
Describe the Calvin cycle with a ray diagram.
Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint: During photosynthesis in plants two types of reactions occur in their chloroplasts namely- light reaction and dark reaction. The light reaction is responsible for trapping the light energy and ultimately producing the ATP and NADPH. These products of the light reaction are further utilised during the dark reaction to drive the process leading to the synthesis of food (more accurately sugars). This is called the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis.
Complete answer:
Dark reaction operates in different photosynthetic organisms through three different ways- C3 - pathway, C4 - pathway and CAM pathway. C3 - pathway consists of the Calvin cycle (C3 - cycle) while the C4- pathway and CAM pathway consists of both C3 cycle and C4 cycle. Calvin cycle can be described under three stages named as - carboxylation, reduction and regeneration.
Carboxylation is the most crucial step because in this step the enzyme RUBISCO binds with atmospheric carbon dioxide and this carbon dioxide is utilised for the carboxylation of substrate RUBP. This step yields two molecules of three phosphoglycerides.
The next step is a reduction. It includes a series of reactions that leads to the formation of glucose by the glycolytic reversal. This step uses two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADPH. The regeneration of carbon dioxide acceptor molecule RUBP is crucial if the cycle is to be continued uninterrupted. This step uses one molecule of ATP.
Hence in a complete Calvin cycle for every carbon dioxide molecule, three molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADPH are required.
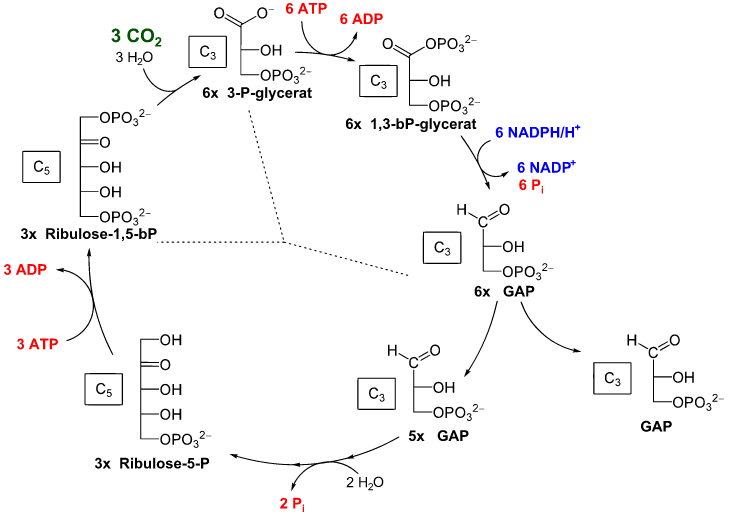
Note: The fixation of six molecules of carbon dioxide and for this fixation, six turns of the Calvin cycle are required for the removal of one molecule of glucose from the pathway. Thus during the complete dark reaction, in the Calvin cycle, there is an input of six carbon dioxide molecules for the production of one molecule of glucose.
Complete answer:
Dark reaction operates in different photosynthetic organisms through three different ways- C3 - pathway, C4 - pathway and CAM pathway. C3 - pathway consists of the Calvin cycle (C3 - cycle) while the C4- pathway and CAM pathway consists of both C3 cycle and C4 cycle. Calvin cycle can be described under three stages named as - carboxylation, reduction and regeneration.
Carboxylation is the most crucial step because in this step the enzyme RUBISCO binds with atmospheric carbon dioxide and this carbon dioxide is utilised for the carboxylation of substrate RUBP. This step yields two molecules of three phosphoglycerides.
The next step is a reduction. It includes a series of reactions that leads to the formation of glucose by the glycolytic reversal. This step uses two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADPH. The regeneration of carbon dioxide acceptor molecule RUBP is crucial if the cycle is to be continued uninterrupted. This step uses one molecule of ATP.
Hence in a complete Calvin cycle for every carbon dioxide molecule, three molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADPH are required.

Note: The fixation of six molecules of carbon dioxide and for this fixation, six turns of the Calvin cycle are required for the removal of one molecule of glucose from the pathway. Thus during the complete dark reaction, in the Calvin cycle, there is an input of six carbon dioxide molecules for the production of one molecule of glucose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




