
Define Work done by a constant force and give some examples of it.
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: If the force is constant, we can define the work done on an object as the product of the force applied on the object and the distance travelled by the object in the direction of the force. All the conditions where acceleration of a body is constant, the force will be will be constant.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us suppose a block lying stationary on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure. Suppose a force $F$ is applied to the block and it moves a distance $d$ in the direction of the force.
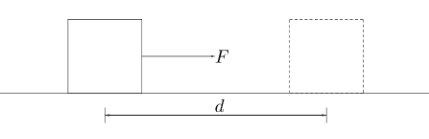
We can understand that if the distance travelled is more, the change in velocity will also be more (from ${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2ad$ ) . Similarly, we can understand that if the magnitude of force will be more, the change in velocity or acceleration would be more (from $F=ma$ ).Hence, the magnitude of change in velocity is dependent on the magnitude of force and magnitude of distance travelled.
Hence, if the force and distance travelled are in the same direction and the magnitude of the force is constant, the work can be defined as “The product of the magnitude of the force applied and the total distance travelled in the direction of the force is known as work done.”Work done is mathematically expressed as $W=F\times d$ and its unit is $Joule(J)$.This was the case where the force was in the direction of the distance travelled.Let us suppose that the force makes an angle $\theta$ with the horizontal direction as shown in the figure below
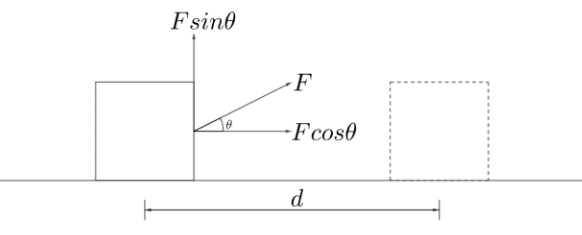
In this case the work is defined as “The product of the magnitude of the component of the force in the direction of the distance travelled and the magnitude of the displacement or the distance.”
Hence, as work depends on the angle between force and displacement, the value of work can be positive, negative and zero. Certain examples of work done by constant force are work done by gravitational force, work done in rotating an object around a fixed point, work done by applying a force of some constant magnitude, etc.
Note: From physics point of view, we can understand that work is only said to be done when there is a net displacement in the direction of the force. However when an object is moving in a rotational manner, the force is perpendicular to the direction of motion, but still work is required to be done. Similarly for electrical work, Magnetic work, spring work etc. there is no displacement, but still work is obtained or required to be done.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us suppose a block lying stationary on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure. Suppose a force $F$ is applied to the block and it moves a distance $d$ in the direction of the force.

We can understand that if the distance travelled is more, the change in velocity will also be more (from ${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2ad$ ) . Similarly, we can understand that if the magnitude of force will be more, the change in velocity or acceleration would be more (from $F=ma$ ).Hence, the magnitude of change in velocity is dependent on the magnitude of force and magnitude of distance travelled.
Hence, if the force and distance travelled are in the same direction and the magnitude of the force is constant, the work can be defined as “The product of the magnitude of the force applied and the total distance travelled in the direction of the force is known as work done.”Work done is mathematically expressed as $W=F\times d$ and its unit is $Joule(J)$.This was the case where the force was in the direction of the distance travelled.Let us suppose that the force makes an angle $\theta$ with the horizontal direction as shown in the figure below

In this case the work is defined as “The product of the magnitude of the component of the force in the direction of the distance travelled and the magnitude of the displacement or the distance.”
Hence, as work depends on the angle between force and displacement, the value of work can be positive, negative and zero. Certain examples of work done by constant force are work done by gravitational force, work done in rotating an object around a fixed point, work done by applying a force of some constant magnitude, etc.
Note: From physics point of view, we can understand that work is only said to be done when there is a net displacement in the direction of the force. However when an object is moving in a rotational manner, the force is perpendicular to the direction of motion, but still work is required to be done. Similarly for electrical work, Magnetic work, spring work etc. there is no displacement, but still work is obtained or required to be done.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




