
Define photophosphorylation and describe cyclic phosphorylation.
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: In the word, photophosphorylation - Photo means light and phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphoryl group to a molecule. Cyclic phosphorylation is termed due to the movement of electrons in a cyclic manner.
Complete answer:
As understood from the etymology, photophosphorylation is a process in which plants convert adenosine diphosphate (\[ADP\]) to adenosine triphosphate (\[ATP\]) through phosphorylation using sunlight as an energy source. The \[ATP\] produced is the source for energy for the cells. This phosphorylation is of two types: cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Cyclic photophosphorylation, occurring on the stroma lamellae or fret channels, is initiated by the high-energy electron produced by chlorophyll A in \[p700\] of photosystem \[1\] (PS \[1\]) through sunlight. The electron produced activates a series of events starting from the primary acceptor to ferredoxin to plastoquinone then to cytochrome \[b6f\] to plastocyanin and finally goes back to PS \[1\]. During this excitation, two \[ATP\] molecules are released. The proton motive force generates a concentration gradient which can be used during chemiosmosis.
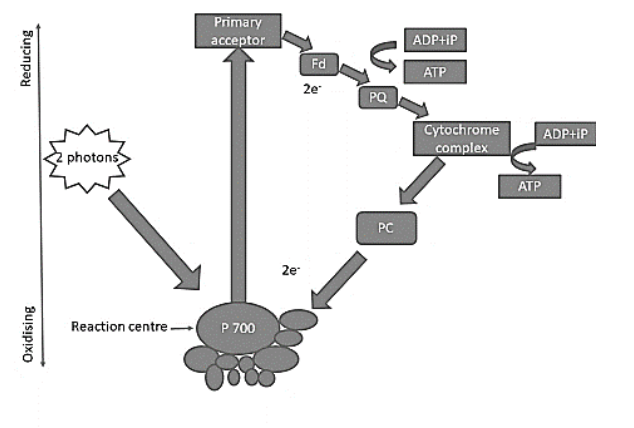
Note: Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation are entirely different. In cyclic photophosphorylation, only PS \[1\] is involved whereas in non-cyclic both PS \[1\] and PS \[2\] are involved. Neither oxygen nor \[NADPH\] is released during cyclic photophosphorylation but both are released during non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Similarly, cyclic photophosphorylation also occurs in photosynthetic bacteria to meet their energy needs. Bacteria have only one photosystem \[1\] whose chlorophyll absorbs wavelengths of \[800 - 1000nm\], unlike plants which absorb \[650 - 750nm\]. However, cyanobacteria possesses two photosystems and performs similar to plants. In plants \[H2O\] donates electrons to photophosphorylation. But in bacteria \[H2S\]and other chemical compounds donate electrons to generate energy.
Complete answer:
As understood from the etymology, photophosphorylation is a process in which plants convert adenosine diphosphate (\[ADP\]) to adenosine triphosphate (\[ATP\]) through phosphorylation using sunlight as an energy source. The \[ATP\] produced is the source for energy for the cells. This phosphorylation is of two types: cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Cyclic photophosphorylation, occurring on the stroma lamellae or fret channels, is initiated by the high-energy electron produced by chlorophyll A in \[p700\] of photosystem \[1\] (PS \[1\]) through sunlight. The electron produced activates a series of events starting from the primary acceptor to ferredoxin to plastoquinone then to cytochrome \[b6f\] to plastocyanin and finally goes back to PS \[1\]. During this excitation, two \[ATP\] molecules are released. The proton motive force generates a concentration gradient which can be used during chemiosmosis.

Note: Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation are entirely different. In cyclic photophosphorylation, only PS \[1\] is involved whereas in non-cyclic both PS \[1\] and PS \[2\] are involved. Neither oxygen nor \[NADPH\] is released during cyclic photophosphorylation but both are released during non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Similarly, cyclic photophosphorylation also occurs in photosynthetic bacteria to meet their energy needs. Bacteria have only one photosystem \[1\] whose chlorophyll absorbs wavelengths of \[800 - 1000nm\], unlike plants which absorb \[650 - 750nm\]. However, cyanobacteria possesses two photosystems and performs similar to plants. In plants \[H2O\] donates electrons to photophosphorylation. But in bacteria \[H2S\]and other chemical compounds donate electrons to generate energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




