
Describe the internal structure of a dorsiventral leaf with the help of labelled diagram.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint:Dicot plants are those plants in which two cotyledons are found. In dicot plants, dorsive central leaves are found. These leaves possess distinct ventral and dorsal sides.
Complete answer:
The dorsive central leaf comprises three parts.
Epidermis: Epidermis is present on both the upper surface (adaxial epidermis) and the lower surface (abaxial epidermis). The epidermis on the outside is covered with a thick cuticle. The abaxial epidermis bears more stomata than the adaxial epidermis. The outermost covering of the leaf on the upper side is called adaxial epidermis and on the lower side, it is known as the abaxial epidermis. A waxy thick layer cuticle is present and distinct. Stomata are higher on the abaxial epidermis and either lower or absent on the adaxial epidermis.
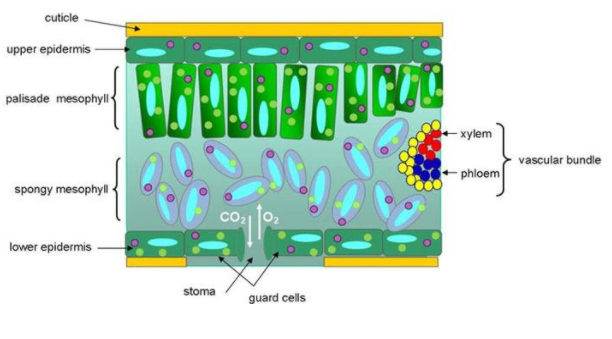
Mesophyll: Mesophyll is a tissue of the leaf present between the adaxial and abaxial epidermis. It is differentiated into the palisade parenchyma (composed of tall, compactly-placed cells) and the spongy parenchyma (comprising oval or round, loosely-arranged cells with intercellular spaces). Mesophyll contains the chloroplasts which perform the function of photosynthesis.
Vascular system: The vascular bundles present in leaves are conjoint and closed. They are surrounded by thick layers of bundle-sheath cells or these are surrounded by thick bundle sheath cells and can be seen in veins and midrib. These are distinct in size due to reticulate venation.
Note:It is to be noted that the male components of the flower are referred to as the stamens while the female flower part is called pistil.
Complete answer:
The dorsive central leaf comprises three parts.
Epidermis: Epidermis is present on both the upper surface (adaxial epidermis) and the lower surface (abaxial epidermis). The epidermis on the outside is covered with a thick cuticle. The abaxial epidermis bears more stomata than the adaxial epidermis. The outermost covering of the leaf on the upper side is called adaxial epidermis and on the lower side, it is known as the abaxial epidermis. A waxy thick layer cuticle is present and distinct. Stomata are higher on the abaxial epidermis and either lower or absent on the adaxial epidermis.

Mesophyll: Mesophyll is a tissue of the leaf present between the adaxial and abaxial epidermis. It is differentiated into the palisade parenchyma (composed of tall, compactly-placed cells) and the spongy parenchyma (comprising oval or round, loosely-arranged cells with intercellular spaces). Mesophyll contains the chloroplasts which perform the function of photosynthesis.
Vascular system: The vascular bundles present in leaves are conjoint and closed. They are surrounded by thick layers of bundle-sheath cells or these are surrounded by thick bundle sheath cells and can be seen in veins and midrib. These are distinct in size due to reticulate venation.
Note:It is to be noted that the male components of the flower are referred to as the stamens while the female flower part is called pistil.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




