
Citric acid cycle is ______ step in carbohydrate metabolism.
(a) First
(b) Second
(c) Third
(d) Fourth
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: The citric acid cycle is a step in the metabolism of carbohydrates that produces high-energy molecules like NADH and $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$. Usually, people who win the race in this position are awarded bronze medals.
Complete answer:
Glycolysis, pyruvate conversion to Acetyl CoA, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation are the four steps of carbohydrate metabolism.
Thus, the third stage in the metabolism of carbohydrates is the citric acid cycle.
- The digestion of carbohydrates starts in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and finishes with the absorption of monosaccharides in the small intestine epithelium. The mechanism of cellular respiration begins once the ingested monosaccharides are transferred to the tissues.
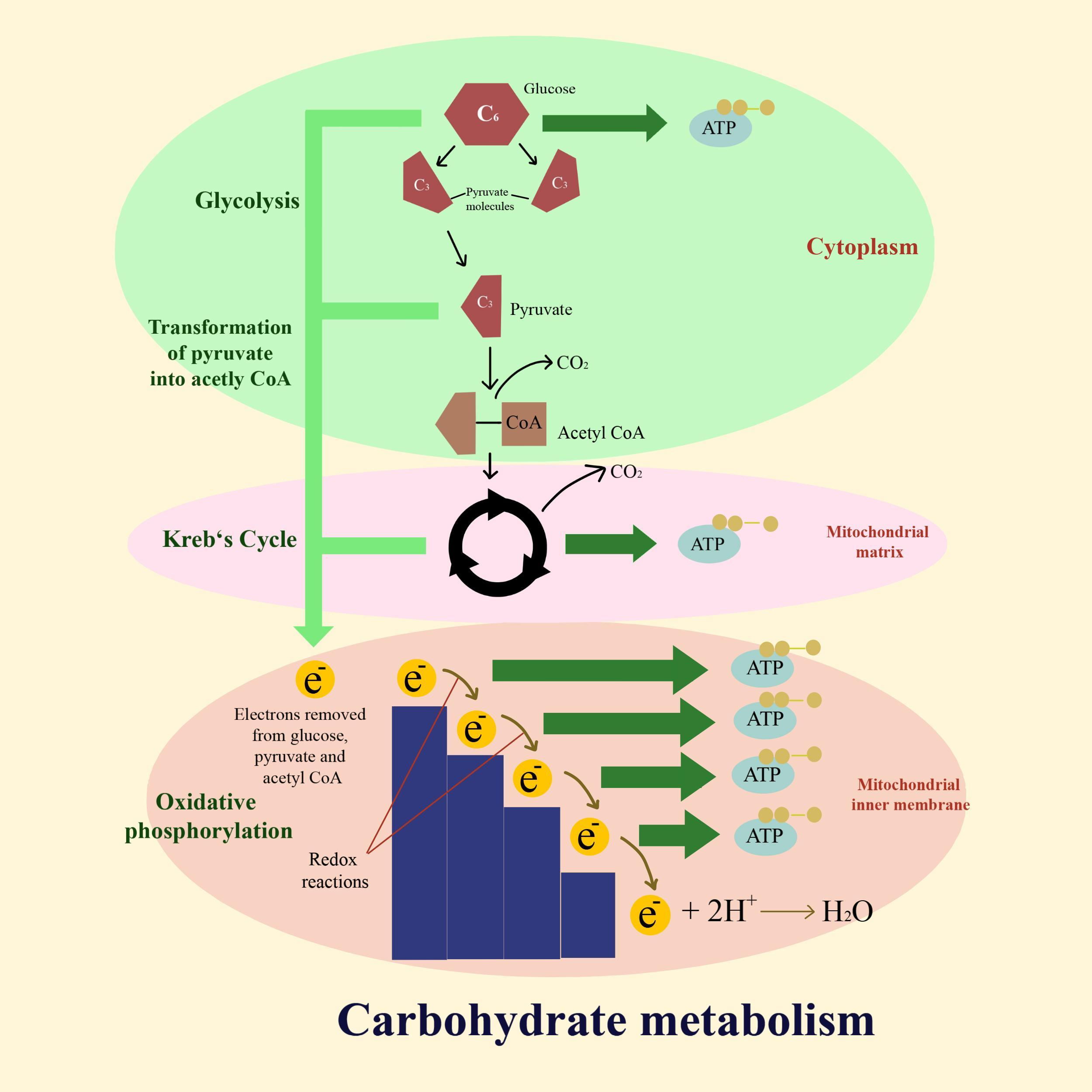
- This segment will first concentrate on glycolysis, a mechanism in which the glucose monosaccharide is oxidized and the energy retained in its bonds to generate ATP is released. Cells in the body take up circulating glucose in response to insulin and transfer some of the energy in glucose to ADP to form ATP via a sequence of reactions called glycolysis. The product pyruvate is formed by the last step in glycolysis.
- The pyruvate molecules generated during glycolysis are carried into the inner mitochondrial matrix through the mitochondrial membrane, where they are metabolized in a pathway called the Krebs cycle by enzymes. The cycle of Krebs is often generally called the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA). High-energy molecules, including ATP, NADH, and $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$, are created during the Krebs process. To produce more ATP molecules, NADH and $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$ then transfer electrons through the electron transport chain in the mitochondria.
- A NADH and $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$ generated by the Krebs cycle are used by the electron transport chain (ETC) to generate ATP. A sequence of enzymatic reactions transfer electrons from NADH and $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$ via protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(c) Third’.
Note:
- Carbohydrates are organic molecules that are made up of atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Both simple and complex sugars are found in the family of carbohydrates.
- Carbohydrates are broken down into basic, soluble sugars during digestion that can be transported via the intestinal wall through the circulatory system to be transported around the body.
Complete answer:
Glycolysis, pyruvate conversion to Acetyl CoA, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation are the four steps of carbohydrate metabolism.
Thus, the third stage in the metabolism of carbohydrates is the citric acid cycle.
- The digestion of carbohydrates starts in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and finishes with the absorption of monosaccharides in the small intestine epithelium. The mechanism of cellular respiration begins once the ingested monosaccharides are transferred to the tissues.

- This segment will first concentrate on glycolysis, a mechanism in which the glucose monosaccharide is oxidized and the energy retained in its bonds to generate ATP is released. Cells in the body take up circulating glucose in response to insulin and transfer some of the energy in glucose to ADP to form ATP via a sequence of reactions called glycolysis. The product pyruvate is formed by the last step in glycolysis.
- The pyruvate molecules generated during glycolysis are carried into the inner mitochondrial matrix through the mitochondrial membrane, where they are metabolized in a pathway called the Krebs cycle by enzymes. The cycle of Krebs is often generally called the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA). High-energy molecules, including ATP, NADH, and $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$, are created during the Krebs process. To produce more ATP molecules, NADH and $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$ then transfer electrons through the electron transport chain in the mitochondria.
- A NADH and $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$ generated by the Krebs cycle are used by the electron transport chain (ETC) to generate ATP. A sequence of enzymatic reactions transfer electrons from NADH and $FAD{ H }_{ 2 }$ via protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(c) Third’.
Note:
- Carbohydrates are organic molecules that are made up of atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Both simple and complex sugars are found in the family of carbohydrates.
- Carbohydrates are broken down into basic, soluble sugars during digestion that can be transported via the intestinal wall through the circulatory system to be transported around the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




