
Describe in brief the functions of ribs and diaphragm in breathing.
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: They contract and move downward as you breathe in or inhale. In your chest cavity, this increases the room, and your lungs expand into it. The muscles between your ribs also allow the cavity of the chest to widen.
Complete answer:
The diaphragm, a large muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity, and also the movement of the ribs, performs the act of breathing primarily.
The diaphragm contracts during inspiration and becomes flat, causing a vacuum in the thoracic cavity. Through pulling air through the trachea, or windpipe, into the body, this vacuum inflates the lungs.
The diaphragm relaxes during natural exhalation, helping the air to pass out as the lungs deflate.
Like the diaphragm, the ribs shield the lungs and expand while we inhale to promote room for the lungs to expand. Then the ribs contract, expelling the air from the lungs.
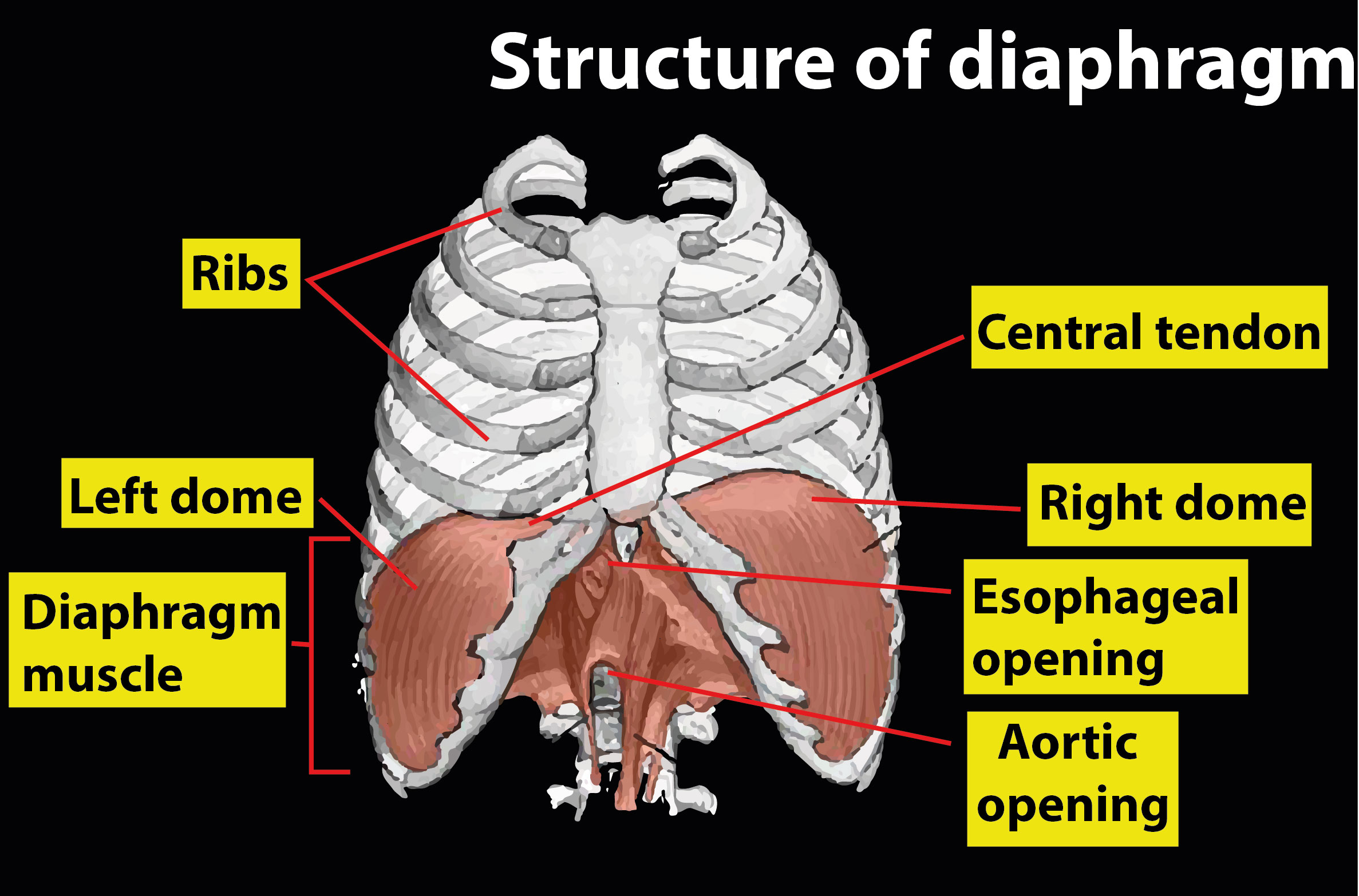
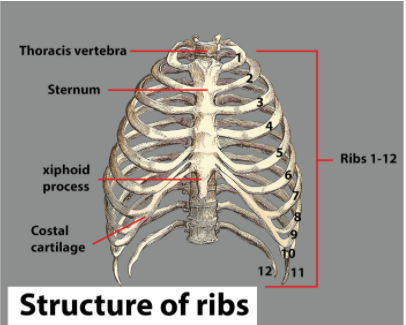
Additional Information: The ribs are a group of twelve bones forming the thorax's protective 'cage.' They articulate posteriorly with the vertebral column, and end as cartilage (known as costal cartilage) anteriorly. The ribs shield the internal thoracic organs as part of the bony thorax.
The primary muscle used in respiration, which is the breathing operation, is the diaphragm. Situated just below the lungs and heart is this dome-shaped muscle. When you breathe in and out, it contracts constantly.
Note: -The diaphragm is the only organ that only and without which no mammals can exist, and all mammals have.
-The origin of the diaphragm is found along the inferior border of the ribs and sternum and the lumbar vertebrae of the spine.
Complete answer:
The diaphragm, a large muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity, and also the movement of the ribs, performs the act of breathing primarily.
The diaphragm contracts during inspiration and becomes flat, causing a vacuum in the thoracic cavity. Through pulling air through the trachea, or windpipe, into the body, this vacuum inflates the lungs.
The diaphragm relaxes during natural exhalation, helping the air to pass out as the lungs deflate.
Like the diaphragm, the ribs shield the lungs and expand while we inhale to promote room for the lungs to expand. Then the ribs contract, expelling the air from the lungs.


Additional Information: The ribs are a group of twelve bones forming the thorax's protective 'cage.' They articulate posteriorly with the vertebral column, and end as cartilage (known as costal cartilage) anteriorly. The ribs shield the internal thoracic organs as part of the bony thorax.
The primary muscle used in respiration, which is the breathing operation, is the diaphragm. Situated just below the lungs and heart is this dome-shaped muscle. When you breathe in and out, it contracts constantly.
Note: -The diaphragm is the only organ that only and without which no mammals can exist, and all mammals have.
-The origin of the diaphragm is found along the inferior border of the ribs and sternum and the lumbar vertebrae of the spine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




