
Why is the cosine of an obtuse angle negative?
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: An angle \[\phi \] , which is greater than the right angle, i.e. \[\phi > 90^\circ \] but less than the straight angles i.e. \[\phi < 180^\circ \] is called as an obtuse angle. Hence, an obtuse angle is\[90^\circ < \phi < 180^\circ \] .
The cosine of an obtuse angle is negative because of the range of the cosine function which is between 1 and -1. Therefore, when the cosine function completes its half cycle, it is at the middle of 1 and -1, that is 0. Thus, as a result when the cosine function reaches further the half cycle, it crosses 0 from the positive direction and becomes less than 0 i.e. negative.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The cosine functions, or \[\cos \theta \] for an angle \[\theta \] is a trigonometric function whose range is defined as \[\left( { - 1,1} \right)\] i.e.
\[ \Rightarrow - 1 < \cos \theta < 1\] \[\forall \theta \]
The cosine function is positive only in the first and the fourth quadrant.
This is why for an obtuse angle, where \[\theta < 90^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {90^\circ + \theta } \right) = - \sin \theta \]
Which is a negative real number because sine function positive for \[\theta < 90^\circ \] .
For example,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos 120^\circ = \cos \left( {90^\circ + 30^\circ } \right)\]
That gives,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos 120^\circ = - \sin 30^\circ \]
i.e.
\[ \Rightarrow \cos 120^\circ = - \dfrac{1}{2}\]
We can also understand this by plotting the graph of a cosine function.
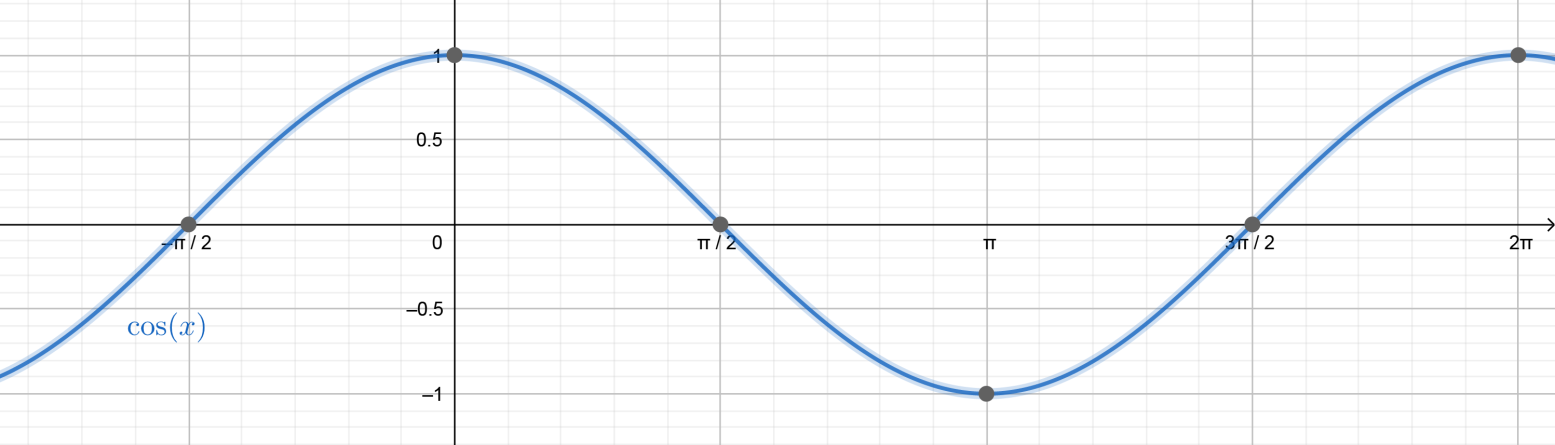
We can see that the cosine function is positive before \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] and then crosses \[0\] downwards at \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] and becomes negative for obtuse angles i.e. between the values \[\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right)\] and therefore oscillates everywhere between \[\left( { - 1,1} \right)\] .
Note: In a right-triangle, cosine function is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to that of the longest side i.e. the hypotenuse. Suppose a triangle ABC is taken with AB as the hypotenuse and \[\theta \] as the angle between hypotenuse and base. Then,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = Base/Hypotenuse\]
The cosine function is one of the three main primary trigonometric functions (sine, cosine and tangent) and it is itself the complement of the sine function.
The cosine of an obtuse angle is negative because of the range of the cosine function which is between 1 and -1. Therefore, when the cosine function completes its half cycle, it is at the middle of 1 and -1, that is 0. Thus, as a result when the cosine function reaches further the half cycle, it crosses 0 from the positive direction and becomes less than 0 i.e. negative.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The cosine functions, or \[\cos \theta \] for an angle \[\theta \] is a trigonometric function whose range is defined as \[\left( { - 1,1} \right)\] i.e.
\[ \Rightarrow - 1 < \cos \theta < 1\] \[\forall \theta \]
The cosine function is positive only in the first and the fourth quadrant.
This is why for an obtuse angle, where \[\theta < 90^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {90^\circ + \theta } \right) = - \sin \theta \]
Which is a negative real number because sine function positive for \[\theta < 90^\circ \] .
For example,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos 120^\circ = \cos \left( {90^\circ + 30^\circ } \right)\]
That gives,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos 120^\circ = - \sin 30^\circ \]
i.e.
\[ \Rightarrow \cos 120^\circ = - \dfrac{1}{2}\]
We can also understand this by plotting the graph of a cosine function.

We can see that the cosine function is positive before \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] and then crosses \[0\] downwards at \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] and becomes negative for obtuse angles i.e. between the values \[\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right)\] and therefore oscillates everywhere between \[\left( { - 1,1} \right)\] .
Note: In a right-triangle, cosine function is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to that of the longest side i.e. the hypotenuse. Suppose a triangle ABC is taken with AB as the hypotenuse and \[\theta \] as the angle between hypotenuse and base. Then,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = Base/Hypotenuse\]
The cosine function is one of the three main primary trigonometric functions (sine, cosine and tangent) and it is itself the complement of the sine function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




