
Derive the Fourier`s conduction equation for general bodies.
$\left( {\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} = - kA\dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}} \right)$

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Fourier law of heat conduction is the governing law for conduction equations. It states that the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the area normal to the direction of heat flow and temperature gradient i.e., drop in temperature per unit length.
Complete solution:
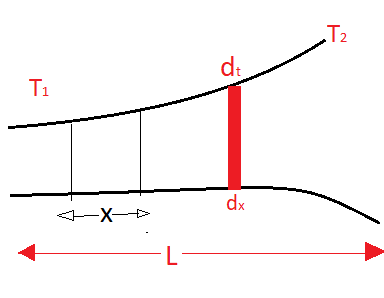
Let us consider a small elemental area from the above body
Let the width of this elemental part be $dx$
The small change in temperature be $dt$
A temperature gradient will be the change in temperature per unit area or $\dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$
And let $A$ be the area perpendicular to the direction of heat flow
Refer to the diagram
Now as per Fourier’s law
$\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} \propto {\rm A}$and,
$\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} \propto \dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$
$\therefore \dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} \propto {\rm A}\dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$
$\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}}$ is the rate of heat transferred?
Here to remove the proportionality a constant of proportionality is inserted which
$k$ which is known as Thermal conductivity of the material or wall and is expressed in $\left( {\dfrac{w}{m}K} \right)$
$\therefore \dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} = - kA\dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$
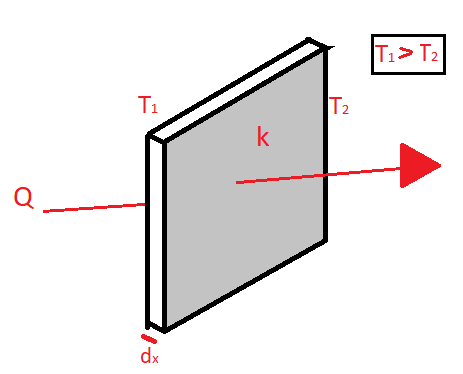
Here the negative sign indicates the drop in temperature across the body
Since $dt$ is the change in temperature so it will be expressed as
$dt = {T_2} - {T_1}$
And as it is evident that ${T_2}$ will be lower than ${T_1}$ so we`ll get a negative value of $dt$ so we use a negative sign before $k$ to nullify this and make heat transfer rate positive
The heat flow rate $\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}}$ across a body will be $\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} = - kA\dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$.
Note: The heat always flows from higher temperature to lower temperature that’s why ${T_1}$ will always be greater than ${T_2}$.
The area perpendicular to heat flow rate will always be considered because it is the only area which will cause resistance to the flow of heat and thus will reduce its temperature.
The thermal conductivity $\left( k \right)$is the internal property of the body; it is the measure of how easily heat can be conducted through a body. It is generally higher for metals and lowers for non-metals .
Complete solution:
Let us consider a small elemental area from the above body

Let the width of this elemental part be $dx$
The small change in temperature be $dt$
A temperature gradient will be the change in temperature per unit area or $\dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$
And let $A$ be the area perpendicular to the direction of heat flow
Refer to the diagram
Now as per Fourier’s law
$\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} \propto {\rm A}$and,
$\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} \propto \dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$
$\therefore \dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} \propto {\rm A}\dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$
$\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}}$ is the rate of heat transferred?
Here to remove the proportionality a constant of proportionality is inserted which
$k$ which is known as Thermal conductivity of the material or wall and is expressed in $\left( {\dfrac{w}{m}K} \right)$
$\therefore \dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} = - kA\dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$
Here the negative sign indicates the drop in temperature across the body
Since $dt$ is the change in temperature so it will be expressed as
$dt = {T_2} - {T_1}$
And as it is evident that ${T_2}$ will be lower than ${T_1}$ so we`ll get a negative value of $dt$ so we use a negative sign before $k$ to nullify this and make heat transfer rate positive
The heat flow rate $\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}}$ across a body will be $\dfrac{{dq}}{{dt}} = - kA\dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}}$.
Note: The heat always flows from higher temperature to lower temperature that’s why ${T_1}$ will always be greater than ${T_2}$.
The area perpendicular to heat flow rate will always be considered because it is the only area which will cause resistance to the flow of heat and thus will reduce its temperature.
The thermal conductivity $\left( k \right)$is the internal property of the body; it is the measure of how easily heat can be conducted through a body. It is generally higher for metals and lowers for non-metals .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




