
Coenocytic mycelium is found in
(a) Rhizopus
(b) Mucor
(c) Penicillium
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: These are fungi that belong to the phylum Zygomycota, found in soil and decaying fruits and vegetables. Mucormycosis is a common fungal infection caused by them.
Correct step by step answer:
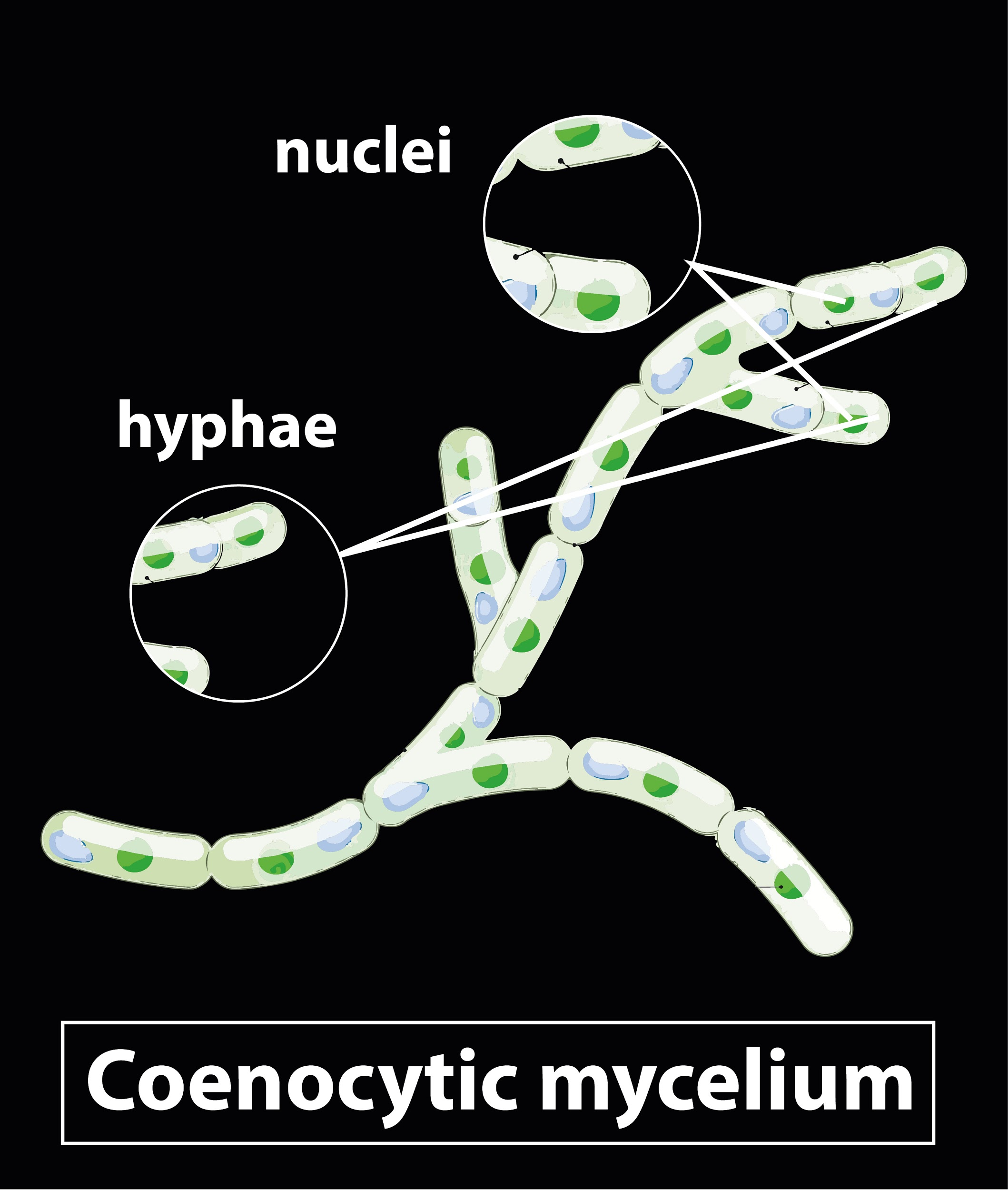
Coenocytic mycelium is found in both Rhizopus and Mucor. Coenocytic hyphae are continuous tubes like structures with multi- nucleated cytoplasm and mycelium is a network of hyphae. Thus we can conclude from the above two statements that a coenocytic mycelium is a network of multinucleated hyphae.
