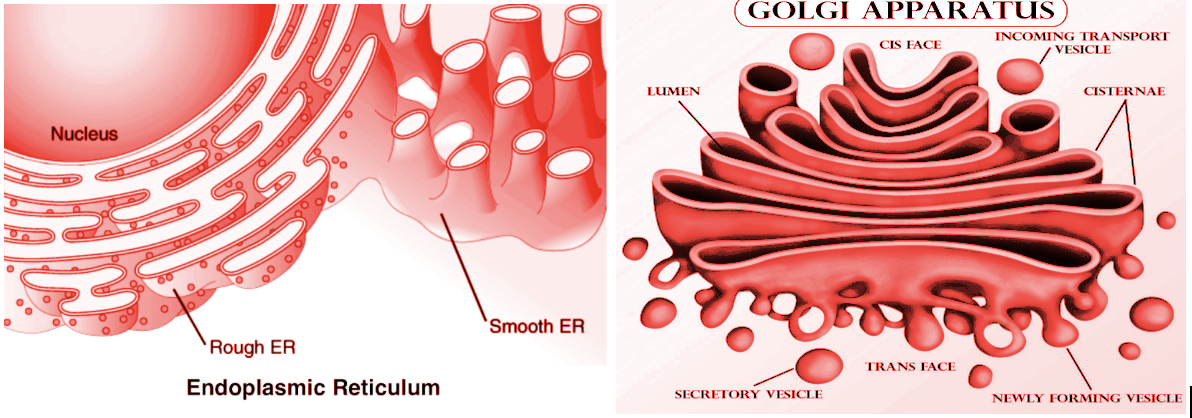
The Golgi apparatus consists of a set of compartments in most eukaryotes and is a collection of fused, flattened membrane-enclosed discs known as cisternae (singular: cisterna, also known as 'dictyosomes'), produced from vesicular clusters budding from the endoplasmic reticulum.
The endoplasmic reticulum ( ER) consists of two subunits-rough endoplasmic reticulum ( RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) a type of organelle. In most eukaryotic cells, the endoplasmic reticulum forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs in the SER known as cisternae (in the RER) and tubular structures. With the external nuclear membrane, the membranes of the ER are continuous.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi body’.
Note: There are usually 40 to 100 stacks of cisternae in a mammalian cell. There are normally between four and eight cisternae present in a stack, but as many as sixty cisternae have been found in some protists. This collection of cisternae consists of two major networks: the cis Golgi network (CGN) and the trans-Golgi network (TGN). Cis, medial, and trans compartments are formed when the cisternae collection is broken down. CGN is the first structure of the cistern, and TGN is the final structure from which proteins are packed into vesicles for lysosomes, secretory vesicles, or the surface of the cell.
Complete answer:
The flattened membrane-bound tube-like structure found in both the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus is a cisternae. In the Golgi apparatus, the cis-cisternae, followed by the medial cisternae, then the trans-cisternae as they pass away from the endoplasmic reticulum. It assists in the transport of proteins and other enzymes from Golgi. Cisternae transport proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum to the vesicles of the Golgi apparatus.

The Golgi apparatus consists of a set of compartments in most eukaryotes and is a collection of fused, flattened membrane-enclosed discs known as cisternae (singular: cisterna, also known as 'dictyosomes'), produced from vesicular clusters budding from the endoplasmic reticulum.
The endoplasmic reticulum ( ER) consists of two subunits-rough endoplasmic reticulum ( RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) a type of organelle. In most eukaryotic cells, the endoplasmic reticulum forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs in the SER known as cisternae (in the RER) and tubular structures. With the external nuclear membrane, the membranes of the ER are continuous.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi body’.
Note: There are usually 40 to 100 stacks of cisternae in a mammalian cell. There are normally between four and eight cisternae present in a stack, but as many as sixty cisternae have been found in some protists. This collection of cisternae consists of two major networks: the cis Golgi network (CGN) and the trans-Golgi network (TGN). Cis, medial, and trans compartments are formed when the cisternae collection is broken down. CGN is the first structure of the cistern, and TGN is the final structure from which proteins are packed into vesicles for lysosomes, secretory vesicles, or the surface of the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




