
Coke powder is spread over the molten electrolyte to:
(A)- prevent the heat radiation from the surface
(B)- prevent the corrosion of graphite anode
(C)- prevent the oxidation of molten aluminum by air
(D)- both (a) and (b)

Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Coke acts as a reducing agent. Reducing agents prevent oxidation reactions like burning, corrosion. Electrolysis reduction of aluminium is carried out in a cell made of iron using carbon electrodes. The temperature inside the electrolytic cell is very high.
Complete step by step solution:
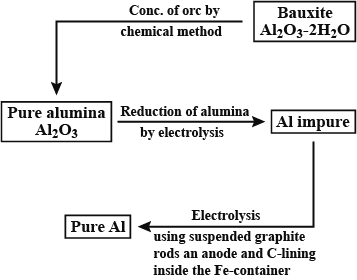
Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of alumina ($A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$) mixed with cryolite ($N{{a}_{3}}Al{{F}_{6}}$). This process is known as Hall and Heroult’s process. The molten mass to be electrolyzed, which is formed by the mixing of alumina and cryolite, is covered with a layer of powdered coke. The role of coke in the process of electrolysis is twofold.
The molten electrolyte has to be maintained at high temperature inside the bath. Layer of powdered coke on the molten electrolyte acts as insulation and does not allow the heat to dissipate. So, coke reduces or prevents the loss of heat due to radiation from the surface.
Graphite is used as anode. The reactions taking place at anode and cathode during the electrolytic reduction of alumina are given below:
At cathode: \[2A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}\to 4Al+3{{O}_{2}}\] or $A{{l}^{3+}}(melt)+3{{e}^{-}}\to Al$
At anode: \[\begin{align}
& C(s)+{{O}^{2-}}(melt)\to CO(g)+2{{e}^{-}} \\
& C(s)+2{{O}^{2-}}(melt)\to C{{O}_{2}}(g)+4{{e}^{-}} \\
\end{align}\]
Carbon electrode (graphite electrode) reacts with the oxygen released at anode to form carbon dioxide ($C{{O}_{2}}$) and carbon monoxide (CO).
For one kg of aluminum to be obtained, 0.5 kg of graphite anode is burned. That is why the mass at the carbon anode slowly decreases. Coke prevents this burning of graphite electrodes in air (oxygen).
Therefore, we can say that powdered coke prevents loss of heat due to radiation and prevents corrosion of graphite anode.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
Note that coke prevents the burning or corrosion of graphite electrodes in oxygen. Do not get confused between the options. Coke helps to prevent the oxidation of graphite and it does not prevent the oxidation of aluminium formed.
Complete step by step solution:
Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of alumina ($A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$) mixed with cryolite ($N{{a}_{3}}Al{{F}_{6}}$). This process is known as Hall and Heroult’s process. The molten mass to be electrolyzed, which is formed by the mixing of alumina and cryolite, is covered with a layer of powdered coke. The role of coke in the process of electrolysis is twofold.
The molten electrolyte has to be maintained at high temperature inside the bath. Layer of powdered coke on the molten electrolyte acts as insulation and does not allow the heat to dissipate. So, coke reduces or prevents the loss of heat due to radiation from the surface.
Graphite is used as anode. The reactions taking place at anode and cathode during the electrolytic reduction of alumina are given below:
At cathode: \[2A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}\to 4Al+3{{O}_{2}}\] or $A{{l}^{3+}}(melt)+3{{e}^{-}}\to Al$
At anode: \[\begin{align}
& C(s)+{{O}^{2-}}(melt)\to CO(g)+2{{e}^{-}} \\
& C(s)+2{{O}^{2-}}(melt)\to C{{O}_{2}}(g)+4{{e}^{-}} \\
\end{align}\]
Carbon electrode (graphite electrode) reacts with the oxygen released at anode to form carbon dioxide ($C{{O}_{2}}$) and carbon monoxide (CO).
For one kg of aluminum to be obtained, 0.5 kg of graphite anode is burned. That is why the mass at the carbon anode slowly decreases. Coke prevents this burning of graphite electrodes in air (oxygen).
Therefore, we can say that powdered coke prevents loss of heat due to radiation and prevents corrosion of graphite anode.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
Note that coke prevents the burning or corrosion of graphite electrodes in oxygen. Do not get confused between the options. Coke helps to prevent the oxidation of graphite and it does not prevent the oxidation of aluminium formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