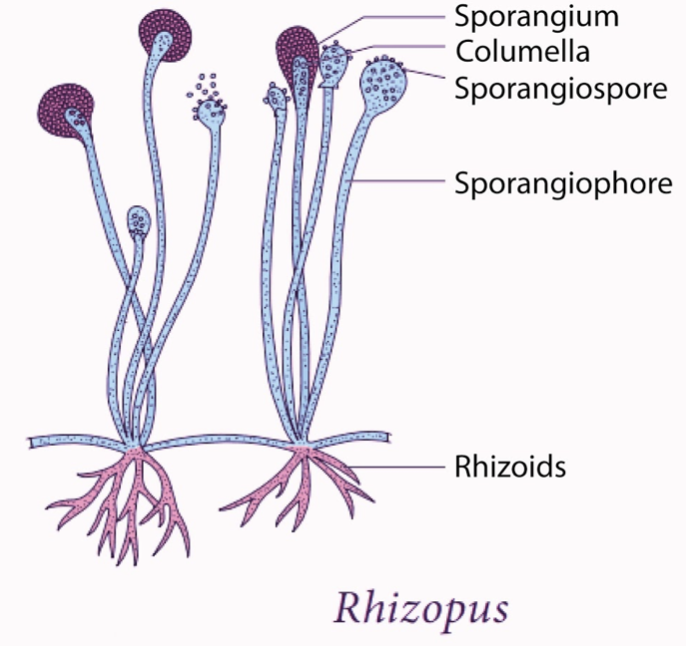
- Rhizopus belongs to the phylum Zygomycota is a filamentous fungus found in soil, decaying fruit and vegetables, animal feces, and old bread. They are common contaminants, also occasional causes of serious infections in humans. The best grow at 45- degree Celsius. The sporangium is spherical in shape and sporangiophore is mostly brown and unbranched. The columella is spherical or elongated. The apophysis is not prominent.
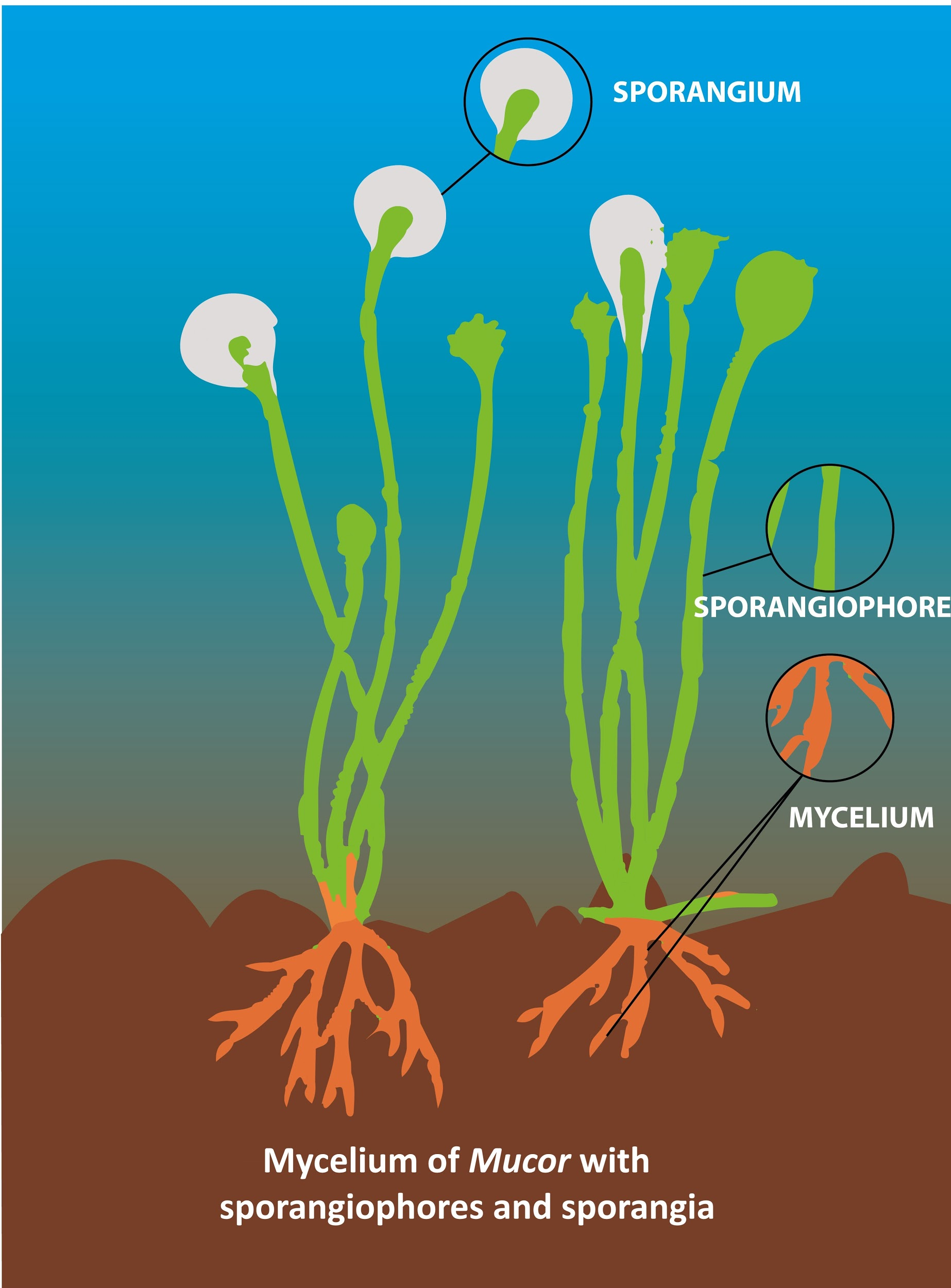
- Mucor also belongs to the phylum Zygomycota is also a filamentous fungus found in soil, plants, decaying fruits, and vegetables. The best growth is below 37degree Celcius. The sporangium is spherical and sporangiophore is branched or unbranched and hyaline. The columella was found in varying shapes.
- Penicillium belongs to the phylum Ascomycota. The mycelium consists of highly branched networks of multinucleated and colorless hyphae, with each pair of cells separated by a septum. Conidiophores are present at the end of each branch accompanied by green spherical conidia. These propagules play a significant role in reproduction as conidia are the main dispersal strategy of these fungi.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(d) both (a) and (b) '.
Note:
- The main difference between Mucor and Rhizopus is that the Mucor does not have rhizoids and stolons while Rhizopus has both rhizoids and stolons.
- Mucor has branched sporangiophore while the sporangiophore of Rhizopus is generally unbranched.
- Mucor is a filamentous fungus found in soil, plants, decaying fruits, and vegetables. They are ubiquitous and a common laboratory contaminant may cause infections in men, frogs, amphibians, cattle, and swine.
Correct step by step answer:
