
Describe the development of female gametophyte in Angiosperms.
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: This is also known as the embryo sac or megagametophyte, developed within the ovule, which remains embedded within the ovary of the carpel.
Complete answer:
Within sporophytic tissues, the angiosperm gametophytes develop that constitute the sexual parts or organs of the flower. The female gametophyte of angiosperm is critical for plant reproduction. Female gametophyte development begins early in ovule development with the formation of a diploid megaspore cell that undergoes meiosis.
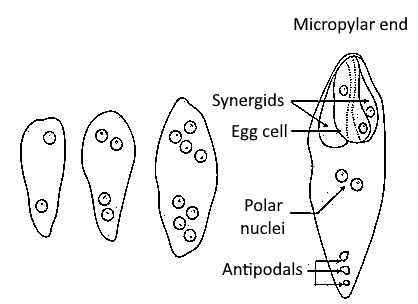
On resulting in a haploid megaspore the megaspore cell produces four megaspores, under which only one megaspore is functional and the other three remain degenerate. The nuclei of the functional megaspore divide mitotically into 2 nuclei and go to the other end. Another two mitotic cell divisions occur to make 4 nucleate and then 8 nucleate embryo sac. After the completion of the 8 nucleate stage, the cell walls are arranged and the female gametophyte is formed.
The mature female gametophyte secretes peptides that guide the plant part structure to the embryo sac and contains protein complexes that prevent seed development before fertilization. Post-fertilization, the feminine gametophyte influences seed development through maternal-effect genes and by regulating parental contributions. Spores undergo cell proliferation and differentiation to become gametophytes.
Note:
-The main function of the gametophyte generation is to supply haploid gametes.
-The method by which the 'megaspore mother cell' converted into the megaspore is named the megasporogenesis.
-The 'megaspore mother cell' contains a nucleus and a dense cytoplasm is contained by the ‘megaspore mother cell’.
Complete answer:
Within sporophytic tissues, the angiosperm gametophytes develop that constitute the sexual parts or organs of the flower. The female gametophyte of angiosperm is critical for plant reproduction. Female gametophyte development begins early in ovule development with the formation of a diploid megaspore cell that undergoes meiosis.
On resulting in a haploid megaspore the megaspore cell produces four megaspores, under which only one megaspore is functional and the other three remain degenerate. The nuclei of the functional megaspore divide mitotically into 2 nuclei and go to the other end. Another two mitotic cell divisions occur to make 4 nucleate and then 8 nucleate embryo sac. After the completion of the 8 nucleate stage, the cell walls are arranged and the female gametophyte is formed.
The mature female gametophyte secretes peptides that guide the plant part structure to the embryo sac and contains protein complexes that prevent seed development before fertilization. Post-fertilization, the feminine gametophyte influences seed development through maternal-effect genes and by regulating parental contributions. Spores undergo cell proliferation and differentiation to become gametophytes.

Note:
-The main function of the gametophyte generation is to supply haploid gametes.
-The method by which the 'megaspore mother cell' converted into the megaspore is named the megasporogenesis.
-The 'megaspore mother cell' contains a nucleus and a dense cytoplasm is contained by the ‘megaspore mother cell’.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




