
Describe the dihybrid cross experiment performed by Mendel. Explain the law postulated by this experiment.
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Dihybrid cross is a cross involving crossing 2 characters at a time like Mendel crossed yellow colored round seeded plants with green colored wrinkled seeded plants; thereby observing two characters in a single cross. When characters are taken in pairs then also in a cross, the characters separate independently i.e., the cross of one character is not influenced by the crossing of other characters.
Complete answer:
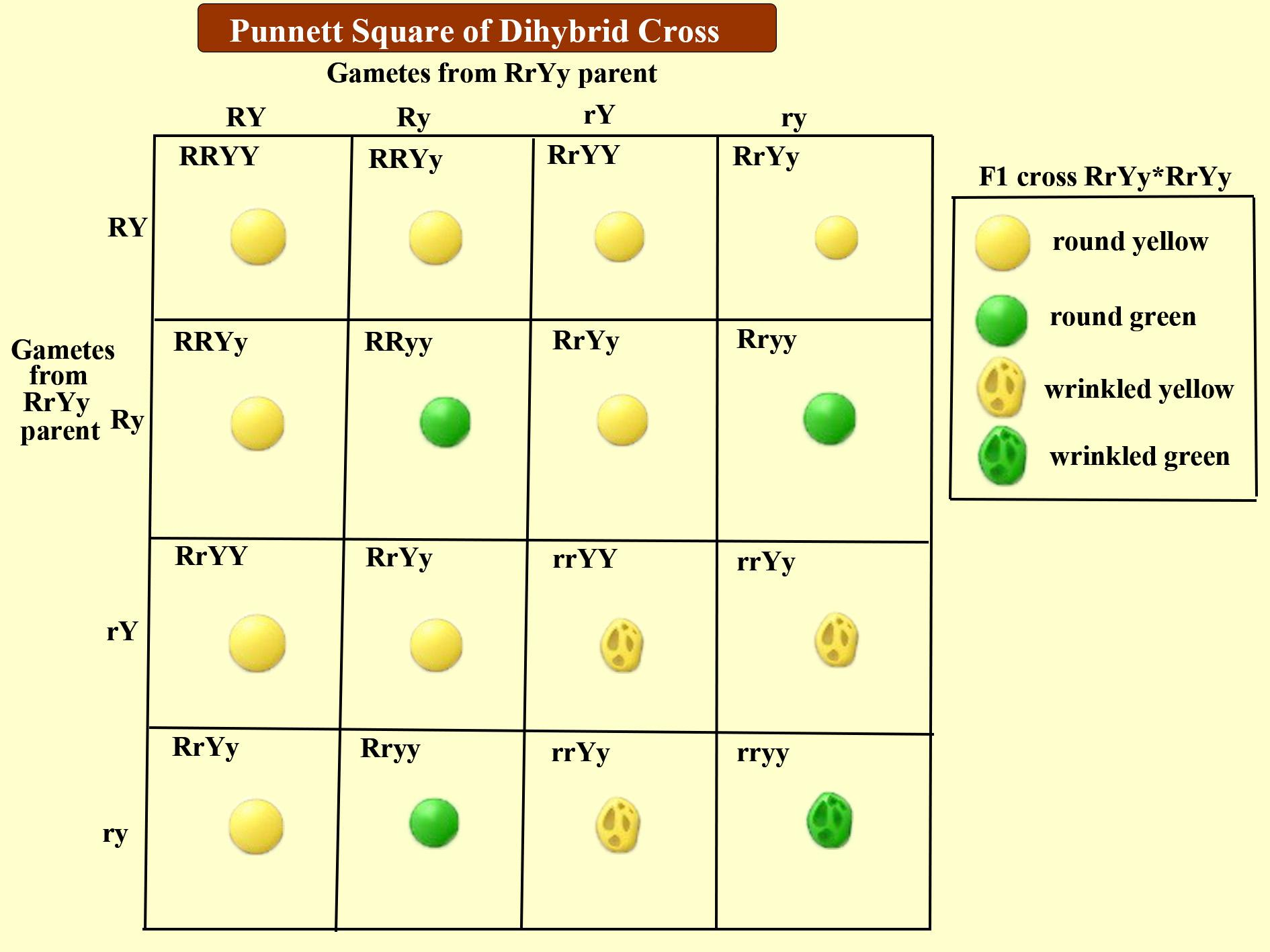
Dihybrid cross performed by Mendel included yellow colored round seeded plants(RRYY) and green colored wrinkled seeded plants(rryy). When Mendel crossed these plants he obtained a progeny (RrYy) in the F1 generation which was phenotypically a yellow colored round seeded plant. When he self crossed this plant obtained in the F1 generation (RrYy) he obtained 4 phenotypically different plants- yellow colored round seeded (RRYY/RrYy), yellow-colored wrinkled seeded (YYrr/Yyrr), green-colored round seeded plants (yyRR/yyRr), and green colored wrinkled seeded plants (rryy) as shown in the figure. From this experiment, Mendel derived the third law, the law of independent assortment. This law explains to us that whenever two characters (or factors as said by Mendel) are taken at one time, they separate independently, the separation of one character is not affected by the other character and vice-versa. Phenotypically, the dihybrid cross gave a ratio of 9(yellow colored, round seeded) :3 (yellow-colored, wrinkled seeded) :3 (green colored, round seeded):1 (green colored, wrinkled seeded). Genotypically, the ratio is 1:2:2:4:2:1:2:1.
Mendel gave three laws- the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment. The law of dominance states that one of the traits of a character will be dominant and the other would be recessive. The recessive does not express itself until it is present in homozygous condition. The law of segregation states that alleles are distributed randomly in the gamete. An offspring receives one allele from each parent which is passed on from the parent randomly for a particular trait.
Note: Only the law of segregation is universal whereas the law of dominance and law of independent assortment have their exceptions. The Law of independent assortment has exceptions which lead to incomplete dominance and codominance. The law of dominance has an exception in the case of Mirabilis jalapa.
Complete answer:
Dihybrid cross performed by Mendel included yellow colored round seeded plants(RRYY) and green colored wrinkled seeded plants(rryy). When Mendel crossed these plants he obtained a progeny (RrYy) in the F1 generation which was phenotypically a yellow colored round seeded plant. When he self crossed this plant obtained in the F1 generation (RrYy) he obtained 4 phenotypically different plants- yellow colored round seeded (RRYY/RrYy), yellow-colored wrinkled seeded (YYrr/Yyrr), green-colored round seeded plants (yyRR/yyRr), and green colored wrinkled seeded plants (rryy) as shown in the figure. From this experiment, Mendel derived the third law, the law of independent assortment. This law explains to us that whenever two characters (or factors as said by Mendel) are taken at one time, they separate independently, the separation of one character is not affected by the other character and vice-versa. Phenotypically, the dihybrid cross gave a ratio of 9(yellow colored, round seeded) :3 (yellow-colored, wrinkled seeded) :3 (green colored, round seeded):1 (green colored, wrinkled seeded). Genotypically, the ratio is 1:2:2:4:2:1:2:1.

Mendel gave three laws- the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment. The law of dominance states that one of the traits of a character will be dominant and the other would be recessive. The recessive does not express itself until it is present in homozygous condition. The law of segregation states that alleles are distributed randomly in the gamete. An offspring receives one allele from each parent which is passed on from the parent randomly for a particular trait.
Note: Only the law of segregation is universal whereas the law of dominance and law of independent assortment have their exceptions. The Law of independent assortment has exceptions which lead to incomplete dominance and codominance. The law of dominance has an exception in the case of Mirabilis jalapa.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




