
Define the circle segment and sector of a circle.
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Segment of a circle is the region bounded by a chord and the arc subtended by the chord.
Sector of the circle looks like a pizza slice.
Complete step by step solution: Segment is the region of a circle bounded by chord and an arc.
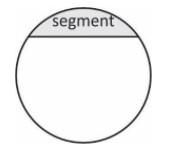
The segments are explained in two parts:
As we show in the above diagram a line divides the circle in two parts in which the biggest part of the circle is called the major segment.
Or the lower part or portion is known as a minor segment.
We also calculate the area of segment:
The area of the segment is equal to area of sector minus of area of triangular piece.
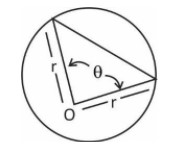
\[Area\,\,of\,\,segment = \dfrac{{\left( {\theta - \sin \theta } \right) \times {r^2}}}{2}\,\,\left[ {When\,\,\theta \,\,in\,\,radians} \right]\]
\[Area\,\,of\,\,segment = \left( {\dfrac{{\theta \times \pi }}{{360}} - \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{2}} \right) \times {r^2}\] (when \[\theta \]is in degrees)
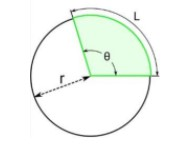
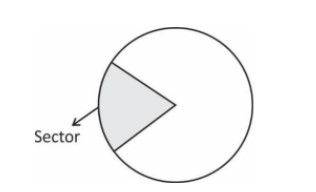
Sector of Circle
The shaded region is the sector of circle.
A sector is created by the central angle formed with two radii and it includes the area inside the circle from that center point to the circle itself. The portion of the circle's circumference bounded by the radii, the arc, is part of the sector.
Common Sectors
The quadrant and semicircle are two special types of sector:
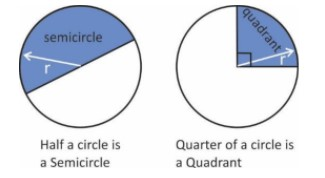
Area of sector\[ = \left( {\dfrac{{\theta ^\circ }}{{360^\circ }}} \right) \times \pi \times {r^2}\]
Where
\[\theta ^\circ \] = degree of the circle
\[R{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}radius{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}circle\]
Note: A circle has an angle of\[2\pi \]and an area of $ [ \pi \times {r^2}] $ . A sector has an angle of\[\theta \]instead of \[2\pi \] ,so it has an area which can be simplified to:\[\dfrac{\theta }{2} \times {r^2}\]
Sector of the circle looks like a pizza slice.
Complete step by step solution: Segment is the region of a circle bounded by chord and an arc.

The segments are explained in two parts:
As we show in the above diagram a line divides the circle in two parts in which the biggest part of the circle is called the major segment.
Or the lower part or portion is known as a minor segment.
We also calculate the area of segment:
The area of the segment is equal to area of sector minus of area of triangular piece.

\[Area\,\,of\,\,segment = \dfrac{{\left( {\theta - \sin \theta } \right) \times {r^2}}}{2}\,\,\left[ {When\,\,\theta \,\,in\,\,radians} \right]\]
\[Area\,\,of\,\,segment = \left( {\dfrac{{\theta \times \pi }}{{360}} - \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{2}} \right) \times {r^2}\] (when \[\theta \]is in degrees)

Sector of Circle
The shaded region is the sector of circle.

A sector is created by the central angle formed with two radii and it includes the area inside the circle from that center point to the circle itself. The portion of the circle's circumference bounded by the radii, the arc, is part of the sector.
Common Sectors
The quadrant and semicircle are two special types of sector:

Area of sector\[ = \left( {\dfrac{{\theta ^\circ }}{{360^\circ }}} \right) \times \pi \times {r^2}\]
Where
\[\theta ^\circ \] = degree of the circle
\[R{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}radius{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}circle\]
Note: A circle has an angle of\[2\pi \]and an area of $ [ \pi \times {r^2}] $ . A sector has an angle of\[\theta \]instead of \[2\pi \] ,so it has an area which can be simplified to:\[\dfrac{\theta }{2} \times {r^2}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




