
What is the correct electronic configuration of the central atom in $K_{ 4 }[Fe(CN)_{ 6 }]$ on crystal field theory?
(A.) ${ t }_{ 2g }^{ 4 }{ e }_{ g }^{ 2 }$
(B.) ${ t }_{ 2g }^{ 6 }{ e }_{ g }^{ 0 }$
(C.) ${ e }^{ 3 }{ t }_{ 2 }^{ 3 }$
(D.) ${ e }^{ 4 }{ t }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }$
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: To find the correct answer first try to find the oxidation state of Fe in this complex and then write its electronic configuration. Here you have to remember that ${ CN }^{ - }$ is a strong ligand that would pair up the electrons present in the d-orbitals.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s find the correct answer to this question,
First, we need to calculate the oxidation state of iron -
4(+1) + x + 6(-1) = 0
+4 + x -6 = 0
x = +2
In $K_{ 4 }[Fe(CN)_{ 6 }]$,
Electronic configuration of Fe in ground state = [Ar]$3d^{ 6 }4s^{ 2 }$
Electronic configuration of Fe in excited state = ${ Fe }^{ 2+ }$= [Ar]$3d^{ 6 }4s^{ 0 }$
We can represent them as:
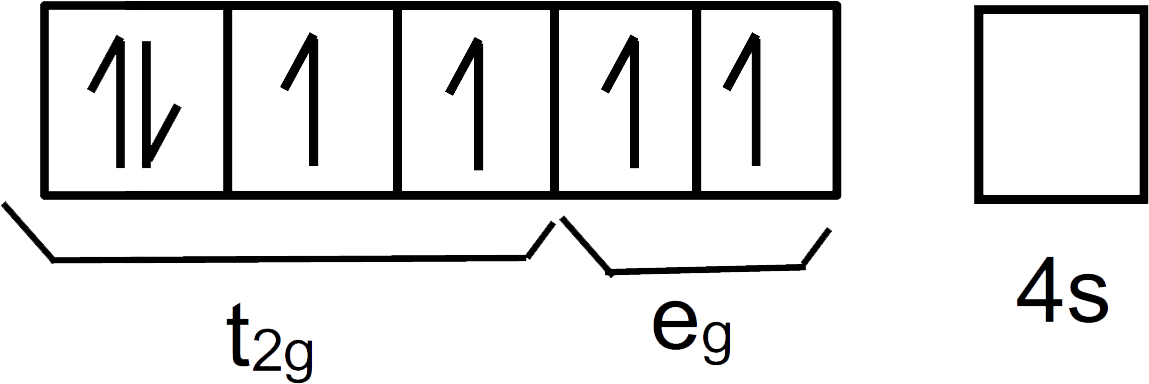
In this compound ${ CN }^{ - }$ is a strong field ligand that would pair up the electrons present in the d-orbitals.
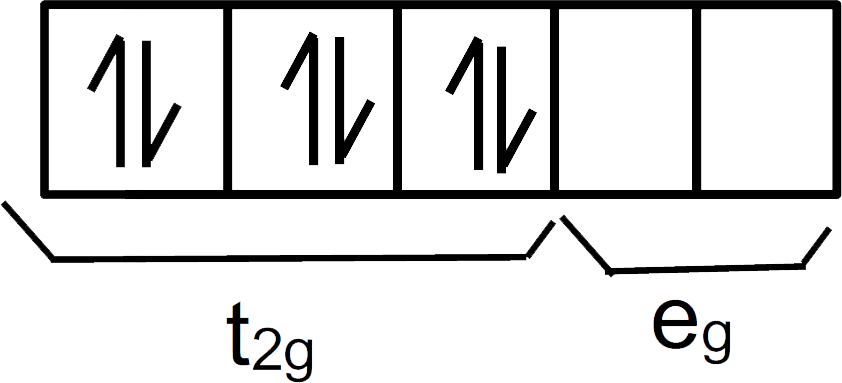
We can see there are 3 pairs of electrons in ${ t }_{ 2g }$ and 0 pairs of electrons in ${ e }_{ g }$.
