
Describe ball and socket joint and hinge joint
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: A joint is generally a point where two or more things are connected together.
Joint means an articulation or a strong connection that joins the bones, teeth, and cartilage together. These joints are named according to their structure and function.
Complete answer:
Joints are classified as fibrous, cartilaginous or synovial joints by the type of the tissue present. They can also be classified as synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis or diarthrosis by the degree of movement permitted.
Synovial Joints: Synovial joints have fluid-filled joint cavities contained within a fibrous capsule. They are freely movable joints.
They are further classified as:
Hinge, Saddle, Plane, Pivot, Condyloid, and Ball and Socket type of joints based on their structures, degree and axes of movements.
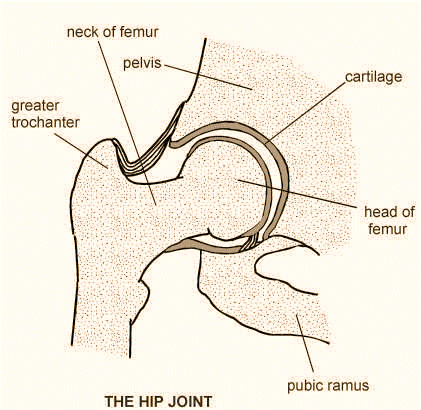
Ball and Socket Joints: It is a kind of joint where the ball-shaped articulating surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, with one common centre. This permits free movement along numerous axes and movement in many directions. E.g. hip joint, shoulder joint.
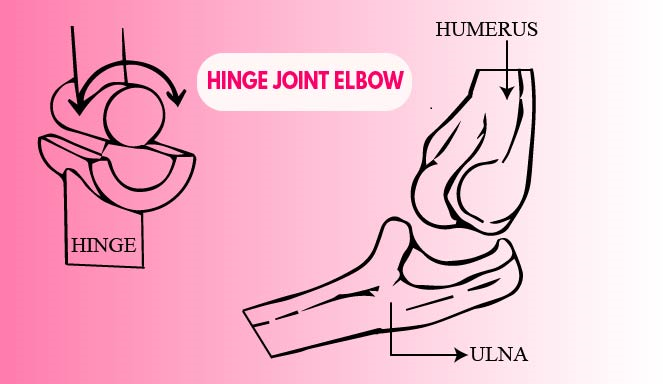
Hinge Joint: A hinge joint is a that allows movement in only one direction. Hinge joints include ankles, elbows, knee joints, and other such joints that have a movement along one plane only. These joints are two or more bones that meet and move along a single axis to bend.
Hinge joints are generally assisted by other tissues, like cartilage and ligaments, to connect and bend. These connective tissues protect the bones from rubbing and wearing as they bend at varying degrees to keep our bodies mobile. Eg- Knee joint, Elbow Joint
Additional Information:
Note: While the Ball and Socket joint allows for a wide range of motions, the hinge has a restricted axis of movement. The other synovial joints like pivot and saddle joints allow for more movement as compared to the hinge joint.
Complete answer:
Joints are classified as fibrous, cartilaginous or synovial joints by the type of the tissue present. They can also be classified as synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis or diarthrosis by the degree of movement permitted.
Synovial Joints: Synovial joints have fluid-filled joint cavities contained within a fibrous capsule. They are freely movable joints.
They are further classified as:
Hinge, Saddle, Plane, Pivot, Condyloid, and Ball and Socket type of joints based on their structures, degree and axes of movements.
Ball and Socket Joints: It is a kind of joint where the ball-shaped articulating surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, with one common centre. This permits free movement along numerous axes and movement in many directions. E.g. hip joint, shoulder joint.

Hinge Joint: A hinge joint is a that allows movement in only one direction. Hinge joints include ankles, elbows, knee joints, and other such joints that have a movement along one plane only. These joints are two or more bones that meet and move along a single axis to bend.
Hinge joints are generally assisted by other tissues, like cartilage and ligaments, to connect and bend. These connective tissues protect the bones from rubbing and wearing as they bend at varying degrees to keep our bodies mobile. Eg- Knee joint, Elbow Joint

Additional Information:
Note: While the Ball and Socket joint allows for a wide range of motions, the hinge has a restricted axis of movement. The other synovial joints like pivot and saddle joints allow for more movement as compared to the hinge joint.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




