
Correct order of acidic strength
(P)
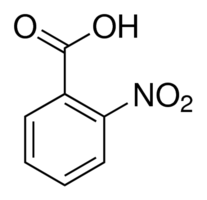
(Q)
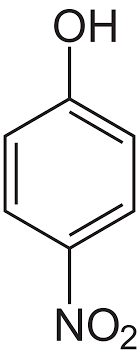
(R)
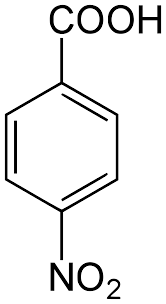
(S)
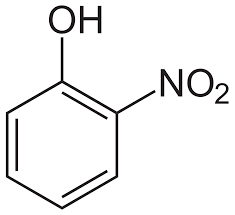




Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of acidic strength and how to compare the acidic strength between different molecules. The more stable is the conjugate base, more acidic is the compound.
Complete Step by step solution:
The acidic strength of ortho-nitrobenzoic acid is higher as compared to para-nitrobenzoic acid. This is because of the 'ortho effect'. Presence of any group at the ortho position of aryl ring in carboxylic acids increases the acidic strength due to inhibition of resonance is known as ortho effect. Pi bonds must lie on the same plane for resonance to occur. But groups at ortho position forces carboxyl group to bend. Due to this pi bond in the carbonyl group lies on a different plane than pi bonds in the aryl ring.
This leads to the inhibition of the resonance, due to which only two equivalent resonating structures are possible for ortho-substituted carboxylic acids. This enhances the acidic strength. Also, carboxylate anion \[CO{O^ - }\] is believed to be less sterically hindered and more apt to be in the energetically favourable planar configuration. This makes an additional reason for the ortho-substituted acid to pass to the anion form, thereby increasing its acidity as compared with the meta and para-substituted acids.
Benzoic acid is a carboxylic acid. It dissociates to give \[{H^ + }\]ions and carboxylate anion. Carboxylate anion is stabilised by resonance. On other hand, phenol dissociates to a very lesser extent compared to \[{H^ + }\]and phenoxide ions. Phenoxide ion is resonance stabilised but resonating structures are non-equivalent. Thus benzoic acid is more acidic than phenol.
p- Nitrophenol is a stronger acid than o-nitrophenol. Because intramolecular H-bond makes ortho isomer weaker than para isomer. In the ortho isomer, due to intramolecular hydrogen bond, the H atom of OH group is tightly attached and is difficult to remove. This decreases the acidity of ortho isomers.
Hence the correct order of acidic strength is : \[{\text{P > R > Q > S}}\]
Note: You should remember the difference between strong bases and weak bases: a strong base is a base that is $100\% $ ionized in solution but if it is less than $100\% $ ionized in solution, it is a weak base. There are very few strong bases and certain salts will also affect the acidity or basicity of aqueous solutions because some of the ions will undergo hydrolysis. The general rule is that salts with ions that are part of strong acids or bases will not hydrolyse, while salts with ions that are part of weak acids or bases will hydrolyse.
Complete Step by step solution:
The acidic strength of ortho-nitrobenzoic acid is higher as compared to para-nitrobenzoic acid. This is because of the 'ortho effect'. Presence of any group at the ortho position of aryl ring in carboxylic acids increases the acidic strength due to inhibition of resonance is known as ortho effect. Pi bonds must lie on the same plane for resonance to occur. But groups at ortho position forces carboxyl group to bend. Due to this pi bond in the carbonyl group lies on a different plane than pi bonds in the aryl ring.
This leads to the inhibition of the resonance, due to which only two equivalent resonating structures are possible for ortho-substituted carboxylic acids. This enhances the acidic strength. Also, carboxylate anion \[CO{O^ - }\] is believed to be less sterically hindered and more apt to be in the energetically favourable planar configuration. This makes an additional reason for the ortho-substituted acid to pass to the anion form, thereby increasing its acidity as compared with the meta and para-substituted acids.
Benzoic acid is a carboxylic acid. It dissociates to give \[{H^ + }\]ions and carboxylate anion. Carboxylate anion is stabilised by resonance. On other hand, phenol dissociates to a very lesser extent compared to \[{H^ + }\]and phenoxide ions. Phenoxide ion is resonance stabilised but resonating structures are non-equivalent. Thus benzoic acid is more acidic than phenol.
p- Nitrophenol is a stronger acid than o-nitrophenol. Because intramolecular H-bond makes ortho isomer weaker than para isomer. In the ortho isomer, due to intramolecular hydrogen bond, the H atom of OH group is tightly attached and is difficult to remove. This decreases the acidity of ortho isomers.
Hence the correct order of acidic strength is : \[{\text{P > R > Q > S}}\]
Note: You should remember the difference between strong bases and weak bases: a strong base is a base that is $100\% $ ionized in solution but if it is less than $100\% $ ionized in solution, it is a weak base. There are very few strong bases and certain salts will also affect the acidity or basicity of aqueous solutions because some of the ions will undergo hydrolysis. The general rule is that salts with ions that are part of strong acids or bases will not hydrolyse, while salts with ions that are part of weak acids or bases will hydrolyse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




