
Describe the cell structure of spirogyra.
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: The underwater bodies of both plants and animals have various characteristics which make them survive in the deep conditions. Some do not need sunlight while some grow in sunlight. They can be green and no-green plants also. They even reproduce inside the water. They are visible in clear eutrophic water.
Complete answer:
Spirogyra is a water aquatic plant. It has a filamentous body. It grows under the water when it has enough access to sunlight. They produce oxygen in large quantities.
It is also called blanket weed. It is a green alga belonging to order Zygnematales. It belongs to this order due to the spiral arrangement of the chloroplast in it.
It has an unbranched body. The cells are mostly arranged linearly in the filament. The filamentous body becomes massive and rises to the surface becoming visible as slimy green mats.
It has a cell wall made up of cellulose and pectose. Pectose makes the outer layer while the cellulose forms the inner layer.
Mucilage is present on the surroundings of the cell wall. Spirogyra’s cytoplasm has a very large nucleus.
It has many vacuoles in the cytoplasm. There are spiral, coiled chloroplasts in the entire cell.
Pyrenoids are extensively scattered in the cytoplasm to store the food. They are subcellular parts of the chloroplast.
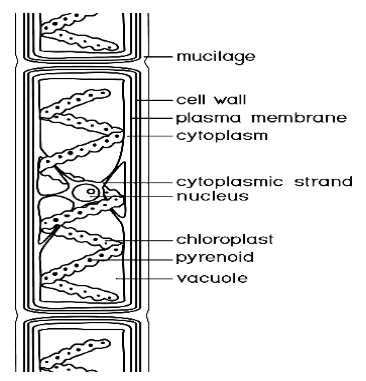
The thallus is the vegetative structure of the plant body. This is formed by the cylindrical cells placed head to head in a row. A double cell wall surrounds the thallus.
The protoplasm of the cell has-
Semi-permeable plasma membrane.
Vacuole filled with fluids.
Cytoplasm placed towards the periphery due to large vacuole present.
Specially shaped chloroplast called pyrenoids will store starch.
Note: Spirogyra reproduces via both sexual and asexual methods. Fragmentation is a common method for asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction can take place by scalariform conjugation and lateral conjugation. The scalariform takes between two filaments while the lateral conjugation occurs between two adjacent cells.
Complete answer:
Spirogyra is a water aquatic plant. It has a filamentous body. It grows under the water when it has enough access to sunlight. They produce oxygen in large quantities.
It is also called blanket weed. It is a green alga belonging to order Zygnematales. It belongs to this order due to the spiral arrangement of the chloroplast in it.
It has an unbranched body. The cells are mostly arranged linearly in the filament. The filamentous body becomes massive and rises to the surface becoming visible as slimy green mats.
It has a cell wall made up of cellulose and pectose. Pectose makes the outer layer while the cellulose forms the inner layer.
Mucilage is present on the surroundings of the cell wall. Spirogyra’s cytoplasm has a very large nucleus.
It has many vacuoles in the cytoplasm. There are spiral, coiled chloroplasts in the entire cell.
Pyrenoids are extensively scattered in the cytoplasm to store the food. They are subcellular parts of the chloroplast.

The thallus is the vegetative structure of the plant body. This is formed by the cylindrical cells placed head to head in a row. A double cell wall surrounds the thallus.
The protoplasm of the cell has-
Semi-permeable plasma membrane.
Vacuole filled with fluids.
Cytoplasm placed towards the periphery due to large vacuole present.
Specially shaped chloroplast called pyrenoids will store starch.
Note: Spirogyra reproduces via both sexual and asexual methods. Fragmentation is a common method for asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction can take place by scalariform conjugation and lateral conjugation. The scalariform takes between two filaments while the lateral conjugation occurs between two adjacent cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




