
Describe briefly the structure of the nerve cell.
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: A nerve cell is the elementary functional unit of the nervous system. It is also known as a neuron. It is composed of a cell body that possesses a nucleus and remaining cell organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus. It contains tiny branches called dendrites all over the cell body.
Complete answer:
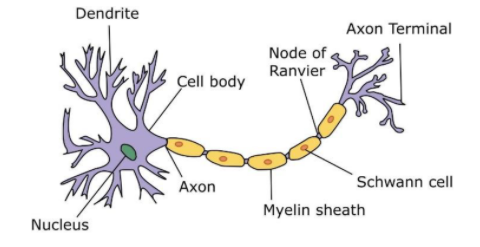
Nerve cells may be designated as receivers and transmitters of information that permit an organism to respond properly. Neuron’s dendrites accept signals from other cells and transfer them toward the cell body. Axon is the sole long output from the cell body.
It carries data from the cell body over long distances rapidly. The Axon terminal is located at the end of the axons. It makes the real connection to other neurons. In a few nerve cells, axons are encompassed by a myelin sheath. It acts as protection for the axon. The spaces between myelin sheath cells are called Nodes of Ranvier. The Schwann cell plays a significant role in myelinating the axons of the PNS.
Additional information:
For most of the neurons, nerve impulses originate when the membrane potential of the neuron is adequately depolarized and reaches a definite threshold. This permits some of the neurons to start impulses and hence information to specific targets.
Note: Neurons come into interaction with other cells at sites called synapses. This is the site at which the nerve endings of the cells come in contact letting for positive communication.
In such a case, neurons play an accessible function by getting information that is initiated from the stimuli. It is this receptive function of the neurons that guarantees the operative transmission of information and therefore the suitable response to stimuli.
Complete answer:
Nerve cells may be designated as receivers and transmitters of information that permit an organism to respond properly. Neuron’s dendrites accept signals from other cells and transfer them toward the cell body. Axon is the sole long output from the cell body.
It carries data from the cell body over long distances rapidly. The Axon terminal is located at the end of the axons. It makes the real connection to other neurons. In a few nerve cells, axons are encompassed by a myelin sheath. It acts as protection for the axon. The spaces between myelin sheath cells are called Nodes of Ranvier. The Schwann cell plays a significant role in myelinating the axons of the PNS.

Additional information:
For most of the neurons, nerve impulses originate when the membrane potential of the neuron is adequately depolarized and reaches a definite threshold. This permits some of the neurons to start impulses and hence information to specific targets.
Note: Neurons come into interaction with other cells at sites called synapses. This is the site at which the nerve endings of the cells come in contact letting for positive communication.
In such a case, neurons play an accessible function by getting information that is initiated from the stimuli. It is this receptive function of the neurons that guarantees the operative transmission of information and therefore the suitable response to stimuli.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