Coenocytic mycelium is found in both Rhizopus and Mucor. Coenocytic hyphae are continuous tubes like structures with multi- nucleated cytoplasm and mycelium is a network of hyphae. Thus we can conclude from the above two statements that a coenocytic mycelium is a network of multinucleated hyphae.

- Rhizopus belongs to the phylum Zygomycota is a filamentous fungus found in soil, decaying fruit and vegetables, animal feces, and old bread. They are common contaminants, also occasional causes of serious infections in humans. The best grow at 45- degree Celsius. The sporangium is spherical in shape and sporangiophore is mostly brown and unbranched. The columella is spherical or elongated. The apophysis is not prominent.
- Mucor also belongs to the phylum Zygomycota is also a filamentous fungus found in soil, plants, decaying fruits, and vegetables. The best growth is below 37degree Celcius. The sporangium is spherical and sporangiophore is branched or unbranched and hyaline. The columella was found in varying shapes.


- Penicillium belongs to the phylum Ascomycota. The mycelium consists of highly branched networks of multinucleated and colorless hyphae, with each pair of cells separated by a septum. Conidiophores are present at the end of each branch accompanied by green spherical conidia. These propagules play a significant role in reproduction as conidia are the main dispersal strategy of these fungi.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(d) both (a) and (b) '.
Note:
- The main difference between Mucor and Rhizopus is that the Mucor does not have rhizoids and stolons while Rhizopus has both rhizoids and stolons.
- Mucor has branched sporangiophore while the sporangiophore of Rhizopus is generally unbranched.
- Mucor is a filamentous fungus found in soil, plants, decaying fruits, and vegetables. They are ubiquitous and a common laboratory contaminant may cause infections in men, frogs, amphibians, cattle, and swine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




