
Why current flows in a resistor connected with a battery although there is zero potential difference between one end of the battery and one end of the resistor?
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Firstly, understand that terminals used to measure the potential difference across the resistor are wrong. If you want to see whether there is potential difference across a given resistor or any element, you have to measure it across it. Maybe, you could recall the ohm’s law to give a better justification.
Complete answer:
In the given question, we are given a simple electric circuit in which a resistor is connected with a battery. Then, we are asked why there is a flow of current in the resistor when there is zero potential difference between one end of the battery and one end of the resistor.
For a student who is thorough with the concepts of current electricity may find this question quite meaningless.
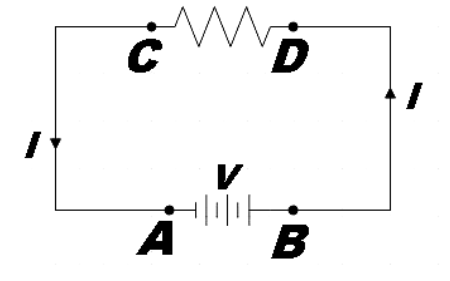
As per the question, the potential difference when measured between the points A and C (or B and D) is found to be zero. But that is not how we measure potential difference for an element (here, resistor).
The battery here provides a voltage of V volts. So when we keep a voltmeter across A and B we find the reading to be V volts. Similarly, when we measure the potential difference for the resistor we have to measure it across its two terminals that are C and D and we find it also to be V volts. And wherever there is a potential difference, the current will surely flow.
Note:
We know ohm’s law which is given by,
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$
Where, V is the potential difference (voltage), I is the current and R is the resistance. So for zero potential difference there will be no flow of current. But when the resistance is zero, there will be infinite current flowing through the circuit. So if there is current flowing through a circuit there surely is a potential difference.
Complete answer:
In the given question, we are given a simple electric circuit in which a resistor is connected with a battery. Then, we are asked why there is a flow of current in the resistor when there is zero potential difference between one end of the battery and one end of the resistor.
For a student who is thorough with the concepts of current electricity may find this question quite meaningless.

As per the question, the potential difference when measured between the points A and C (or B and D) is found to be zero. But that is not how we measure potential difference for an element (here, resistor).
The battery here provides a voltage of V volts. So when we keep a voltmeter across A and B we find the reading to be V volts. Similarly, when we measure the potential difference for the resistor we have to measure it across its two terminals that are C and D and we find it also to be V volts. And wherever there is a potential difference, the current will surely flow.
Note:
We know ohm’s law which is given by,
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$
Where, V is the potential difference (voltage), I is the current and R is the resistance. So for zero potential difference there will be no flow of current. But when the resistance is zero, there will be infinite current flowing through the circuit. So if there is current flowing through a circuit there surely is a potential difference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




