
Components of crude petroleum can be separated by :
(A) Distillation
(B) Evaporation
(C) Filtration
(D) Fractional distillation
Answer
512.4k+ views
Hint :Petroleum, often known as crude oil or oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid found deep under the Earth's surface in geological formations. The majority of petroleum has been obtained by oil drilling. Drilling occurs after structural geology, sedimentary basin analysis, and reservoir characterization investigations have been completed. Other unconventional deposits, such as oil sands and oil shale, have also been exploited as a result of recent technological advancements.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The separation of a mixture into its constituent elements, or fractions, is known as fractional distillation. Heating chemical compounds to a temperature where one or more fractions of the mixture evaporate allows them to be separated. To fractionate, it employs distillation. Under one atmosphere of pressure, the boiling points of the component elements should deviate by no more than 25 °C (45 °F). A simple distillation is usually utilised when the difference in boiling points is higher than 25 °C.
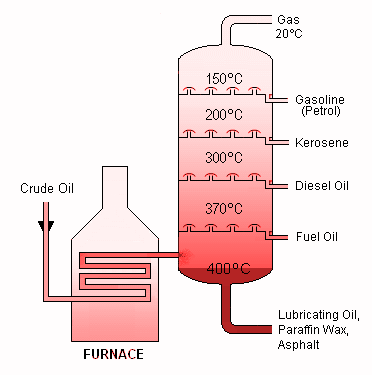
Fractional distillation divides a mixture into several portions, known as fractions. Above the mixture is a tall fractionating column with multiple condensers coming out at varying heights. The bottom of the column is heated, while the top is cold. High-boiling-point compounds condense near the bottom, whereas lower-boiling-point chemicals condense on their way to the top. Crude oil is made up of a variety of hydrocarbons. In the fractionating column, the crude oil evaporates and its vapours condense at different temperatures. Hydrocarbon molecules with a comparable amount of carbon atoms and a comparable range of boiling temperatures are found in each percentage. The graphic below summarises the major crude oil fractions, their applications, and property trends. The gases depart at the top, the liquids condense in the centre, and the solids remain at the bottom of the column. The hydrocarbons have: as they go up the fractionating column
boiling points that are lower
reduced viscosity (they flow more easily)
increased flammability (they ignite more easily).
Hence option D is correct.
Note :
The design and operation of fractionation towers in the oil refining industry is still primarily done on an empirical basis. In ordinary practise, the calculations required in the construction of petroleum fractionation columns need the employment of numerable charts, tables, and sophisticated empirical equations. However, in recent years, a lot of effort has gone into developing efficient and dependable computer-aided design techniques for fractional distillation.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The separation of a mixture into its constituent elements, or fractions, is known as fractional distillation. Heating chemical compounds to a temperature where one or more fractions of the mixture evaporate allows them to be separated. To fractionate, it employs distillation. Under one atmosphere of pressure, the boiling points of the component elements should deviate by no more than 25 °C (45 °F). A simple distillation is usually utilised when the difference in boiling points is higher than 25 °C.
Fractional distillation divides a mixture into several portions, known as fractions. Above the mixture is a tall fractionating column with multiple condensers coming out at varying heights. The bottom of the column is heated, while the top is cold. High-boiling-point compounds condense near the bottom, whereas lower-boiling-point chemicals condense on their way to the top. Crude oil is made up of a variety of hydrocarbons. In the fractionating column, the crude oil evaporates and its vapours condense at different temperatures. Hydrocarbon molecules with a comparable amount of carbon atoms and a comparable range of boiling temperatures are found in each percentage. The graphic below summarises the major crude oil fractions, their applications, and property trends. The gases depart at the top, the liquids condense in the centre, and the solids remain at the bottom of the column. The hydrocarbons have: as they go up the fractionating column
boiling points that are lower
reduced viscosity (they flow more easily)
increased flammability (they ignite more easily).

Hence option D is correct.
Note :
The design and operation of fractionation towers in the oil refining industry is still primarily done on an empirical basis. In ordinary practise, the calculations required in the construction of petroleum fractionation columns need the employment of numerable charts, tables, and sophisticated empirical equations. However, in recent years, a lot of effort has gone into developing efficient and dependable computer-aided design techniques for fractional distillation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




