
What is compound C?
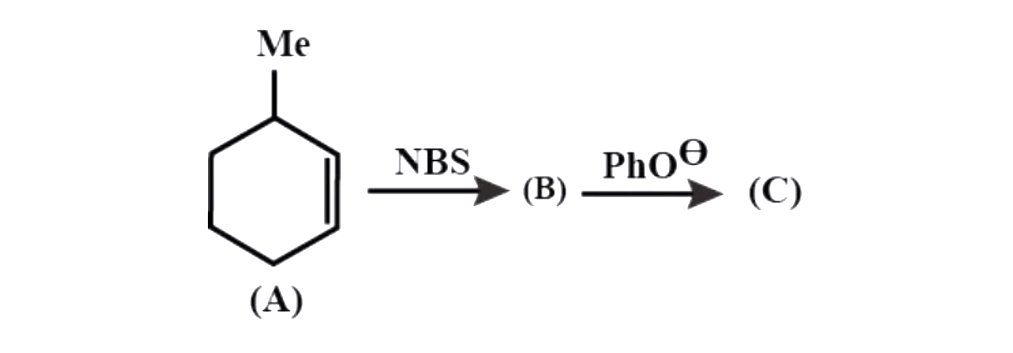
a. Methylene cyclohex-2-ene
b. Methylene cyclohexane
c. Methylene cyclohex-3-ene
d. None of the above

Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: The action of NBS on an allylic halide results in the bromination of the compound on an adjacent atom. With this in mind, try to find the result of the subsequent reaction with the bulky base that is the phenolate ion.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first look into NBS as a reagent and the properties it possesses before moving onto subsequent steps of the reaction.
N-Bromosuccinimide or NBS is a chemical reagent mostly used in reactions of Organic Chemistry such as free radical substitution, electrophilic addition, and electrophilic substitution reactions. NBS is a very convenient source of the Br•, which is the bromine free radical.
NBS reacts with doubly saturated organic compounds i.e. alkenes in aqueous solvents to give bromohydrins. The preferred conditions for this reaction requires the portion-wise addition of NBS to a solution of the alkene in 50% aqueous DMSO, DME, THF, or tert-butanol at 0 °C (which are all non-polar organic solvents). This results in the formation of a bromonium ion and the immediate attack of water which follows the initial step results in the production of a strong Markovnikov product and anti-stereochemical selectivity.
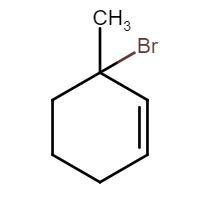
Therefore, from this we can conclude that product (B) is 3-methyl-3-bromo cyclohexene, the structure of which is given by:
Analysing the second step of the reaction, we realise that a Hoffman elimination product must be formed with the bulky base that is the phenolate ion.
The Hofmann elimination is an elimination reaction of an amine where the least stable alkene, the Hofmann product, is formed. This tendency, known as the Hofmann alkene synthesis rule, is in contrast to most normal elimination reactions, where Zaitsev's rule predicts the formation of the most stable alkene on the basis of how substituted the resultant alkene is.
Therefore, we can conclude that the final product formed would be Methylene cyclohex-2-ene, the structure of which is given by:
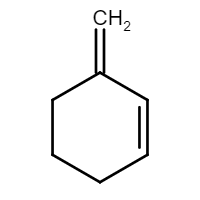
Thus, we can conclude that the answer to this question is a).
Note: Conventional elimination reactions that occur via the E2 mechanism follow Zaitsev’s rule. The major product will be the more substituted alkene (that is, the alkene with the most carbons directly attached to the alkene).
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first look into NBS as a reagent and the properties it possesses before moving onto subsequent steps of the reaction.
N-Bromosuccinimide or NBS is a chemical reagent mostly used in reactions of Organic Chemistry such as free radical substitution, electrophilic addition, and electrophilic substitution reactions. NBS is a very convenient source of the Br•, which is the bromine free radical.
NBS reacts with doubly saturated organic compounds i.e. alkenes in aqueous solvents to give bromohydrins. The preferred conditions for this reaction requires the portion-wise addition of NBS to a solution of the alkene in 50% aqueous DMSO, DME, THF, or tert-butanol at 0 °C (which are all non-polar organic solvents). This results in the formation of a bromonium ion and the immediate attack of water which follows the initial step results in the production of a strong Markovnikov product and anti-stereochemical selectivity.
Therefore, from this we can conclude that product (B) is 3-methyl-3-bromo cyclohexene, the structure of which is given by:

Analysing the second step of the reaction, we realise that a Hoffman elimination product must be formed with the bulky base that is the phenolate ion.
The Hofmann elimination is an elimination reaction of an amine where the least stable alkene, the Hofmann product, is formed. This tendency, known as the Hofmann alkene synthesis rule, is in contrast to most normal elimination reactions, where Zaitsev's rule predicts the formation of the most stable alkene on the basis of how substituted the resultant alkene is.
Therefore, we can conclude that the final product formed would be Methylene cyclohex-2-ene, the structure of which is given by:

Thus, we can conclude that the answer to this question is a).
Note: Conventional elimination reactions that occur via the E2 mechanism follow Zaitsev’s rule. The major product will be the more substituted alkene (that is, the alkene with the most carbons directly attached to the alkene).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




