
Define the function of Afferent pathway, Dorsal root ganglion, Efferent pathway, and Motor neuron.

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: All the above mentioned four terms are associated with the central nervous system. They are all together responsible for carrying signals to and from the brain.
Correct step by step answer:
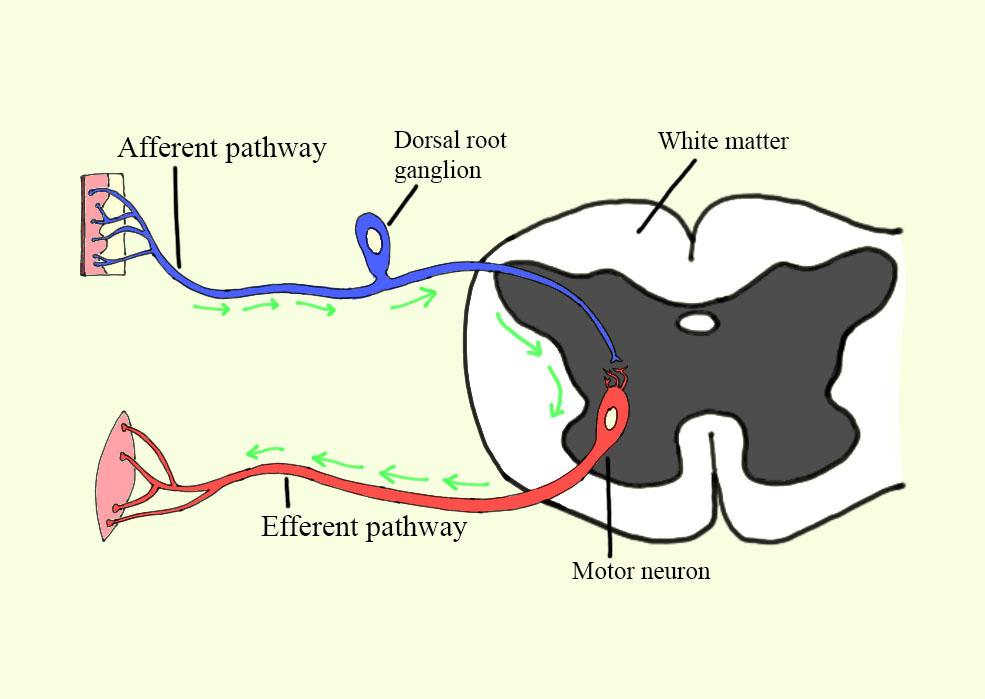
Afferent pathway: Afferent signals come from outside stimuli and tell our brain what they are sensing, such as temperature. That means it is a pathway that is responsible for carrying nerve impulses from the sensory organs to the spinal cord through the sensory neurons. In the brain when afferent neurons bring stimuli, then the signal is integrated and processed.
Dorsal root ganglion: The dorsal root ganglion is the region in the pathway that contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons. dorsal root ganglion or spinal ganglion; also referred to as a posterior root ganglion may be a cluster of neurons or a ganglion during a dorsal root of a nervous spinalis. The cell bodies of sensory neurons referred to as first-order neurons are located within the dorsal root ganglia. The axons of dorsal root ganglion neurons are referred to as afferents. In the peripheral nervous system, the afferents are referred to as the axons that relay sensory information into the central nervous system i.e. the brain and the spinal cord.
Efferent pathway: The efferent pathway is the pathway involved in carrying nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the peripheral or efferent organs. Different pathways carry signals faraway from the central systema nervosum. Essentially, they're signals that your brain sends to inform your body to try something, like blinking. The brain then coordinates a response via different signals back to the remainder of the body. Different neurons communicate information from the brain/spinal cord to the acceptable portion of the body.
Motor neurons: These are the neurons involved in the efferent pathway and also in carrying impulses away from the spinal cord. Because the motor neurons carry information from the brain to effector organs like muscles or glands they are considered different. Motor neurons connect to muscles, glands, and organs throughout the body and are also part of the central nervous system (CNS). These neurons transmit impulses from the medulla spinalis to skeletal and smooth muscles (such as those in your stomach), then directly control all of our muscle movements
Note:
- Different neurons enter the medulla spinalis through the dorsal root, carrying signals from the body to the brain.
- The dorsal root ganglion is the region within the pathway that contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons.
- The efferent pathway involved in carrying nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the peripheral (efferent) organs.
- The motor neurons are involved in carrying impulses away from the spinal cord.
Correct step by step answer:
Afferent pathway: Afferent signals come from outside stimuli and tell our brain what they are sensing, such as temperature. That means it is a pathway that is responsible for carrying nerve impulses from the sensory organs to the spinal cord through the sensory neurons. In the brain when afferent neurons bring stimuli, then the signal is integrated and processed.
Dorsal root ganglion: The dorsal root ganglion is the region in the pathway that contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons. dorsal root ganglion or spinal ganglion; also referred to as a posterior root ganglion may be a cluster of neurons or a ganglion during a dorsal root of a nervous spinalis. The cell bodies of sensory neurons referred to as first-order neurons are located within the dorsal root ganglia. The axons of dorsal root ganglion neurons are referred to as afferents. In the peripheral nervous system, the afferents are referred to as the axons that relay sensory information into the central nervous system i.e. the brain and the spinal cord.
Efferent pathway: The efferent pathway is the pathway involved in carrying nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the peripheral or efferent organs. Different pathways carry signals faraway from the central systema nervosum. Essentially, they're signals that your brain sends to inform your body to try something, like blinking. The brain then coordinates a response via different signals back to the remainder of the body. Different neurons communicate information from the brain/spinal cord to the acceptable portion of the body.
Motor neurons: These are the neurons involved in the efferent pathway and also in carrying impulses away from the spinal cord. Because the motor neurons carry information from the brain to effector organs like muscles or glands they are considered different. Motor neurons connect to muscles, glands, and organs throughout the body and are also part of the central nervous system (CNS). These neurons transmit impulses from the medulla spinalis to skeletal and smooth muscles (such as those in your stomach), then directly control all of our muscle movements
Note:
- Different neurons enter the medulla spinalis through the dorsal root, carrying signals from the body to the brain.
- The dorsal root ganglion is the region within the pathway that contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons.
- The efferent pathway involved in carrying nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the peripheral (efferent) organs.
- The motor neurons are involved in carrying impulses away from the spinal cord.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




