
Define Cellular Respiration.
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: When you are trying to lift a heavy bag or running to catch a bus or even reading a book. All these functions require energy in different amounts, which is provided to our muscles and other body parts through respiration. This helps us in performing at the cost of energy produced from the food that you intake.
Complete answer:
Respiration in a living being is one of the fundamental processes that ensure their survival. To survive, we need energy, and breathing makes sure we receive while performing any work.
- It occurs in all living organisms.
- The products of cellular respiration are water and carbon dioxide.
- Electrons carrier are: ${FADH}_2 $ and $NADH$
- The metabolic process of cellular respiration is catabolic and reactants is oxygen + glucose
- Location of cellular respiration is Mitochondria and energy source is glucose.
Equation of cellular respiration is:
$C_6 H_{12} O_6 { + 6O}_2 \to {6CO}_2 { + 6H}_2 O$
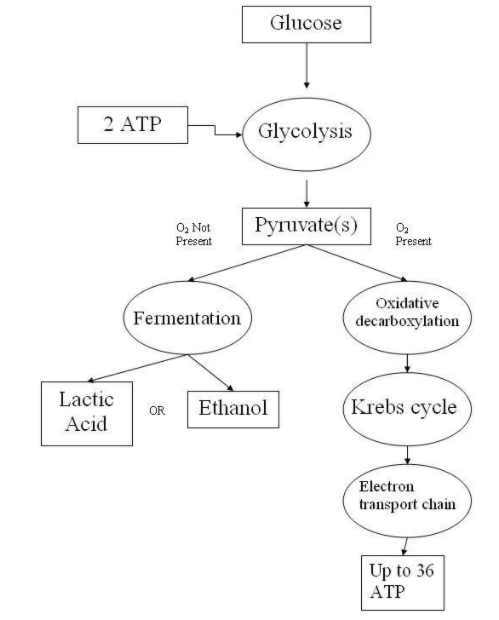
The respiration occurring at the cellular level wherein the cells produce energy by combining oxygen with food molecules is called cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration helps in providing the body with energy to carry out regular tasks. Therefore, it is evident that in order to survive, cellular respiration has to take place at times.
In simple words, the cells turn the food that you intake into energy.
On oxidation, the energy released through carbohydrates and other vital substrates gets absorbed in ATP. Nevertheless, a fraction of energy is lost as heat amidst the process.
Additionally, Glycolysis and oxidation of pyruvic acid take place during cellular respiration. It is expressed as
$C_6 H_{12} O_6 { + 6O}_2 \to {6CO}_2 { + 6H}_2 O $.
Note: During the simultaneous process of oxidative phosphorylation, ATP molecules are produced from the oxidation of carbohydrates. Subsequently. Synthesised ATP is used during stages of the metabolic process.
Complete answer:
Respiration in a living being is one of the fundamental processes that ensure their survival. To survive, we need energy, and breathing makes sure we receive while performing any work.
- It occurs in all living organisms.
- The products of cellular respiration are water and carbon dioxide.
- Electrons carrier are: ${FADH}_2 $ and $NADH$
- The metabolic process of cellular respiration is catabolic and reactants is oxygen + glucose
- Location of cellular respiration is Mitochondria and energy source is glucose.
Equation of cellular respiration is:
$C_6 H_{12} O_6 { + 6O}_2 \to {6CO}_2 { + 6H}_2 O$

The respiration occurring at the cellular level wherein the cells produce energy by combining oxygen with food molecules is called cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration helps in providing the body with energy to carry out regular tasks. Therefore, it is evident that in order to survive, cellular respiration has to take place at times.
In simple words, the cells turn the food that you intake into energy.
On oxidation, the energy released through carbohydrates and other vital substrates gets absorbed in ATP. Nevertheless, a fraction of energy is lost as heat amidst the process.
Additionally, Glycolysis and oxidation of pyruvic acid take place during cellular respiration. It is expressed as
$C_6 H_{12} O_6 { + 6O}_2 \to {6CO}_2 { + 6H}_2 O $.
Note: During the simultaneous process of oxidative phosphorylation, ATP molecules are produced from the oxidation of carbohydrates. Subsequently. Synthesised ATP is used during stages of the metabolic process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




