
Describe four types of Phloem tissue.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Phloem is a complex permanent tissue that carries food materials from the place it is available to the place where it is needed. Each type of tissue has a unique role to play and all four types are only seen in angiosperms.
Complete answer:
Phloem transport the organic materials, usually from leaves to other parts of the plant like roots, growing tips of stem and leaves, flower, fruits, etc. The food prepared in the leaves through the process of photosynthesis needs to be transported to each part of the plant body which is facilitated by this conducting tissue called phloem.
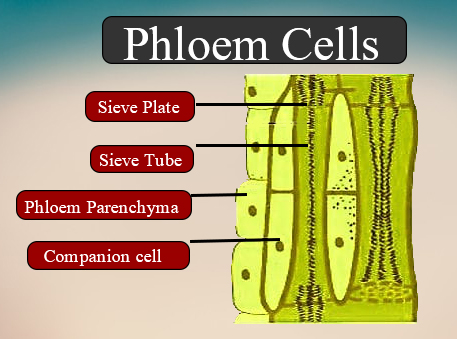
The four elements of phloem are Sieve tubes, Companion cells, phloem fibers, phloem parenchyma. Sieve tube elements: Like each vessel, sieve tubes are also made up of many cells called sieve tube elements and sieve tube members. - Sieve tube elements are the long, tube-like structures that are arranged longitudinally. These are thin-walled living structures having cellulosic cell walls. - A mature sieve tube element possesses a mature cytoplasm and a large central vacuole but lacks a nucleus.
Companion cells: These are the specialized parenchymatous cells that are closely associated with sieve tube elements due to which they are called the companion cells.
Phloem fibers: They are also called blast fibers. These are sclerenchymatous, elongated, unbranched fibers.
Phloem parenchyma: It is composed of living parenchymatous cells. These are the elongated cells that have tapering cells. They are cylindrical.
Note: - Xylem fibers contain tracheids and vessels along with xylem fibers and xylem parenchyma whereas phloem lacks tracheids and vessels instead has sieve tube elements and companion cells. - Types of phloem are: - Primary Phloem: The phloem which is formed during the primary growth of the plant body is called the primary phloem. It is further of two types based on relative states of maturity, protophloem, and metaphloem. The first formed primary phloem is called protophloem and later formed is called metaphloem. - Secondary Phloem: The phloem which is formed during secondary growth of the plant body is called secondary phloem. It is formed by the vascular cambial ring.
Complete answer:
Phloem transport the organic materials, usually from leaves to other parts of the plant like roots, growing tips of stem and leaves, flower, fruits, etc. The food prepared in the leaves through the process of photosynthesis needs to be transported to each part of the plant body which is facilitated by this conducting tissue called phloem.
The four elements of phloem are Sieve tubes, Companion cells, phloem fibers, phloem parenchyma. Sieve tube elements: Like each vessel, sieve tubes are also made up of many cells called sieve tube elements and sieve tube members. - Sieve tube elements are the long, tube-like structures that are arranged longitudinally. These are thin-walled living structures having cellulosic cell walls. - A mature sieve tube element possesses a mature cytoplasm and a large central vacuole but lacks a nucleus.
Companion cells: These are the specialized parenchymatous cells that are closely associated with sieve tube elements due to which they are called the companion cells.
Phloem fibers: They are also called blast fibers. These are sclerenchymatous, elongated, unbranched fibers.
Phloem parenchyma: It is composed of living parenchymatous cells. These are the elongated cells that have tapering cells. They are cylindrical.

Note: - Xylem fibers contain tracheids and vessels along with xylem fibers and xylem parenchyma whereas phloem lacks tracheids and vessels instead has sieve tube elements and companion cells. - Types of phloem are: - Primary Phloem: The phloem which is formed during the primary growth of the plant body is called the primary phloem. It is further of two types based on relative states of maturity, protophloem, and metaphloem. The first formed primary phloem is called protophloem and later formed is called metaphloem. - Secondary Phloem: The phloem which is formed during secondary growth of the plant body is called secondary phloem. It is formed by the vascular cambial ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




