
Describe the following chemical equations-
A.Friedel crafts reaction
B.Decarboxylation reaction
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: Before answering this question, we should first know about Friedel-Crafts reaction and decarboxylation reaction. An organic coupling reaction that includes an electrophilic aromatic substitution that is important for the joining of substituents to aromatic rings is called the Friedel-Crafts reaction. The chemical reaction which eliminates a carboxyl group and gives out carbon dioxide is known as the decarboxylation reaction.
Complete answer:
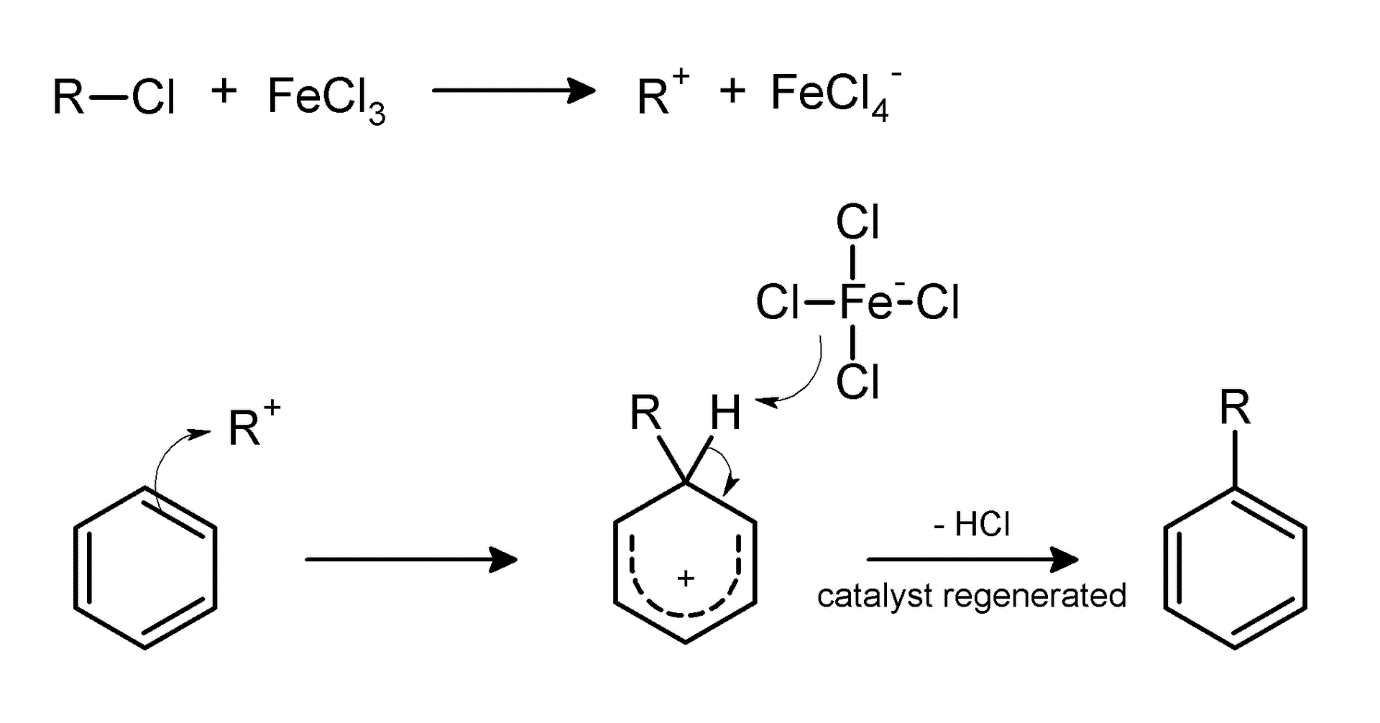
There are two types of Friedel-Crafts reaction which are alkylation and acylation. Charles Friedel and James Craft developed these reactions in 1877. Here, both of the reactions face substitution of the Hydrogen atom (linked to the aromatic ring) with an electrophile. The catalyst used in the Friedel-crafts reaction is Aluminium trichloride as it acts as a Lewis base and works with halogens in order to create electrophile in the reaction.
