
Describe the internal structure of the dicot leaf with the help of diagrams.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Dicot leaf lamina are generally bifacial or dorsiventral. Dicot leaf is characterized by upper and lower epidermis, cuticle, mesophyll cells are vascular bundles.
Complete answer:
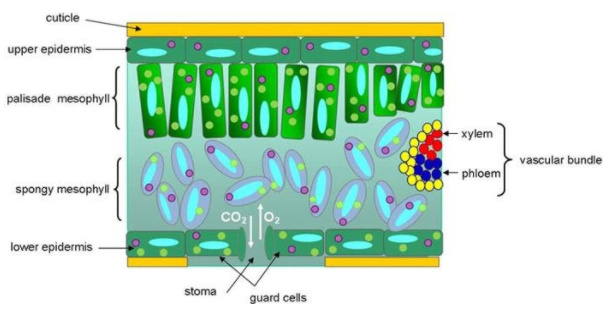
>Cuticle- The outer walls of the epidermis is coated by a cuticle of variable thickness. It may have extra layers of wax.
>Epidermis- Upper and lower epidermis has completely arranged parenchymatous cells. It is a single layer, but in new plants multilayered epidermis can be seen Example: Ficus elastica. Epidermis may possess glandular or non-glandular hairs.
>Stomata- Stomata are present more in lower epidermis as compared to upper epidermis. However, in some free-floating hydrophytes the stomata are confirmed in the upper epidermis. In xerophytes, the stomata are sunken or borne in pits Example: Nerium.
>Mesophyll- It is made up of palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma. Palisade parenchyma are found towards the upper surface, chloroplast and palisade parenchyma are found towards the lower surface.
>Mesophyll also possess different kinds of sclereids. Example: Leaves of Hakea possess osteosclereids i.e. rod-shaped stone cells among palisades. Some hydrophytes possess branched sclereids in their large air space (Nymphaea) or sphaeraphides in specialization cells Example: Trapa bispinosa.
>Vascular bundles- The vascular bundles in mid-rib are conjoint and collateral. Phloem lies towards the lower side, xylem lies toward the upper side. Nerium, Cannabis, Prunus etc. have a single vascular bundle. Sunflower vitis etc have many vascular bundles.
>Bulliform cells are absent in dicot leaves.
Additional information: On the other hand monocot leaves have bulliform cells, they are found in epidermis of grasses which are filled by liquid upward folding of leaves during the sunny day take place due to the presence of these specific cells. This is an adaptation to reduce the transpiration.
Note:In Dorsiventral leaves upper surface receive more sunlight as compared to lower surface, so there occurs a difference between internal structure of upper and cover surfaces, exceptional case is Eucalyptus. As more stomata are present on the cover surface and are called hypostomatic.
Complete answer:

>Cuticle- The outer walls of the epidermis is coated by a cuticle of variable thickness. It may have extra layers of wax.
>Epidermis- Upper and lower epidermis has completely arranged parenchymatous cells. It is a single layer, but in new plants multilayered epidermis can be seen Example: Ficus elastica. Epidermis may possess glandular or non-glandular hairs.
>Stomata- Stomata are present more in lower epidermis as compared to upper epidermis. However, in some free-floating hydrophytes the stomata are confirmed in the upper epidermis. In xerophytes, the stomata are sunken or borne in pits Example: Nerium.
>Mesophyll- It is made up of palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma. Palisade parenchyma are found towards the upper surface, chloroplast and palisade parenchyma are found towards the lower surface.
>Mesophyll also possess different kinds of sclereids. Example: Leaves of Hakea possess osteosclereids i.e. rod-shaped stone cells among palisades. Some hydrophytes possess branched sclereids in their large air space (Nymphaea) or sphaeraphides in specialization cells Example: Trapa bispinosa.
>Vascular bundles- The vascular bundles in mid-rib are conjoint and collateral. Phloem lies towards the lower side, xylem lies toward the upper side. Nerium, Cannabis, Prunus etc. have a single vascular bundle. Sunflower vitis etc have many vascular bundles.
>Bulliform cells are absent in dicot leaves.
Additional information: On the other hand monocot leaves have bulliform cells, they are found in epidermis of grasses which are filled by liquid upward folding of leaves during the sunny day take place due to the presence of these specific cells. This is an adaptation to reduce the transpiration.
Note:In Dorsiventral leaves upper surface receive more sunlight as compared to lower surface, so there occurs a difference between internal structure of upper and cover surfaces, exceptional case is Eucalyptus. As more stomata are present on the cover surface and are called hypostomatic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




