
Define electric field strength.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Electric fields are significant in numerous zones of material science. On a nuclear scale, an electric field is liable for the appealing force between the nuclear core and electrons that hold atoms together, and the forces between particles that cause concoction holding.
Complete answer:
Electric field strength is a force experienced by unit tests charge put at that point. It just relies upon source charge, and it is autonomous on the test charge. It is a quantitative articulation of the power of an electric field at a specific area.
The standard unit is volt per meter. A field strength of one v/m speaks to a likely distinction of one volt between focuses isolated by one meter. Electric field strength or electric field force is equivalent to the electric field. The electric field strength can be dictated by Coulomb's law. As indicated by this law, the force 'F' between two-point charges having charge Q1 and Q2 Coulombs separated from d meter from one another is given by,
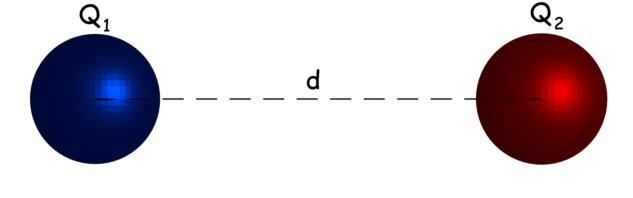
\[\overrightarrow{F=}\,\dfrac{Q1Q2}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{\varepsilon }_{r}}{{d}^{2}}}\]
Contingent upon this articulation, the electric field strength can be communicated in Newton/Coulomb. That is the unit of the electric field strength is Newton/Coulomb. The electric field strength has a course, and consequently, it is a vector quantity.
Force implies the size or sum. Presently field power comparably implies the greatness of the strength of the field.
Note: An electric field (at times E-field) encompasses an electric charge, and applies force on different charges in the field, drawing in or repulsing them. Electric fields are made by electric charges, by time-changing magnetic fields. Electric fields and magnetic fields are the two appearances of the electromagnetic force, amongst one of the four crucial forces (or communications) of nature.
Complete answer:
Electric field strength is a force experienced by unit tests charge put at that point. It just relies upon source charge, and it is autonomous on the test charge. It is a quantitative articulation of the power of an electric field at a specific area.
The standard unit is volt per meter. A field strength of one v/m speaks to a likely distinction of one volt between focuses isolated by one meter. Electric field strength or electric field force is equivalent to the electric field. The electric field strength can be dictated by Coulomb's law. As indicated by this law, the force 'F' between two-point charges having charge Q1 and Q2 Coulombs separated from d meter from one another is given by,
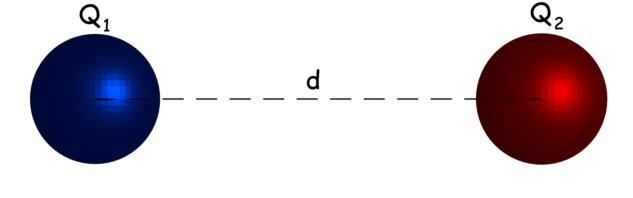
\[\overrightarrow{F=}\,\dfrac{Q1Q2}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{\varepsilon }_{r}}{{d}^{2}}}\]
Contingent upon this articulation, the electric field strength can be communicated in Newton/Coulomb. That is the unit of the electric field strength is Newton/Coulomb. The electric field strength has a course, and consequently, it is a vector quantity.
Force implies the size or sum. Presently field power comparably implies the greatness of the strength of the field.
Note: An electric field (at times E-field) encompasses an electric charge, and applies force on different charges in the field, drawing in or repulsing them. Electric fields are made by electric charges, by time-changing magnetic fields. Electric fields and magnetic fields are the two appearances of the electromagnetic force, amongst one of the four crucial forces (or communications) of nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