So, the correct electronic configuration of the central atom in $K_{ 4 }[Fe(CN)_{ 6 }]$ on crystal field theory is ${ t }_{ 2g }^{ 6 }{ e }_{ g }^{ 0 }$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information: ${ t }_{ 2g }$ and ${ e }_{ g }$ refer to symmetry classes to which the d-orbitals belong in octahedral complexes.
In the crystal field model, the normally degenerate 3d orbitals split into two groups, a doubly degenerate set of two orbitals and lower energy triply degenerate set. When analyzed by mathematical group theory, the wave functions for these two groups fall into different symmetry groups, designated ${ e }_{ g }$ and ${ t }_{ 2g }$ respectively.
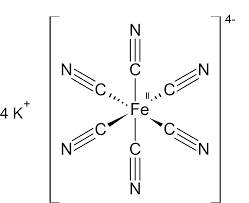
Note: Solid potassium ferrocyanide, both as the hydrate and anhydrous salts, has a complicated polymeric structure. We can also draw the structure of this complex $K_{ 4 }[Fe(CN)_{ 6 }]$ as,
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s find the correct answer to this question,
First, we need to calculate the oxidation state of iron -
4(+1) + x + 6(-1) = 0
+4 + x -6 = 0
x = +2
In $K_{ 4 }[Fe(CN)_{ 6 }]$,
Electronic configuration of Fe in ground state = [Ar]$3d^{ 6 }4s^{ 2 }$
Electronic configuration of Fe in excited state = ${ Fe }^{ 2+ }$= [Ar]$3d^{ 6 }4s^{ 0 }$
We can represent them as:

In this compound ${ CN }^{ - }$ is a strong field ligand that would pair up the electrons present in the d-orbitals.
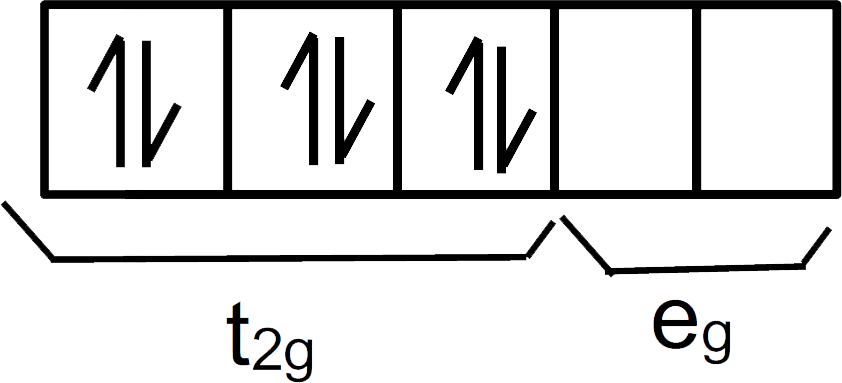
We can see there are 3 pairs of electrons in ${ t }_{ 2g }$ and 0 pairs of electrons in ${ e }_{ g }$.
So, the correct electronic configuration of the central atom in $K_{ 4 }[Fe(CN)_{ 6 }]$ on crystal field theory is ${ t }_{ 2g }^{ 6 }{ e }_{ g }^{ 0 }$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information: ${ t }_{ 2g }$ and ${ e }_{ g }$ refer to symmetry classes to which the d-orbitals belong in octahedral complexes.
In the crystal field model, the normally degenerate 3d orbitals split into two groups, a doubly degenerate set of two orbitals and lower energy triply degenerate set. When analyzed by mathematical group theory, the wave functions for these two groups fall into different symmetry groups, designated ${ e }_{ g }$ and ${ t }_{ 2g }$ respectively.
Note: Solid potassium ferrocyanide, both as the hydrate and anhydrous salts, has a complicated polymeric structure. We can also draw the structure of this complex $K_{ 4 }[Fe(CN)_{ 6 }]$ as,

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




