
Define the structure of the root.
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: Root is a plant organ that supports the absorption of soil nutrients and water. It is found at the end mostly. It consists of three areas: the meristematic zone, the elongation zone and the differentiation zone.
Complete answer:
A typical root system is divided into five regions.
Root cap: The root cap, also known as calyptra, is the root tip. It aids the root in receiving and transmitting environmental signals. It produces mucilage, which aids the plant's penetration of the soil. As the root moves through the soil, it is easily weakened. It also safeguards the meristematic zone.
Meristematic zone (point of development): It is located just above the root tip and provides the root with the basal area. It increases the number of cells in the root cap. Undifferentiated meristematic cells undergo rapid mitosis.
Zone of elongation: increases the root length and lies just behind the meristematic area. This area has external cells that help water and minerals to be absorbed. It lets the root get into the ground deeper.
Zone of differentiation: also, the hair zone of the root. It is the area where xylem, phloem, pericycle, body, periblem and endodermis differentiate. Epiblema cells stretch out to form single-cell root hair.
The maturation zone: It makes up the majority of the root system. Different types of cells emerged as a result of cell differentiation. This zone's primary functions are security, storage, and conductance. The epidermis is the outer layer, the cortex is the deeper layer, and vascular bundles are found in the central area.
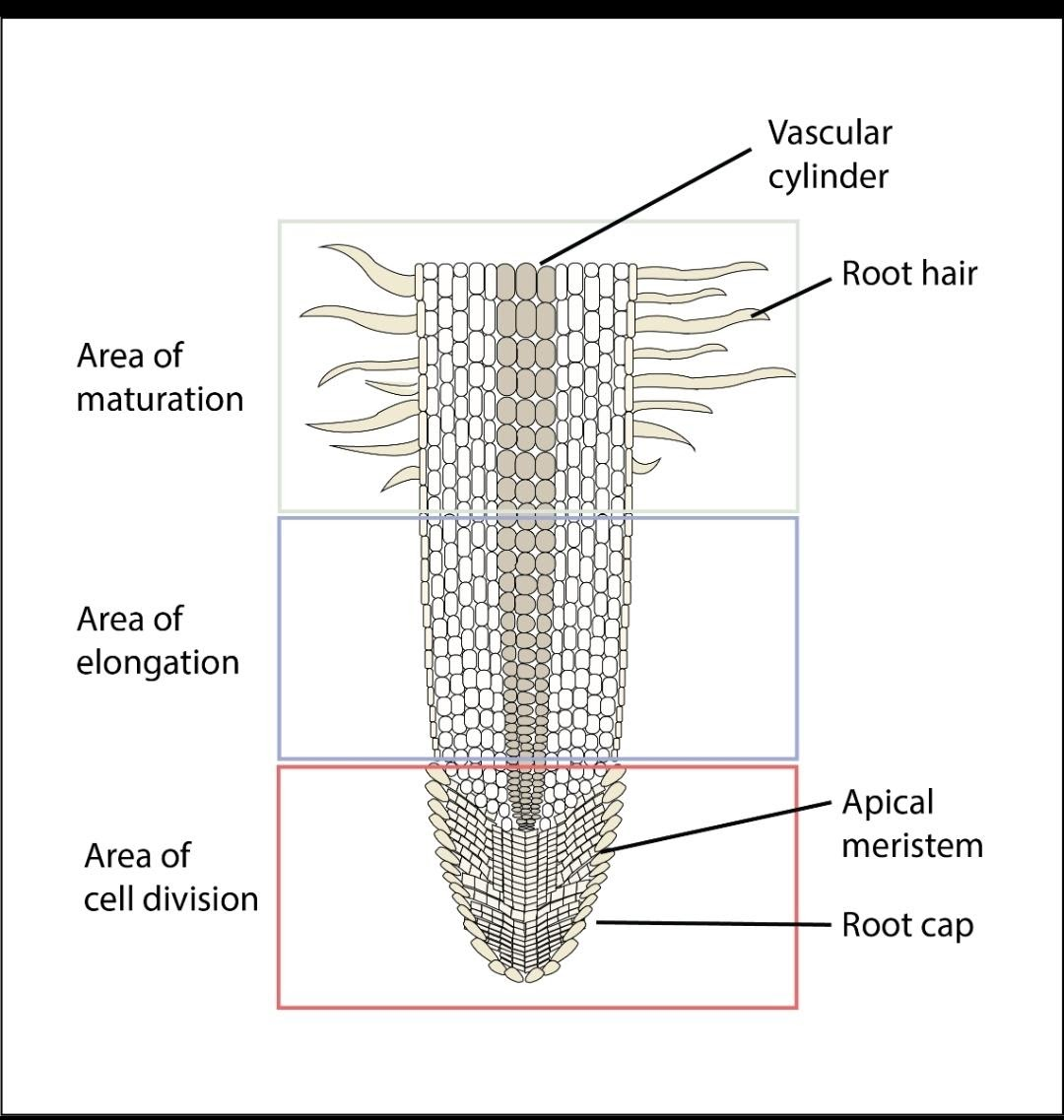
Note: The cortex of the root is located between the epidermis and the vascular tissue, while the pith is located between the epidermis and the vascular tissue. Between the root's centre and the vascular tissue is the pith.
Complete answer:
A typical root system is divided into five regions.
Root cap: The root cap, also known as calyptra, is the root tip. It aids the root in receiving and transmitting environmental signals. It produces mucilage, which aids the plant's penetration of the soil. As the root moves through the soil, it is easily weakened. It also safeguards the meristematic zone.
Meristematic zone (point of development): It is located just above the root tip and provides the root with the basal area. It increases the number of cells in the root cap. Undifferentiated meristematic cells undergo rapid mitosis.
Zone of elongation: increases the root length and lies just behind the meristematic area. This area has external cells that help water and minerals to be absorbed. It lets the root get into the ground deeper.
Zone of differentiation: also, the hair zone of the root. It is the area where xylem, phloem, pericycle, body, periblem and endodermis differentiate. Epiblema cells stretch out to form single-cell root hair.
The maturation zone: It makes up the majority of the root system. Different types of cells emerged as a result of cell differentiation. This zone's primary functions are security, storage, and conductance. The epidermis is the outer layer, the cortex is the deeper layer, and vascular bundles are found in the central area.

Note: The cortex of the root is located between the epidermis and the vascular tissue, while the pith is located between the epidermis and the vascular tissue. Between the root's centre and the vascular tissue is the pith.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




