
Consider the following set of reactions
$C{H_3}COOH\xrightarrow{{SOC{l_2}}}A\xrightarrow[{Benzene}]{{Anhyd.AlC{l_3}}}B\xrightarrow{{HCN}}C\xrightarrow{{HOH}}D$
The structure $D$ will be
A.)
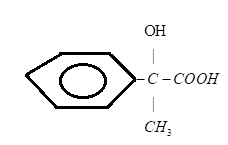
B.)
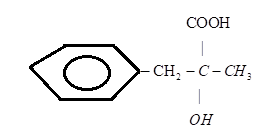
C.)

D.)
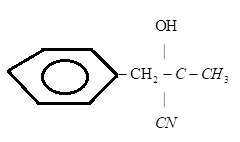




Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: When thionyl chloride that is $SOC{l_2}$ reacts with a carboxylic acid then the $ - OH$ of the carboxylic acid replaces with the chlorine to form an acid chloride or acyl chloride in the product. The benzene with $AlC{l_3}$ reacts with this acyl chloride then chlorine is replaced by the benzene group.
Complete answer:
In the given set of reactions, the first reactant is a carboxylic acid. The $SOC{l_2}$ has the chemical name as Thionyl Chloride. When thionyl chloride ($SOC{l_2}$) reacts with carboxylic acid then the product formed is acid chloride or we can say it is acyl chloride with general chemical formulas as $R - OCl$. In this reaction, $ - OH$ of the carboxylic is replaced by the $ - Cl$ . Hence, this reaction can be written as:
$C{H_3}COOH\xrightarrow{{SOC{l_2}}}C{H_3}COCl$
When the acyl chloride that is formed in the above reaction reacts with the benzene in the presence of aluminium trichloride ($AlC{l_3}$) then the benzene ring will attach in place of chlorine. This reaction is known as Friedel craft acylation. In Friedel crafts acylation, when acyl group that is $C{H_3}COCl$ reacts with an aromatic compound then the chlorine of the acyl chloride gets replaced with the aromatic compound that is benzene here. So, the reaction can be shown as:
$C{H_3}COCl\xrightarrow[{Anhyd.AlC{l_3}}]{{Benzene}}{C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3}$
When ${C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3}$ reacts with $HCN$ then the $CN$ combines with the carbon of carboxylic group and $H$ combines with oxygen of the carboxylic group to form ${C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN$. This reaction can be represented as:
${C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3}\xrightarrow{{HCN}}{C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN$
When the formed product that is ${C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN$ reacts with water then $-CN$ will be replaced by the $-COOH$ group. This reaction can be represented as:
${C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN\xrightarrow{{HOH}}{C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})COOH$
Therefore, the set of reactions can be written as:
$ C{H_3}COOH\xrightarrow{{SOC{l_2}}}C{H_3}COCl\xrightarrow[{Benzene}]{{Anhyd.AlC{l_3}}}{C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3} \\
\xrightarrow{{HCN}}{C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN\xrightarrow{{HOH}}{C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})COOH \\
$
Therefore, the product $D$ is ${C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})COOH$
Hence, the option A.) is the correct answer.
Note: Always remember that when any acyl chloride that is of general formula as $R - OCl$ reacts in the presence of $AlC{l_3}$ with an aromatic compound then it is Friedel craft acylation and when an alkyl halide reacts with these reagents the it is called as Friedel craft alkylation.
Complete answer:
In the given set of reactions, the first reactant is a carboxylic acid. The $SOC{l_2}$ has the chemical name as Thionyl Chloride. When thionyl chloride ($SOC{l_2}$) reacts with carboxylic acid then the product formed is acid chloride or we can say it is acyl chloride with general chemical formulas as $R - OCl$. In this reaction, $ - OH$ of the carboxylic is replaced by the $ - Cl$ . Hence, this reaction can be written as:
$C{H_3}COOH\xrightarrow{{SOC{l_2}}}C{H_3}COCl$
When the acyl chloride that is formed in the above reaction reacts with the benzene in the presence of aluminium trichloride ($AlC{l_3}$) then the benzene ring will attach in place of chlorine. This reaction is known as Friedel craft acylation. In Friedel crafts acylation, when acyl group that is $C{H_3}COCl$ reacts with an aromatic compound then the chlorine of the acyl chloride gets replaced with the aromatic compound that is benzene here. So, the reaction can be shown as:
$C{H_3}COCl\xrightarrow[{Anhyd.AlC{l_3}}]{{Benzene}}{C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3}$
When ${C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3}$ reacts with $HCN$ then the $CN$ combines with the carbon of carboxylic group and $H$ combines with oxygen of the carboxylic group to form ${C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN$. This reaction can be represented as:
${C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3}\xrightarrow{{HCN}}{C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN$
When the formed product that is ${C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN$ reacts with water then $-CN$ will be replaced by the $-COOH$ group. This reaction can be represented as:
${C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN\xrightarrow{{HOH}}{C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})COOH$
Therefore, the set of reactions can be written as:
$ C{H_3}COOH\xrightarrow{{SOC{l_2}}}C{H_3}COCl\xrightarrow[{Benzene}]{{Anhyd.AlC{l_3}}}{C_6}{H_5}COC{H_3} \\
\xrightarrow{{HCN}}{C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})CN\xrightarrow{{HOH}}{C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})COOH \\
$
Therefore, the product $D$ is ${C_6}{H_5}C(OH)(C{H_3})COOH$
Hence, the option A.) is the correct answer.
Note: Always remember that when any acyl chloride that is of general formula as $R - OCl$ reacts in the presence of $AlC{l_3}$ with an aromatic compound then it is Friedel craft acylation and when an alkyl halide reacts with these reagents the it is called as Friedel craft alkylation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




