
Define the cis-trans isomerism? Show the cis-trans isomers of \[{[Co{(N{H_3})_4}C{l_2}]^ + }\].
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Isomers are defined as chemical compounds with the same chemical formula but a different arrangement of atoms and in coordination complexes, the spatial arrangement of ligands around central metal ions gives rise to geometrical isomers. They are classified as cis- and trans- isomers.
Complete step by step answer: First we will discuss about the isomerism,
Isomerism is defined as the existence of molecules that have the same numbers of the same kinds of atoms and same formula but the difference in physical and chemical properties. For example: - Pentane, which has a molecular formula of $C{}_{5}H{}_{12}$, has three different chain isomers.
Cis-trans isomerism can be defined as the pair of molecules which have the same formula but the functional group are rotated into different orientation in three-dimensional space.
Cis-trans isomerisms are also called geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism and are term is used in the organic chemistry. Cis-trans isomers are stereoisomerism. The word “cis” originated from the Latin language which means “on this side” or in context of chemistry it means the functional groups are on the same side of carbon chain and the word “trans” also comes from the Latin language which means “across form” or in context of chemistry it means the functional groups are on the different side of the carbon chain.
For example: - But-2-ene is the good example of small hydrocarbons displaying Cis-trans isomerism.
Now we will describe the structure of cis-trans isomers of ${{\left[ Co\left( NH{}_{3} \right){}_{4}Cl{}_{2} \right]}^{+}}$,
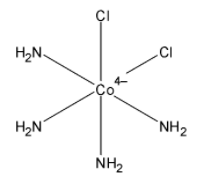
The IUPAC nomenclature in organic chemistry is a systematic system and according to the IUPAC nomenclature, the name of complex ${{\left[ Co\left( NH{}_{3} \right){}_{4}Cl{}_{2} \right]}^{+}}$ is Tetra-ammine dichloro cobalt $\left( III \right)$. In the complex, the two chlorine place in axial position in the trans-isomer and chlorine is present on axial or equatorial each position in cis-isomers.
Note: The cis–trans system for naming alkenes isomers should generally only be used when there are only two different substituent on the double bond, so there is no confusion about which substituent are being described relative to each other.
Complete step by step answer: First we will discuss about the isomerism,
Isomerism is defined as the existence of molecules that have the same numbers of the same kinds of atoms and same formula but the difference in physical and chemical properties. For example: - Pentane, which has a molecular formula of $C{}_{5}H{}_{12}$, has three different chain isomers.
Cis-trans isomerism can be defined as the pair of molecules which have the same formula but the functional group are rotated into different orientation in three-dimensional space.
Cis-trans isomerisms are also called geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism and are term is used in the organic chemistry. Cis-trans isomers are stereoisomerism. The word “cis” originated from the Latin language which means “on this side” or in context of chemistry it means the functional groups are on the same side of carbon chain and the word “trans” also comes from the Latin language which means “across form” or in context of chemistry it means the functional groups are on the different side of the carbon chain.
For example: - But-2-ene is the good example of small hydrocarbons displaying Cis-trans isomerism.
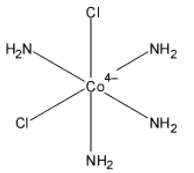
Now we will describe the structure of cis-trans isomers of ${{\left[ Co\left( NH{}_{3} \right){}_{4}Cl{}_{2} \right]}^{+}}$,


The IUPAC nomenclature in organic chemistry is a systematic system and according to the IUPAC nomenclature, the name of complex ${{\left[ Co\left( NH{}_{3} \right){}_{4}Cl{}_{2} \right]}^{+}}$ is Tetra-ammine dichloro cobalt $\left( III \right)$. In the complex, the two chlorine place in axial position in the trans-isomer and chlorine is present on axial or equatorial each position in cis-isomers.
Note: The cis–trans system for naming alkenes isomers should generally only be used when there are only two different substituent on the double bond, so there is no confusion about which substituent are being described relative to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




