
Compare the Mendeleev and Modern Periodic Tables on the basis of the following criteria:
1.Groups
2.Properties of elements
3.Classification.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: What was the one major correction made in the classification of the Modern Periodic Table to help rectify several issues that arose as a result of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table?
Step-by-Step Solution:
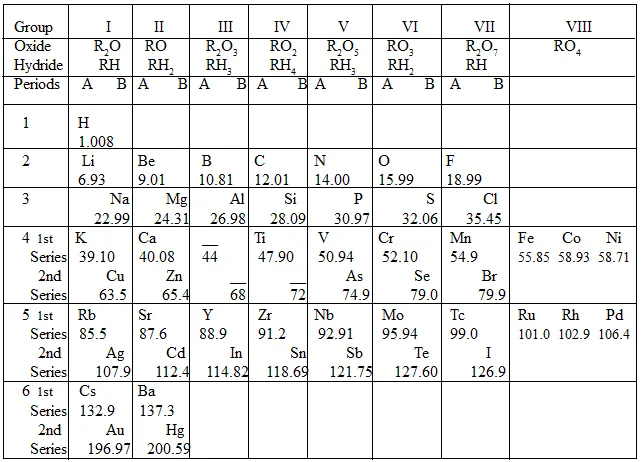
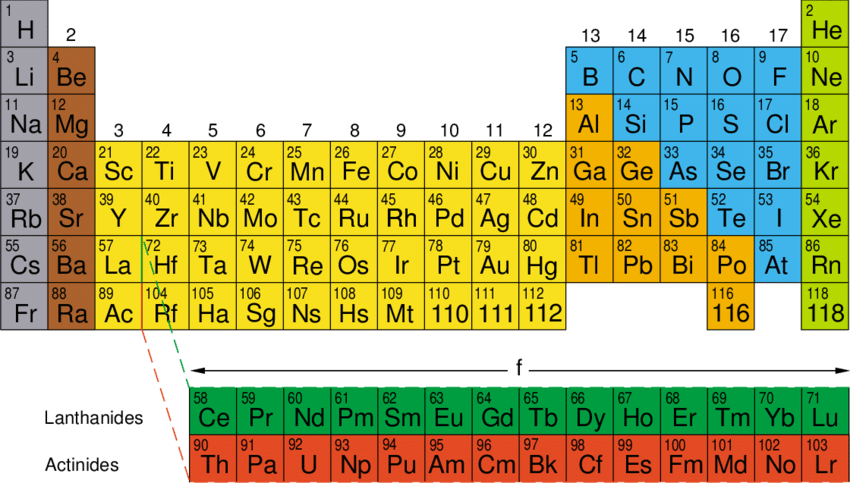
Mendeleev’s periodic table is based on the relation of properties of elements to the atomic weight of elements whereas the Modern periodic table considers atomic number as the fundamental criterion that decides the properties of elements.
Modern periodic table corrects defects of the Mendeleev’s periodic table. For example, in the Mendeleev’s periodic table, in the element pairs, Argon-potassium, cobalt-nickel, tellurium-iodine and thorium and protactinium, elements with higher atomic mass precedes the element with lower atomic weight. Though these are the right places for them, they contradict Mendeleev’s periodic law.
These elements' atomic number show the reverse order compared to their atomic mass. The supposed wrong positions in Mendeleev’s table have the right explanation justifying their positions.
Uneven grouping of elements:
In Mendeleev’s periodic table, coinage metals of copper, silver, and gold are grouped together with very active alkali metals. Manganese metal was grouped with halogens in the seventh group. The defects are rectified in the Modern periodic table.
Thus, to accommodate all possible properties and elements, the modern periodic table has 18 groups and 7 periods in contrast with Mendeleev’s 7 groups and 6 periods.
Position of isotopes:
Isotopes with higher atomic weights could not be accommodated in the Mendeleev’s table. As isotopes have the same atomic number, they do not need any separate location in the modern periodic table.
No reasons were offered for the triad elements of viii group in the Mendeleev’s classification but no such special grouping is required in the modern table.
Note:
Mendeleev’s periodic table was for the arrangement of sixty-three elements known at that time whereas the Modern table accommodates all the 118- natural and synthetic elements.
Atomic number is a much more fundamental property distinguishing each element and hence sets a better criterion to decide the physical and chemical properties of elemental atoms when compared to atomic weights.
Step-by-Step Solution:


Mendeleev’s periodic table is based on the relation of properties of elements to the atomic weight of elements whereas the Modern periodic table considers atomic number as the fundamental criterion that decides the properties of elements.
Modern periodic table corrects defects of the Mendeleev’s periodic table. For example, in the Mendeleev’s periodic table, in the element pairs, Argon-potassium, cobalt-nickel, tellurium-iodine and thorium and protactinium, elements with higher atomic mass precedes the element with lower atomic weight. Though these are the right places for them, they contradict Mendeleev’s periodic law.
These elements' atomic number show the reverse order compared to their atomic mass. The supposed wrong positions in Mendeleev’s table have the right explanation justifying their positions.
Uneven grouping of elements:
In Mendeleev’s periodic table, coinage metals of copper, silver, and gold are grouped together with very active alkali metals. Manganese metal was grouped with halogens in the seventh group. The defects are rectified in the Modern periodic table.
Thus, to accommodate all possible properties and elements, the modern periodic table has 18 groups and 7 periods in contrast with Mendeleev’s 7 groups and 6 periods.
Position of isotopes:
Isotopes with higher atomic weights could not be accommodated in the Mendeleev’s table. As isotopes have the same atomic number, they do not need any separate location in the modern periodic table.
No reasons were offered for the triad elements of viii group in the Mendeleev’s classification but no such special grouping is required in the modern table.
Note:
Mendeleev’s periodic table was for the arrangement of sixty-three elements known at that time whereas the Modern table accommodates all the 118- natural and synthetic elements.
Atomic number is a much more fundamental property distinguishing each element and hence sets a better criterion to decide the physical and chemical properties of elemental atoms when compared to atomic weights.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




