
Describe sky wave propagation in brief.
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint
Sky wave propagation is a type of radio wave propagation, where the wave is either reflected or refracted back to the earth by the upper electrically charged layer of the atmosphere, that is, the Ionosphere.
Complete step by step answer
Sky wave propagation is a behavior of electromagnetic waves of the radio frequency, where after being sent from a transmitter, they propagate in the atmosphere but get either reflected or refracted by the ionosphere to reach the receiver antenna.
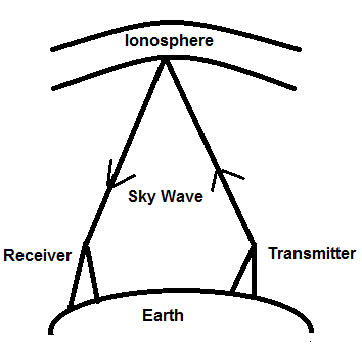
The frequency of a radio wave that can be propagated using the ionosphere ranges from $3MHz$ to $30MHz$, and these are used for broadcast and radio communication using the sky wave propagation.
The ionosphere is divided into three layers D, E, and F based on the ionization density, the F layer is further divided into $F_1$ and $F_2$ sub-layers. The D and E layers can only transmit waves in the daytime, as they are weakly ionized by the sunlight falling into them. Whereas the F layer can primarily refract the waves.
Additional Information
- Skip distance: It is defined as the minimum distance, between the points where the radio wave is transmitted, refracted back from the ionosphere, and received at some other point. Since it is the minimum distance, it is taken horizontally from the surface of the earth.
Ignoring the curvature of the earth, the skip distance for a radio wave can be given by-
$\Rightarrow {D_{skip}} = 2h\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{{{f_{MUF}}}}{{{f_c}}}} \right)}^2} - 1} $
Where the ${D_{skip}}$ is the skip distance,
h is the vertical height where the reflection takes place,
${f_{c}}$ is the critical frequency of the wave for total internal reflection to occur. It depends on the density of electrons in a layer of the ionosphere. And,
${f_{MUF}}$ is the maximum usable frequency.
Note
Because the ionization and formation of the ionosphere depend on the sunlight reaching the molecules, the number of charged particles is less at night and more during the day, this causes a fluctuation in the signal transmission during day and night.
Sky wave propagation is a type of radio wave propagation, where the wave is either reflected or refracted back to the earth by the upper electrically charged layer of the atmosphere, that is, the Ionosphere.
Complete step by step answer
Sky wave propagation is a behavior of electromagnetic waves of the radio frequency, where after being sent from a transmitter, they propagate in the atmosphere but get either reflected or refracted by the ionosphere to reach the receiver antenna.

The frequency of a radio wave that can be propagated using the ionosphere ranges from $3MHz$ to $30MHz$, and these are used for broadcast and radio communication using the sky wave propagation.
The ionosphere is divided into three layers D, E, and F based on the ionization density, the F layer is further divided into $F_1$ and $F_2$ sub-layers. The D and E layers can only transmit waves in the daytime, as they are weakly ionized by the sunlight falling into them. Whereas the F layer can primarily refract the waves.
Additional Information
- Skip distance: It is defined as the minimum distance, between the points where the radio wave is transmitted, refracted back from the ionosphere, and received at some other point. Since it is the minimum distance, it is taken horizontally from the surface of the earth.
Ignoring the curvature of the earth, the skip distance for a radio wave can be given by-
$\Rightarrow {D_{skip}} = 2h\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{{{f_{MUF}}}}{{{f_c}}}} \right)}^2} - 1} $
Where the ${D_{skip}}$ is the skip distance,
h is the vertical height where the reflection takes place,
${f_{c}}$ is the critical frequency of the wave for total internal reflection to occur. It depends on the density of electrons in a layer of the ionosphere. And,
${f_{MUF}}$ is the maximum usable frequency.
Note
Because the ionization and formation of the ionosphere depend on the sunlight reaching the molecules, the number of charged particles is less at night and more during the day, this causes a fluctuation in the signal transmission during day and night.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




