
Define catalyst.
Answer
567k+ views
Hint:
A catalyst is a substance that is added to a chemical reaction to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the process. There are basically two types of catalysts: inorganic catalysts and organic catalysts.
Complete answer:
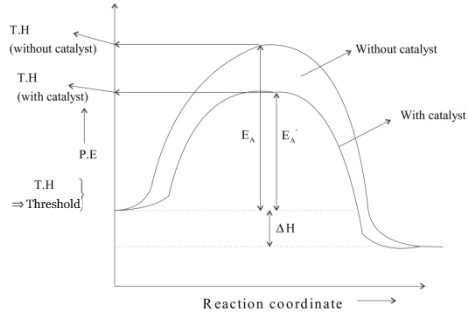
A catalyst is a substance which increases the speed of reaction without itself undergoing any chemical change. This is because the presence of a catalyst lowers the potential energy barrier and the reaction follows a new alternate path which requires less activation energy path which requires less activation energy.
Lesser is the activation energy faster is the reaction because for the energy reactant molecules can cross energy barriers and change into products.
A reaction is considered as homogeneously catalyzed when the catalyst and the reaction are in the same physical state or phase.
An example of this type of catalysis involving liquids in the conversion of percolate and iodide ions to sulfate ion and iodine,
${S_2}{O_8}^{2 - } + 2{I^ - } \to 2S{O_4}^{2 - } + {I_2}$
A reaction is considered heterogeneously catalyzed when the catalyst and the reactants are in the different phases with the reaction occurring at the interface between them.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
Inorganic catalysts: Inorganic catalysts are those that are not used in biological processes. This type of catalysts includes elemental metals and some other inorganic substances. These catalysts change the rate of the reaction but do not change their structure at all. Some examples of inorganic catalysts are potassium permanganate, platinum, palladium, iron and vanadium oxide.
Organic catalysts: Organic catalysts are also known as “organocatalysts”. These catalysts include nonmetals such as carbon, sulfur, hydrogen. Like inorganic catalysts they remain in their original structure even after the reaction is complete. Some examples of organic catalysts are: proline, diastase and lactase.
Note:There are biocatalysts too. Proteins and enzymes are known as biocatalysts. The biocatalysts also fall under the category of organic catalysts. These catalysts are involved in the biological chemical processes.
A catalyst is a substance that is added to a chemical reaction to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the process. There are basically two types of catalysts: inorganic catalysts and organic catalysts.
Complete answer:
A catalyst is a substance which increases the speed of reaction without itself undergoing any chemical change. This is because the presence of a catalyst lowers the potential energy barrier and the reaction follows a new alternate path which requires less activation energy path which requires less activation energy.
Lesser is the activation energy faster is the reaction because for the energy reactant molecules can cross energy barriers and change into products.

A reaction is considered as homogeneously catalyzed when the catalyst and the reaction are in the same physical state or phase.
An example of this type of catalysis involving liquids in the conversion of percolate and iodide ions to sulfate ion and iodine,
${S_2}{O_8}^{2 - } + 2{I^ - } \to 2S{O_4}^{2 - } + {I_2}$
A reaction is considered heterogeneously catalyzed when the catalyst and the reactants are in the different phases with the reaction occurring at the interface between them.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
Inorganic catalysts: Inorganic catalysts are those that are not used in biological processes. This type of catalysts includes elemental metals and some other inorganic substances. These catalysts change the rate of the reaction but do not change their structure at all. Some examples of inorganic catalysts are potassium permanganate, platinum, palladium, iron and vanadium oxide.
Organic catalysts: Organic catalysts are also known as “organocatalysts”. These catalysts include nonmetals such as carbon, sulfur, hydrogen. Like inorganic catalysts they remain in their original structure even after the reaction is complete. Some examples of organic catalysts are: proline, diastase and lactase.
Note:There are biocatalysts too. Proteins and enzymes are known as biocatalysts. The biocatalysts also fall under the category of organic catalysts. These catalysts are involved in the biological chemical processes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




