
Define focal length of a concave mirror. Prove that the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is double its focal length.
Answer
603.9k+ views
Hint: The property of a concave mirror that we should be knowing is that it is bulged inwards in the middle. This means that if there are some parallel rays of light hitting any concave mirror, then the reflected rays will divert so that they appear to come from one single point which is known as the principal focus.
Step by step answer:
The distance between the pole of the concave mirror and the focus is known as the focal length of the concave mirror. The focal length of a concave mirror can be estimated by obtaining a real image of the distant object.
Consider a concave mirror as shown in the figure above.
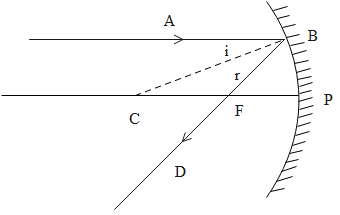
A ray of light AB which is travelling parallel to the principal axis PC is incident on a concave mirror at B. After reflection, it goes through the focus F. P is the pole of the mirror. C is the centre of curvature.
The distance PF = focal length f.
The distance PC = the radius of curvature R of the mirror.
BC is the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence B.
$\angle \text{ABC = }\angle \text{CBF (Law of reflection, }\angle \text{i = }\angle \text{r)}$
$\angle \text{ABC = }\angle \text{BCF (alternate angles)}$
$\Rightarrow \angle \text{BCF = }\angle \text{CBF}$
$\therefore \text{ }\blacktriangle \text{FBC}$ is an isosceles triangle.
Hence, sides $\text{BF=FC}$
For a small aperture of the mirror, the point B is very close to the point P,
$\Rightarrow \text{BF=PF}$
$\begin{align}
& \therefore \text{ PF = FC = }\dfrac{1}{2}\text{PC} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ f = }\dfrac{1}{2}\text{R} \\
\end{align}$
Thus we can say that the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is double its focal length.
Additional Information:
A concave lens is also known as a diverging lens. This is because it possesses one surface which is curved inward. Concave lens spreads out light rays that are then refracted through it.
A concave lens is used to correct short-sightedness which is also known as myopia.
Note: A concave mirror or a converging lens will only produce a virtual image if the image is located beyond the focal point. By focal point, we mean more than one focal length away. The image that will be formed will be upright and reduced in size.
Step by step answer:
The distance between the pole of the concave mirror and the focus is known as the focal length of the concave mirror. The focal length of a concave mirror can be estimated by obtaining a real image of the distant object.
Consider a concave mirror as shown in the figure above.

A ray of light AB which is travelling parallel to the principal axis PC is incident on a concave mirror at B. After reflection, it goes through the focus F. P is the pole of the mirror. C is the centre of curvature.
The distance PF = focal length f.
The distance PC = the radius of curvature R of the mirror.
BC is the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence B.
$\angle \text{ABC = }\angle \text{CBF (Law of reflection, }\angle \text{i = }\angle \text{r)}$
$\angle \text{ABC = }\angle \text{BCF (alternate angles)}$
$\Rightarrow \angle \text{BCF = }\angle \text{CBF}$
$\therefore \text{ }\blacktriangle \text{FBC}$ is an isosceles triangle.
Hence, sides $\text{BF=FC}$
For a small aperture of the mirror, the point B is very close to the point P,
$\Rightarrow \text{BF=PF}$
$\begin{align}
& \therefore \text{ PF = FC = }\dfrac{1}{2}\text{PC} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ f = }\dfrac{1}{2}\text{R} \\
\end{align}$
Thus we can say that the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is double its focal length.
Additional Information:
A concave lens is also known as a diverging lens. This is because it possesses one surface which is curved inward. Concave lens spreads out light rays that are then refracted through it.
A concave lens is used to correct short-sightedness which is also known as myopia.
Note: A concave mirror or a converging lens will only produce a virtual image if the image is located beyond the focal point. By focal point, we mean more than one focal length away. The image that will be formed will be upright and reduced in size.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




