
Complete the reaction:
\[{C_6}{H_5}ONa + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to \] ____________
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: The reaction between sodium phenoxide and alkyl halides is a substitution reaction that depends on the type of alkoxide or phenoxide being used. The rate of the reaction is largely affected by the type of alkyl halide.
Complete answer:
The reaction between phenoxide and ethyl chloride is a well-known example of Williamson’s reaction which involves a substitution bimolecular mechanism to produce the corresponding ethers.
The alkyl group attached to the halogen breaks apart and forms a bond with the oxygen of the phenoxide group to give ethyl phenyl ether. The remaining sodium ions and chloride ions react with each other to form sodium chloride as a byproduct.
The reaction can be initiated by forming phenoxide ions from phenol that can be used to react with alkyl halides.
Since, the mechanism is \[{S_N}2\] in nature, the alkyl halide needs to be a primary alkyl halide as the reactivity decreases with increasing substitutions. A secondary or tertiary alkyl halide fails to produce an ether by substitution mechanism and elimination is preferred over a substitution reaction. Both protic or aprotic solvents can be used for this type of ether synthesis.
The reaction can be written as follows:
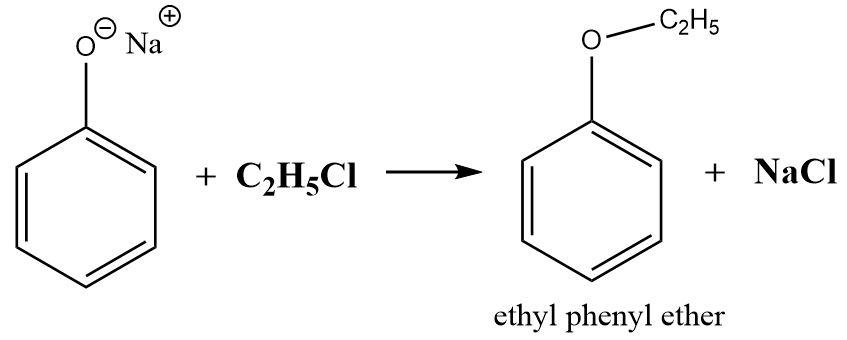
\[ \Rightarrow \] Hence the product formed is ethyl phenyl ether.
Note:
Alcohols are mildly acidic in nature and it is difficult to produce corresponding alkoxides but phenol is more acidic as compared to alcohols due to the resonance stabilization of their conjugate base and their phenoxide can be easily prepared by a simple reaction with sodium hydroxide.
Complete answer:
The reaction between phenoxide and ethyl chloride is a well-known example of Williamson’s reaction which involves a substitution bimolecular mechanism to produce the corresponding ethers.
The alkyl group attached to the halogen breaks apart and forms a bond with the oxygen of the phenoxide group to give ethyl phenyl ether. The remaining sodium ions and chloride ions react with each other to form sodium chloride as a byproduct.
The reaction can be initiated by forming phenoxide ions from phenol that can be used to react with alkyl halides.
Since, the mechanism is \[{S_N}2\] in nature, the alkyl halide needs to be a primary alkyl halide as the reactivity decreases with increasing substitutions. A secondary or tertiary alkyl halide fails to produce an ether by substitution mechanism and elimination is preferred over a substitution reaction. Both protic or aprotic solvents can be used for this type of ether synthesis.
The reaction can be written as follows:

\[ \Rightarrow \] Hence the product formed is ethyl phenyl ether.
Note:
Alcohols are mildly acidic in nature and it is difficult to produce corresponding alkoxides but phenol is more acidic as compared to alcohols due to the resonance stabilization of their conjugate base and their phenoxide can be easily prepared by a simple reaction with sodium hydroxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