It refers to a reaction in which carboxylic acid erases a carbon atom from a chain of carbons whereas carboxylation is an entirely reversible process in which carbon dioxide is added to the compound. It is the first chemical step in photosynthesis. Enzymes that catalyzes decarboxylation are known as decarboxylases
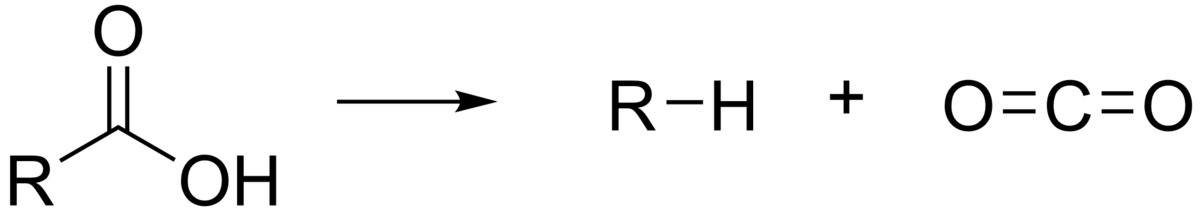
Decarboxylations are the bases of many named reactions that include barton decarboxylation reaction, Kolbe electrolysis reaction, Kochi reaction, and Hunsdiecker reaction. These are all radical reactions. The decarboxylation of an ester is the krapcho decarboxylation.
Note:
Limitation of Friedel-Crafts alkylation are-
Not all alkylbenzene can be formed because of the ability of cation to be rearranged.
Nitrobenzene and strong deactivating systems cannot be formed through this reaction.
The products of Friedel-Crafts are more reactive than the initiating material.
Complete answer:
There are two types of Friedel-Crafts reaction which are alkylation and acylation. Charles Friedel and James Craft developed these reactions in 1877. Here, both of the reactions face substitution of the Hydrogen atom (linked to the aromatic ring) with an electrophile. The catalyst used in the Friedel-crafts reaction is Aluminium trichloride as it acts as a Lewis base and works with halogens in order to create electrophile in the reaction.

It refers to a reaction in which carboxylic acid erases a carbon atom from a chain of carbons whereas carboxylation is an entirely reversible process in which carbon dioxide is added to the compound. It is the first chemical step in photosynthesis. Enzymes that catalyzes decarboxylation are known as decarboxylases
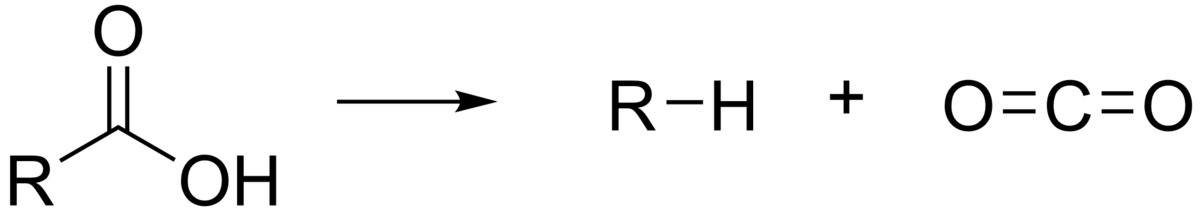
Decarboxylations are the bases of many named reactions that include barton decarboxylation reaction, Kolbe electrolysis reaction, Kochi reaction, and Hunsdiecker reaction. These are all radical reactions. The decarboxylation of an ester is the krapcho decarboxylation.
Note:
Limitation of Friedel-Crafts alkylation are-
Not all alkylbenzene can be formed because of the ability of cation to be rearranged.
Nitrobenzene and strong deactivating systems cannot be formed through this reaction.
The products of Friedel-Crafts are more reactive than the initiating material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




