
How can I convert L-xylose bond line view to Fischer projection?
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint: We know that using wedge and dash notation, solid lines (sticks) represent chemical bonds in the plane of the surface. Black wedges represent chemical bonds coming toward you, while dashed lines are for bonds that extend back behind the surface.
Complete step by step solution:
A Fischer projection represents every chiral center as a cross. The horizontal line represents bonds extending out of the plane of the paper. The vertical line represents bonds extending behind the plane of the paper. The Fischer projection of L-xylose is
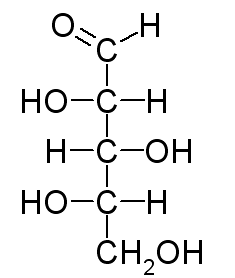
Here's how to convert the wedge-dash structure of L-xylose to its Fischer projection.
Arrange the molecule so that the chiral carbons and the longest continuous chain are in a vertical line. $ C-1 $ (the aldehyde group) goes at the top.
Draw horizontal lines to make crosses at $ C-2,\text{ }C-3, $ and $ C-4. $
Put the $ C-4\text{ }OH $ group on the correct side of the cross. We must view the molecule from the correct angle. This is an L-sugar, so the $ OH $ must be on the left, and $ C-4 $ must be closest to our eye. We must view the molecule from the lower left. We put the $ OH $ on the left arm of the cross. The $ H $ atom goes on the right.
Put the $ C-3\text{ }OH $ group on the correct side of the cross. The $ OH $ is on the left, but $ C-3 $ is furthest from our eye. We must rotate $ C-3 $ to bring it near our eye. The $ OH $ then rotates to the right. We put the $ OH $ on the right arm of the cross. The $ H $ atom goes on the left.
Put the $ C-2\text{ }OH $ group on the correct side of the cross. The $ OH $ group is on the left, and $ C-2 $ is closest to our eye. We put the $ OH $ on the left arm of the cross. The $ H $ atom goes on the right. We now have the Fischer projection of L-xylose.
Note:
Remember that the wedges are now on the right, and the dashes are on the left. It is as if we had wrapped the chain around a cylindrical tube. When you flatten the structure onto the surface of the cylinder, you get the Fischer projection of D-glucose. Understanding the concept of wedge and dash helps to understand stereochemistry and spectroscopy which is an important aspect in research.
Complete step by step solution:
A Fischer projection represents every chiral center as a cross. The horizontal line represents bonds extending out of the plane of the paper. The vertical line represents bonds extending behind the plane of the paper. The Fischer projection of L-xylose is

Here's how to convert the wedge-dash structure of L-xylose to its Fischer projection.
Arrange the molecule so that the chiral carbons and the longest continuous chain are in a vertical line. $ C-1 $ (the aldehyde group) goes at the top.
Draw horizontal lines to make crosses at $ C-2,\text{ }C-3, $ and $ C-4. $
Put the $ C-4\text{ }OH $ group on the correct side of the cross. We must view the molecule from the correct angle. This is an L-sugar, so the $ OH $ must be on the left, and $ C-4 $ must be closest to our eye. We must view the molecule from the lower left. We put the $ OH $ on the left arm of the cross. The $ H $ atom goes on the right.
Put the $ C-3\text{ }OH $ group on the correct side of the cross. The $ OH $ is on the left, but $ C-3 $ is furthest from our eye. We must rotate $ C-3 $ to bring it near our eye. The $ OH $ then rotates to the right. We put the $ OH $ on the right arm of the cross. The $ H $ atom goes on the left.
Put the $ C-2\text{ }OH $ group on the correct side of the cross. The $ OH $ group is on the left, and $ C-2 $ is closest to our eye. We put the $ OH $ on the left arm of the cross. The $ H $ atom goes on the right. We now have the Fischer projection of L-xylose.
Note:
Remember that the wedges are now on the right, and the dashes are on the left. It is as if we had wrapped the chain around a cylindrical tube. When you flatten the structure onto the surface of the cylinder, you get the Fischer projection of D-glucose. Understanding the concept of wedge and dash helps to understand stereochemistry and spectroscopy which is an important aspect in research.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




