
Describe a typical synovial joint with a neat labeled diagram.
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Joints are defined as the junction between two or many bones and cartilages. It helps in the movement of the body. In the human body total 230 joints are present. The Study of joints known as the arthrology. A joint also says the articulation.
Complete Answer:
Joint is the place where two bones come together and it is further three types:
(I) Fibrous (fixed): Sutures, Gomphosis and Syndesmosis
(II) Cartilaginous (slightly movable): Primary and secondary cartilage
(III) Synovial joint (movable): Plane, hinge, pivot, saddle, ellipsoid, bicondylar and ball and socket.
- The two bones are joined by connective tissues which help in the movement of the bones is known as the synovial joint.
- Synovial joint found between the long bones. The two bones are held with fibrous tissue of the ligament.
- Articular cartilage is present at the end of the long bones. There is a capsular structure which is formed by the synovial membrane. This cavity which is formed by synovial membrane is filled with the synovial fluid. Synovial fluid is secreted by membranes which helps to prevent abrasion between the cartilages.
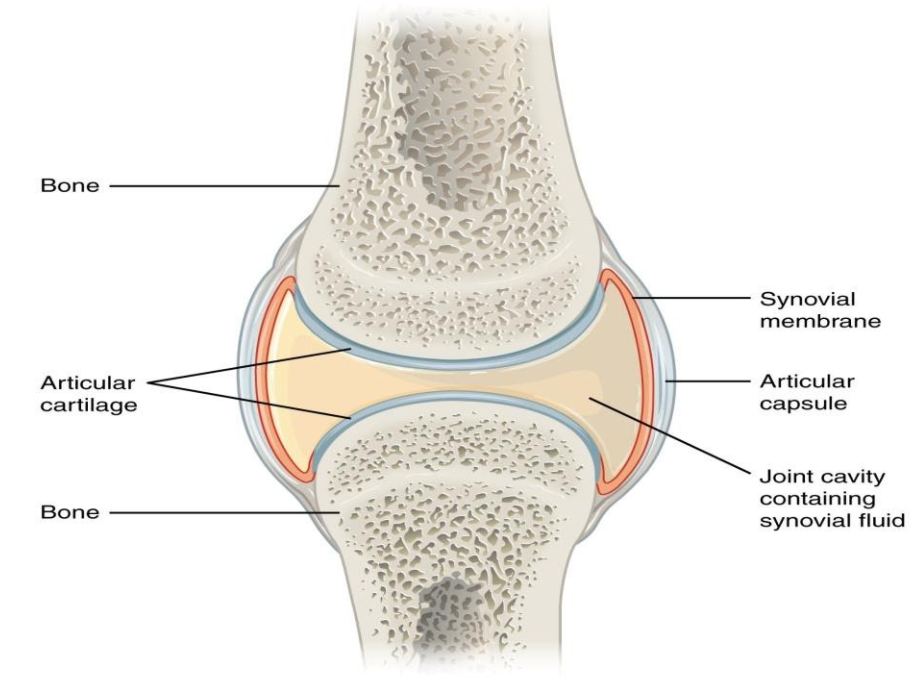
Note: Synovial joint provides nutrients, helps in movement and acts as a lubricant.
Synovial joint are of various type according to the structure:
- Plane: Slightly curved articular surface e.g. carpals
- Ball and socket: Most moveable type e.g. shoulder and hip joints
- Hinge: Uniaxial e.g. elbow, knee and finger
- Pivot: Rotation e.g. radioulnar and atlas
- Saddle: concave and convex surface e.g. base of thumb
- Condyloid: Rounded articular surface e.g. base of finger
- Ellipsoid: Ovoid shaped joint e.g. wrist joint
- Compound: made by two types of joint e.g. temporomandibular joint (Hinge and gliding).
Complete Answer:
Joint is the place where two bones come together and it is further three types:
(I) Fibrous (fixed): Sutures, Gomphosis and Syndesmosis
(II) Cartilaginous (slightly movable): Primary and secondary cartilage
(III) Synovial joint (movable): Plane, hinge, pivot, saddle, ellipsoid, bicondylar and ball and socket.
- The two bones are joined by connective tissues which help in the movement of the bones is known as the synovial joint.
- Synovial joint found between the long bones. The two bones are held with fibrous tissue of the ligament.
- Articular cartilage is present at the end of the long bones. There is a capsular structure which is formed by the synovial membrane. This cavity which is formed by synovial membrane is filled with the synovial fluid. Synovial fluid is secreted by membranes which helps to prevent abrasion between the cartilages.

Note: Synovial joint provides nutrients, helps in movement and acts as a lubricant.
Synovial joint are of various type according to the structure:
- Plane: Slightly curved articular surface e.g. carpals
- Ball and socket: Most moveable type e.g. shoulder and hip joints
- Hinge: Uniaxial e.g. elbow, knee and finger
- Pivot: Rotation e.g. radioulnar and atlas
- Saddle: concave and convex surface e.g. base of thumb
- Condyloid: Rounded articular surface e.g. base of finger
- Ellipsoid: Ovoid shaped joint e.g. wrist joint
- Compound: made by two types of joint e.g. temporomandibular joint (Hinge and gliding).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




